Diabetes Mellitus – A disease, directly responsible for 1.5 million deaths in a year and associated with another 2.2 million deaths in some form. A disease, that is about to become the 7th leading cause of death in the world. This disease is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attack and lower limb amputation. It is high time that people realize its severity and educate themselves about diabetes so that they can prevent it or control it in case they are suffering from diabetes already. Here is all about diabetes that you need to know.
WHAT IS DIABETES?
Commonly diabetes is known for a condition in which blood glucose level or blood sugar level is too high. More accurately it is a weakness or failure in the mechanism of glucose metabolism by Insulin hormone which is responsible for its storage. Diabetes can occur due to inadequate Insulin production or it’s ineffectiveness on Insulin receptors. Because glucose is not properly stored, it stays in the blood and results in high blood sugar.

According to ADA guidelines, following are the normal blood sugar level, level in IGT(Impaired Glucose Tolerance) and Blood sugar level in Diabetes mellitus –
Fasting blood sugar (Empty stomach)-
Normal – <100 mg/dl
IGT – 100 – 125 mg/dl
Diabetes Mellitus – >126 mg/dl
2-hour Postprandial blood sugar (After meal)-
Normal – <140 mg/dl
IGT – 140 – 200 mg/dl
Diabetes Mellitus – >200 mg/dl
It is often seen that diabetic patient is at risk of low blood sugar (Hypoglycemia) as well, in which sugar level drops bellow 70 mg/dl. It happens mainly because of Insulin reaction and partly because high blood sugar filters in urine quickly. Since glucose was not stored, blood does not get glucose again, which leads to hypoglycemia condition.
Patients who are taking Insulin, experience it because of the insulin reaction, or insulin shock. Patients are advised to take 15 – 20 grams of glucose as soon as possible in this condition.
WHAT ARE RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETES?
There are different types of diabetes, therefore risk factors of respective types are also different.
According to WHO’s Diabetes Global Report – Exact causes of type 1 diabetes are unknown. It is generally a result of complex interaction between genes and environmental factors.
Type 1 diabetes occurs in children and adolescent.
Type 2 diabetes risk factors are genetic as well as metabolic. Overweight and obesity are the strongest risk factors for type 2 diabetes. The family history of diabetes, previous gestational diabetes, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and smoking are also a significant contributor.
Gestational diabetes risk factors include age, overweight or obesity, family history of diabetes, excessive weight gain during pregnancy etc.
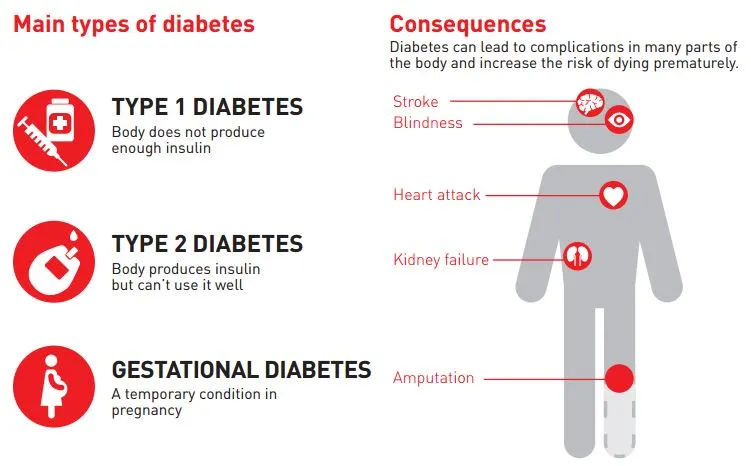
DIABETES TYPES
There are three major types of diabetes mellitus. These are-
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Gestational diabetes
1. Type 1 diabetes Mellitus –
Since type 1 diabetes primarily diagnosed in children and young adults, it is also known as juvenile diabetes or childhood-onset diabetes. As it was previously mentioned – cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. We still don’t know all about diabetes mellitus type 1. We have very less data available on this particular type of diabetes however it has been seen in many cases that the patient has a previous history of some kind of infection. It leads some doctors and scientists to a conclusion that infection can cause insulitis (inflammation of insulin producing Beta cells in the pancreas) which may result in permanent damage of beta cells. Still, we can’t say for sure because of less data availability.
These patient’s beta cells are destroyed so they can’t produce sufficient amount of insulin due to which they are in constant need of insulin injection. These patients are depended on insulin that’s why it is also known as Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are – constant hunger, thirst (polydipsia), excessive urination (polyuria), weight loss, vision changes and fatigue. As we don’t know the cause so we can’t prevent it but it can be managed by insulin shots.
2. Type 2 diabetes Mellitus –
It occurs largely in adults and older people but it can occur at any age. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. According to CDC, type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90% to 95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease (occurs slowly). In this type, the body produces enough insulin but it can not be utilized due to the resistance of insulin receptor against insulin. It means even if insulin goes and attaches to the receptor, receptor does not get stimulation and does not initiate its function, which in this case is glucose storage. It causes a high level of glucose in the blood. In this case, insulin shots will not work. That’s why this type is also known as Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus.
Main factors that cause type 2 diabetes are obesity, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diet. Genetic association or family history of diabetes is also a significant factor.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes are similar to those seen in type 1 diabetes but they take longer to appear in type 2 as compare to type 1. lifestyle modification, exercise, weight loss and a healthy diet can prevent type 2 diabetes. patients can be treated by medication and may require insulin as well.

3. Gestational diabetes Mellitus –
Gestational diabetes is a hyperglycemia condition during pregnancy. In this condition, blood sugar level is usually not as high as seen in type 2 diabetes. Women with gestational diabetes are at comparatively high risk of complication during pregnancy as well as during delivery. Mother and child are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes in future.
Instead of symptoms gestational diabetes is diagnosed by prenatal screening.
There are some less common types of diabetes that can be seen in the population. For example an inherited type of diabetes named Monogenic Diabetes, and cystic fibrosis related diabetes etc.
Stay Informed, Stay Healthy.
Thank You!
Sources –
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3154446/
http://healthblogpost.com/all-about-diabetes/
Image source : WHO http://www.who.int/entity/diabetes/global-report/WHD2016_Diabetes_Infographic_v2.pdf?ua=1