Greetings to everyone! In my previous post, we were discussing about the estimation of water content in natural gas system which acts as an impurity in the separation and purification of natural gas. Today, we shall learn about another processing methods related to the removal of acid gases.
WHAT WE SHALL LEARN?
First we shall be learning about the need for removal of acid gases. Then we will learn about the different methods for acid gas removal and criteria to choose acid gas removal methods. We shall also be learning about absorptive acid gas removal and the applicability of acid gas removal.
ACID GASES IN NATURAL GAS
The acid gases in natural gas are carbon dioxide (CO2) and Hydrogen sulphide (H2S). Acid gases are any gaseous compounds which forms acidic solution when dissolved in water. So, whether a gas is acidic or not is determined after it is mixed with water. Water has a neutral pH of 7, so if the gas after mixing with water has a pH less than 7, then the gas can be termed as an acid gas.
WHY DO WE NEED TO REMOVE H2S?
Hydrogen sulphide forms weak, corrosive acid in presence of water and it is highly toxic. It is easily detectable at lower concentrations by its rotten-egg odour. At higher concentrations, it directly affects our olfactory (smell) system so that it appears to be odourless. It can cause instant death when it reaches concentrations of more than 1000 ppmv. The threshold limit value (TLV) for prolonged exposure is 10 ppmv. At higher concentrations, some other obnoxious smelling sulphur compounds are also formed which are Carbon disulphide(CS2), Mercaptans(RSH) and Sulphides(RSR) etc.
WHY DO WE NEED TO REMOVE CO2
CO2 also forms weak corrosive acid in presences of water like hydrogen sulphide. It is non-flammable and it reduces heating value of natural gas.
RECOMMENDED CONCENTRATIONS IN NATURAL GAS
There is a certain threshold or maximum permissible limit of these acid gases in natural gas.
| Use | CO2 concentration | H2S concentration |
|---|---|---|
| For transportation in a pipleline and used as residential or industrial fuel | < 3-4 mol % | 6 mg/m3 |
| Cryogenic plants producing LNG, LPG and NGL | 50-100 ppmv | 4ppmv |
ACID GAS DISPOSAL
The acid gases should be properly disposed after removing them from the natural gas.
✓ CO2
We can dispose CO2 by disposing it by injecting in an enhanced oil recovery system. This method recovers any residual petroleum oil which are entrapped in the rock formation in the sediment. There, we can use CO2 as it is important for us not only to capture the CO2 but also to find a suitable way out through which it can be sequestered. Another way is to vent out to the atmosphere provided it does not violate environmental regulations.
✓ H2S
We can incinerate and vent it out to the atmosphere provided it meet the environmental regulations. We can react with H2S scavengers like iron sponge. It can also be converted into elemental sulphur by use of the Claus or similar process. It can also be disposed by injecting into suitable underground formation.
ACID GAS REMOVAL METHODS
There are various methods to remove acid gases but mostly these are categorised into absorption, adsorption, membrane permeation, thermodynamic phase change, and chemical conversion to another compound. We shall be focusing on absorption in this particular post.
CRITERIA TO CHOOSE ACID GAS REMOVAL METHODS
The criteria lies on different things when choosing different removal methods. These methods can be altered depending on these criteria.
☑ The type and concentration of impurities
☑ The temperature and pressure of the sour gas.
☑ Outlet gas specification.
☑ Volume of gas to be processed .
☑ The cost (capital and operating cost) of the process.
☑ Environmental regulations.
☑ Size and weight of separating unit for offshore application.
CO2 removal is done offshore but H2S is not remove to avoid problems of handling elemental sulphur.
ABSORPTIVE ACID GAS REMOVAL
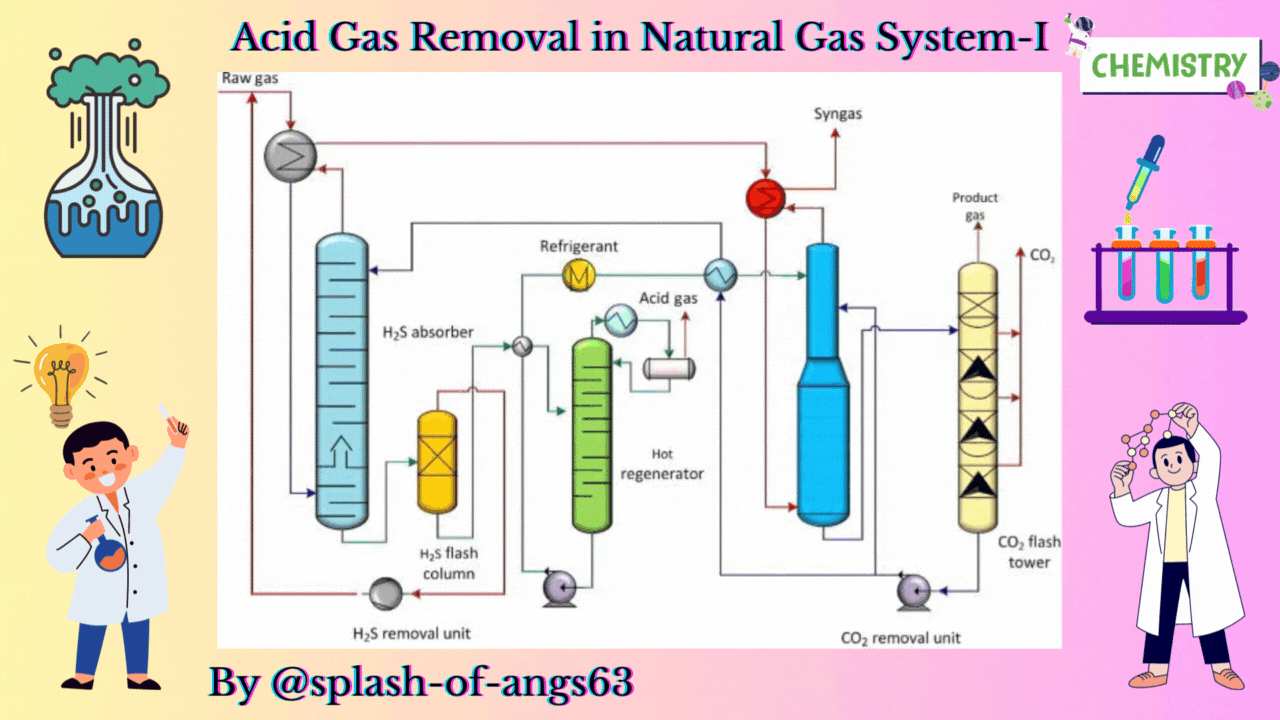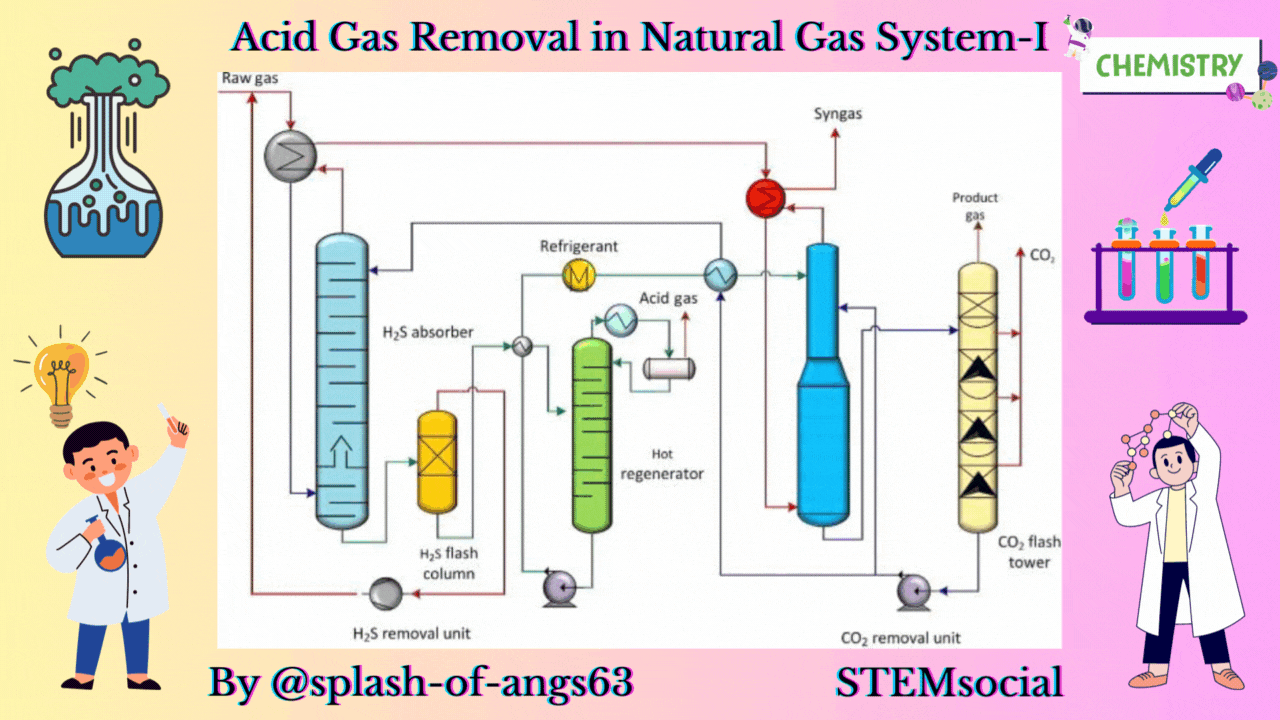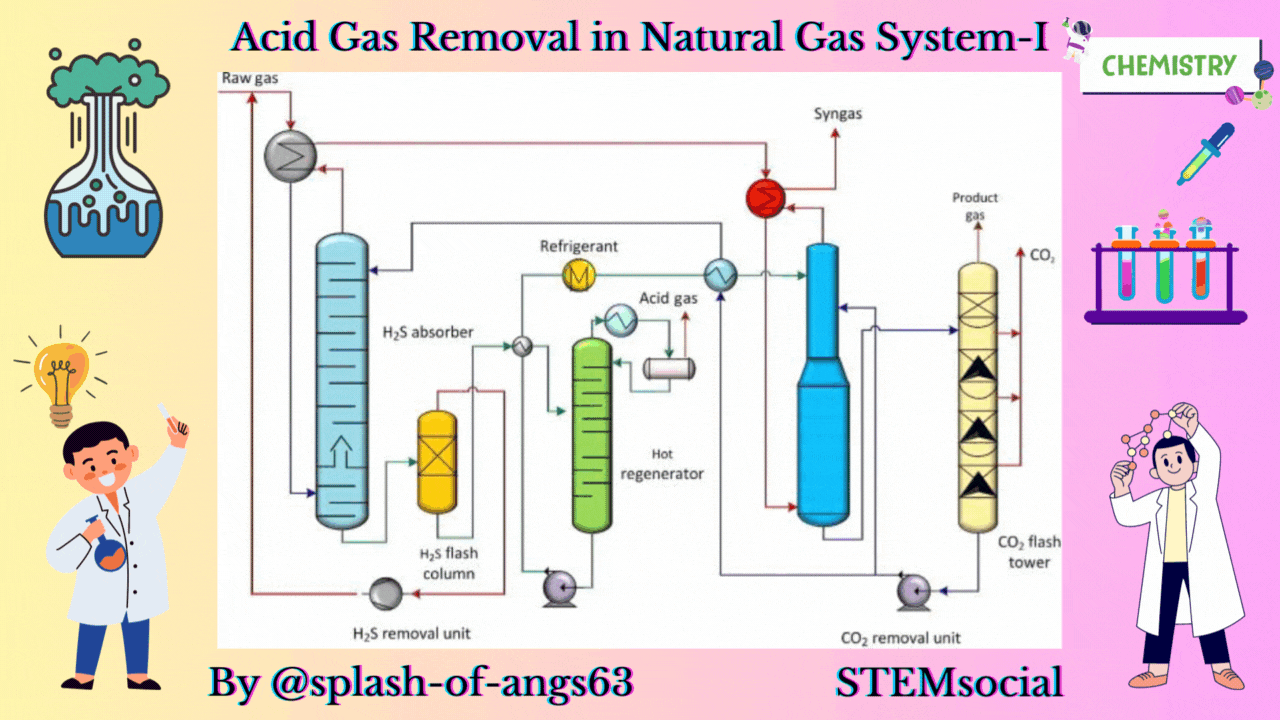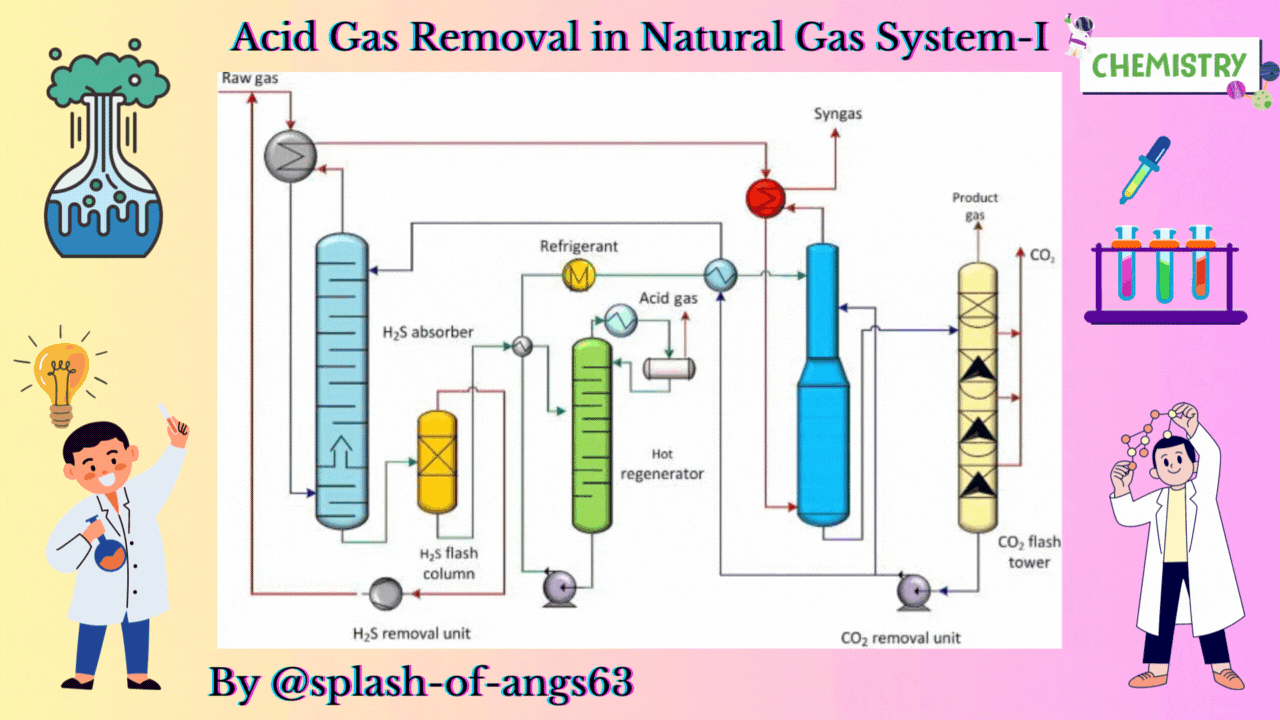
The absorptive acid gas removal is based on the absorption phenomena. We can visualise a typical arrangement to remove these gases by absorption. Here, we have an absorption column and we are feeding the gas from the bottom and at the same time some solvent is fed from the top. They are mixed counter currently and due to this mixing the CO2 and H2S are getting dissolved in the solvent and they are removed from the gas. The gas which is coming out will now be having less amount of these gases whereas the solvent will be rich with CO2 and H2S.

There are various kinds of absorption processes viz. physical (without reaction), chemical (with reaction), hybrid (combination of both).
SOLVENT USED
The solvents used for the physical absorption are Selexol (Dimethyl ether of polyethylene glycol), Rectisol (Methanol), Purisol (N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone).
The solvents used for chemical absorption are Primary amines (monomethanol amine, MEA), Secondary amines (diethanol amine, DEA), Tertiary amines (methyldiethanol amine, MDEA), mixed amines (aqueous blends of MDEA and MEA).
Mixed or hybrid solvents are suited for acid gas partial pressure in natural gas of more than 100 kPa. The various hybrid solvents are Sulfinol-D (DIPA and sulfolane), Sulfinol-M (MDEA and sulfolane), Flexsorb SE (Hindered amine and a physical solvent), Amisol (Methanol with MDEA or diethylamine).
TYPICAL ARRANGEMENT OF PHYSICAL ABSORPTION UNIT FOR ACID GAS REMOVAL
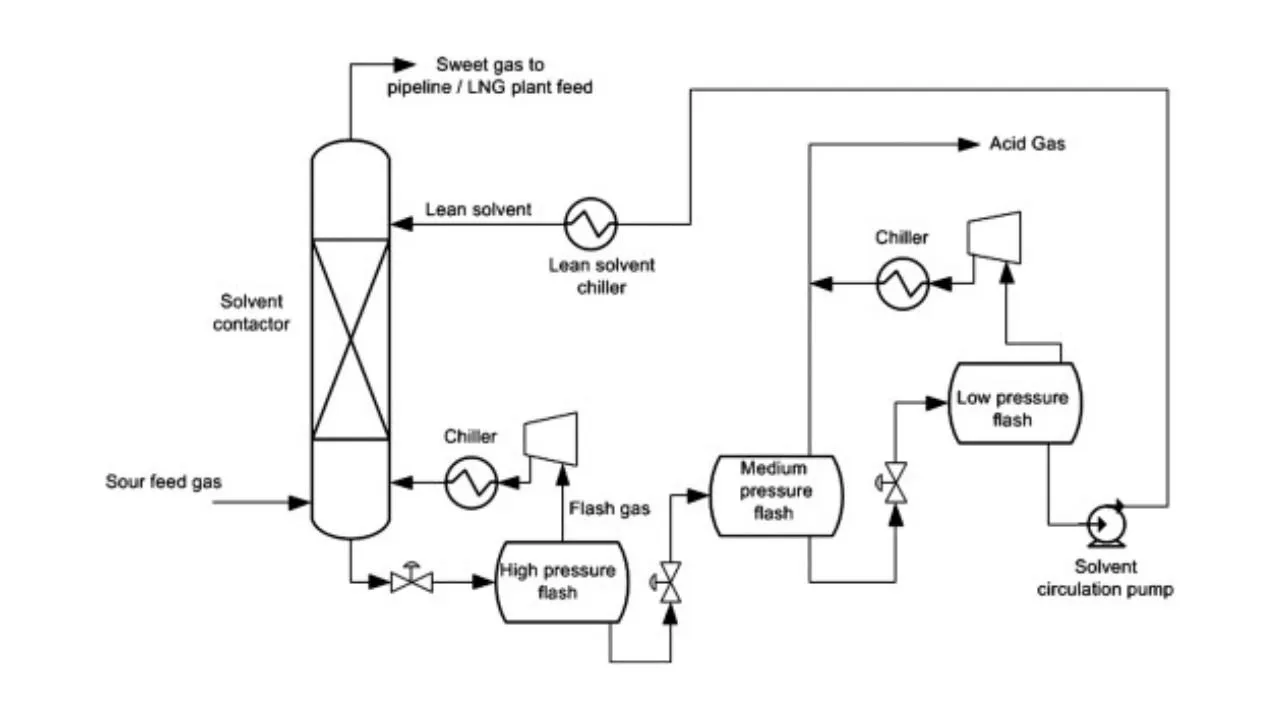
Let us now, come to a typical physical absorption unit. Here, we find that we have the sour feed gas which is fed from the bottom of the absorption column and from the top we are inputting the lean solvent. When this lean solvent comes in contact with the up going gas, then it takes up the carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide. That is how it becomes a rich solvent containing CO2 and H2S. Then it is flashed twice at 2 different pressures and because of flashing we recover more of these solvents. So, just by flashing we recover these gases and from then we take the solvent back to the column after regeneration. So, this cycle is continued until and unless we find that the capacity of the solvent has not come below the requisite capacity.
APPLICABILITY OF HYBRID SOLVENTS
The advantages of the hybrid solvents are that they are highly soluble at low CO2 partial pressure. They have low energy consumption for regenerating the solvent. They have high acid gas loading capacities and they have very low corrosion tendency.
COMPARISON OF CO2 and H2S REMOVAL PROCESSES
| Solvent | Capable of meeting H2S specifications | Remove COS, CS2 and Mercaptan | Selective H2S removal | Minimum CO2 level obtainable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDEA | Yes | Slight | Some | Bulk removal only |
| DGA | Yes | Partial | No | 100 ppmv at moderate to high pressures |
| Sulfinol | Yes | Partial | Yes | 50 ppmv |
| DEA | Yes | Partial | No | 50 ppmv |
Journal of petroleum science and engineering
Acid gas removal-an overview by ScienceDirect
Estimation of Water Content in Natural Gas |ChemFam #17|
Membrane Separation in Natural Gas System |ChemFam #16|
Design of distillation column |ChemFam #15|
Separation Technique: Distillation |ChemFam #14|
Transmission Electron Microscope: Principle and Working |ChemFam #13|
Scanning Electron Microscope: Principle and Working |ChemFam #12|
Drugs: Classification and drug-target interaction |ChemFam #11|
What are orbitals and quantum numbers? |ChemFam #10|
Quantum mechanical model of an atom |ChemFam #09|
A case study about the growth mechanism of CNT |ChemFam #08|
Carbon Nanotubes (Buckytubes): Types and Synthesis |ChemFam #07|
Nanomaterials: Classification and Approach for Synthesis |ChemFam #06|
Azadirachtin: Isolation, Extraction and Mechanism of Action |ChemFam #05|
Woodward-Fieser Rules for Calculating λmax |ChemFam #04|
Chemistry in ancient India |ChemFam #03|
How do soaps clean the dirt? |ChemFam #02|
What is anti egg white injury factor? |ChemFam #01|
PS The thumbnail image is being created by me using canva.com taking template image from ScienceDirect

