Preliminary
Examination using X-ray in the ankle joint is an examination that is often carried out at the Radiology Installation of Teungku Chik Ditiro Sigli Hospital. Almost every day there is an examination request.
The main indication of ankle joint examination is due to a traffic accident or work accident. There are also caused by injuries during exercise. Generally, patients with indications of this examination are from the Emergency Department, patients who come from the Orthopedic Polyclinic for ankle joint examination are usually patients who have repeated control of the previous examination.
Radiography is an examination by utilizing X-rays on the body's organs to produce optimal diagnosis.
While the ankle joint is a joint between the legs with the lower limbs.
Anatomy of Ankle Joint
Ankle Joint is a joint formed by the tibia bone (shin bone), namely the tibial malleolus and fibula bone (calf bone), namely fibularis malleolus and talus bone (ankle bone). These bones are wrapped in ligaments that are strong enough to form joints. These joint-forming ligaments are talofibular anterior ligaments, talofibular posterior ligaments, deltoid ligaments, tibiocalcaneal ligaments, tibionavicular ligaments and fibular collateral ligaments.
Its main task is to produce dorsiflexion and plantar foot flexion, as well as pronation and supination below a certain level.
Pathology of Ankle Joint
Common indications for ankle joints that require radiological examination are:
- Dislocation
Dislocation is the release of compression of bone tissue from joint union. This dislocation can only be the bone component that shifts or releases all the bone components from where they should be (from the joint bowl). - Soft Tissue Injury
Soft tissue injury is divided into 2, namely Sprain and Strains. Common symptoms of this injury are pain, swelling, and often bruising.
Sprain is an injury that occurs in the ligament, the tissue that connects the bone to the bone or other joints. While strains are injuries to muscle tissue or tendons, tendons are tissues that connect muscles to bones.

Image original by: @anroja
Ankle Joint Radiographic Examination Technique in Dislocation Cases at Radiology Installation Teungku Chik Ditiro Sigli Hospital
A. Patient Identity
Name: Mr. MRF
Age: 18 years old
Sex: Male
Medical Record Number: 127059
Address: Sigli
Diagnosis: Dislocation
Date of Examination: September 20, 2018
B. Preparation of Tools and Materials
- X-Ray equipment: Toshiba Winmind KXO 50 XM
- Cassette: Agfa
- Cassette size: 24 x 30 cm
- Computed Radiography: Agfa
- Printer: Agfa Drystar Axis Laser Imager
- Film: Agfa
- Film size: 24 x 30 cm
C. Patient Preparation
There is no special preparation for ankle joint radiographic examination, the patient is only asked to remove metal objects in the ankle joint area.
D. Examination Technique
AP (Anteroposterior) Projection
Patient position:
The patient is laid on the examination table in the supine position
Object Position:
-Ankle joint that will be examined (left) is placed on a cassette with the posterior ankle joint attached to the cassette.
-The patient's foot is upheld as well as the patient.
-Unchecked feet (right) are in a comfortable position.
X-ray Tube Settings:
-FFD (Focus Film Distence): 100 cm.
-CR (Central Ray): Vertical perpendicular to the cassette.
-CP (Central Point): Between the two malleolus.
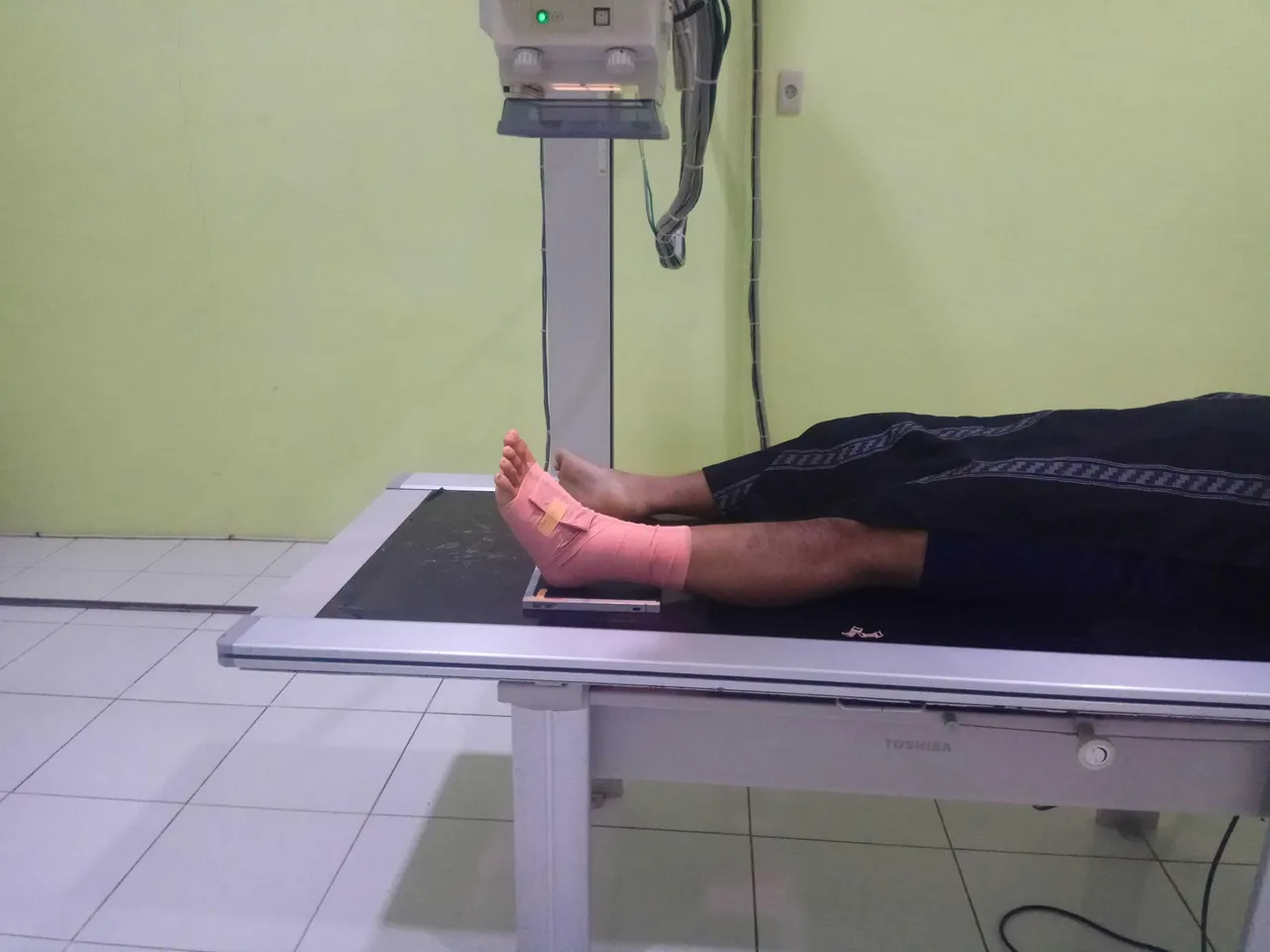
Image original by: @anroja
-kV: 57
-mA: 160
-s: 0.022
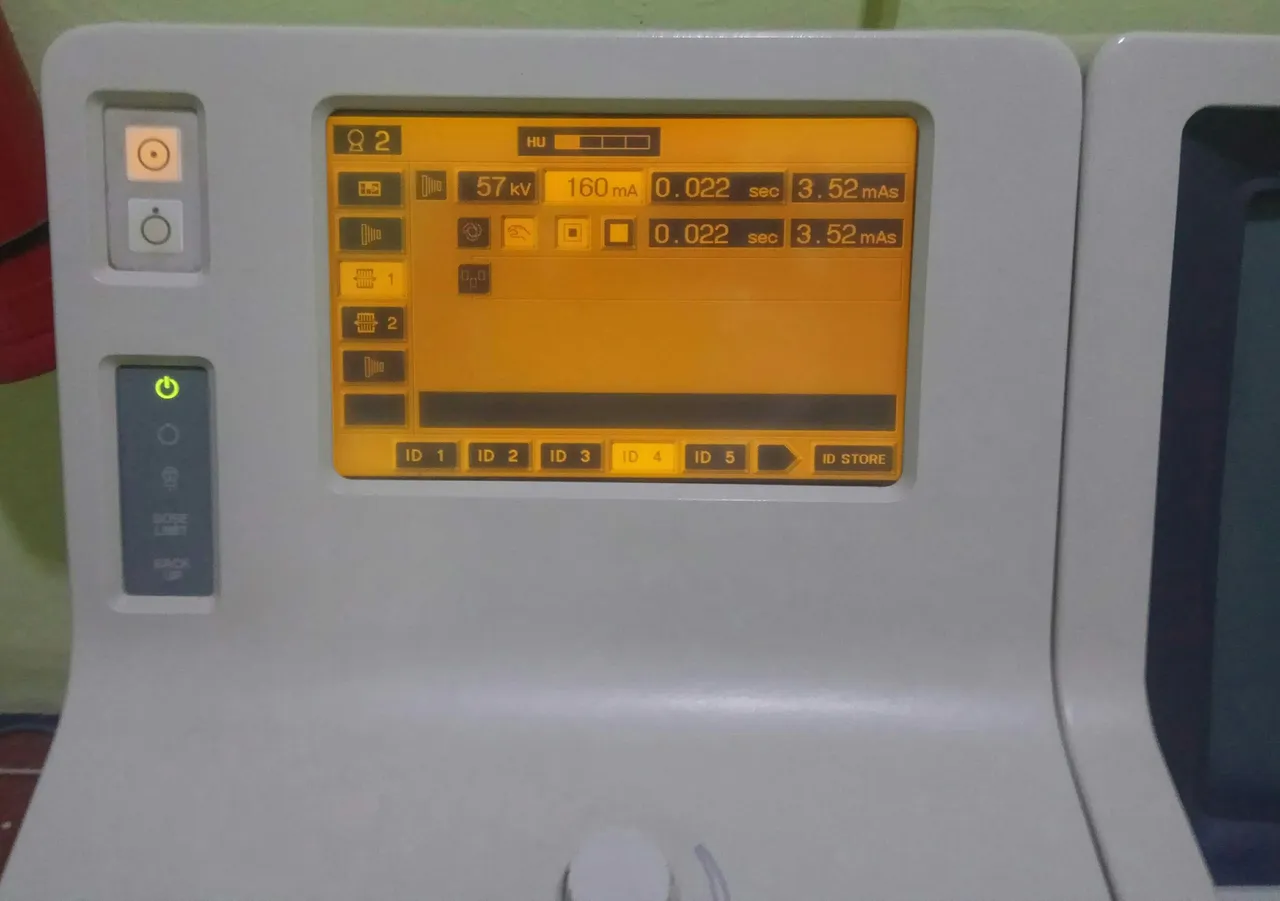

Image original by: @anroja
Visible structure:
-Looks at the ankle joint in the true AP position.
-The fibular and tibial bones of the distal and talus bone are seen in the image.
Lateral Projection
Patient position:
The patient is laid on the examination table in an oblique position to the left.
Object Position:
-Ankle joint that will be examined (left) is placed on the cassette with the outside of the ankle joint attached to the cassette and the knee is flexed (bent).
-Arrange the ankle joint true lateral
-Unchecked legs are in a comfortable position.
X-ray Tube Settings:
-FFD (Focus Film Distence): 100 cm.
-CR (Central Ray): Vertical perpendicular to the cassette.
-CP (Central Point): In medial malleolus.
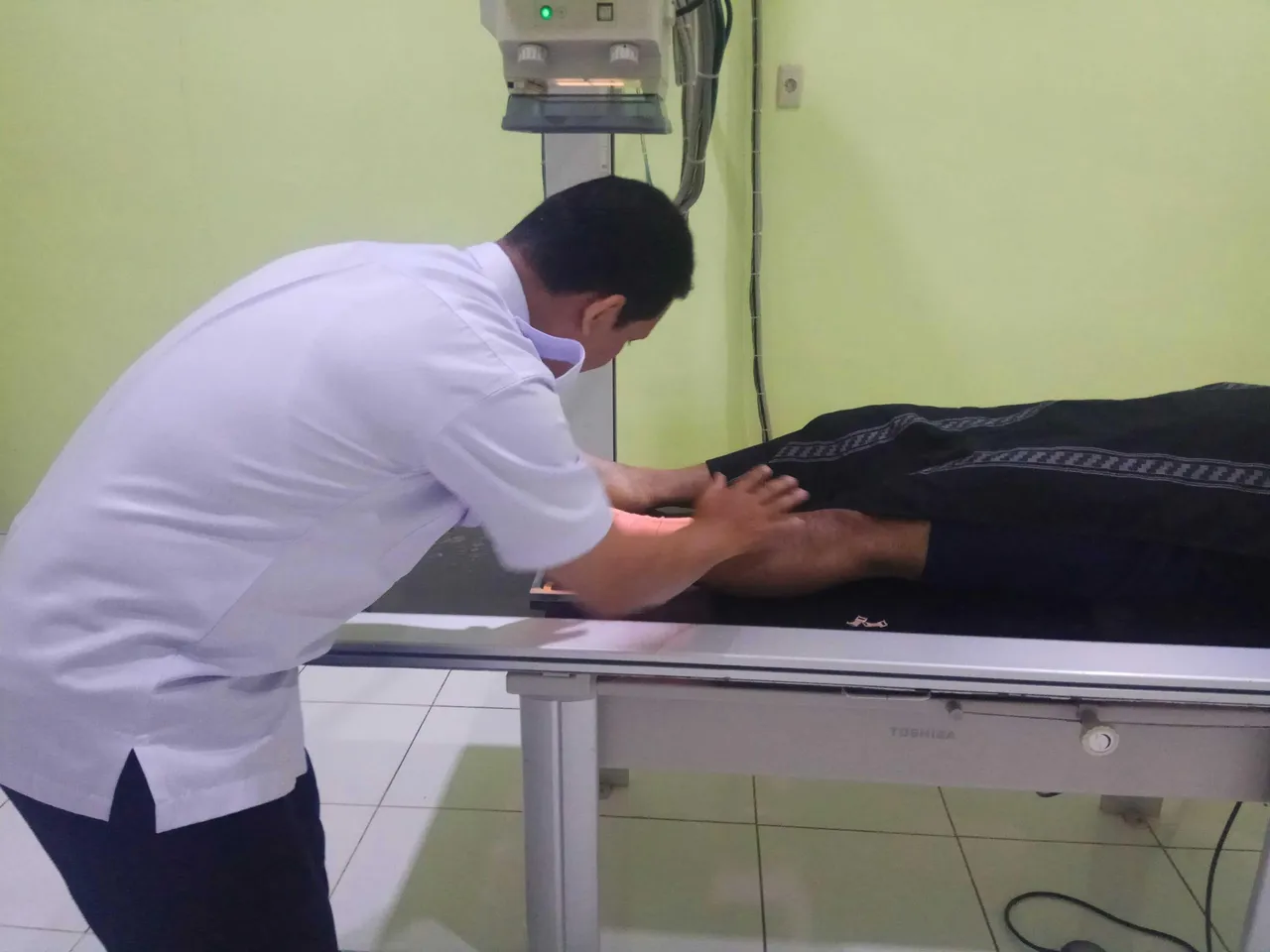
Image original by: @anroja
-kV: 55
-mA: 160
-s: 0.020

Image original by: @anroja
Visible structure:
-The ankle joint appears in true lateral position.
-Superimposition of the tibia bone with fibular bone.
-The talus and calcaneus bones are seen laterally.


Image original by: @anroja
E. Examination result
- Looks dislocated in the ankle joint.
- Does not appear soft tissue swelling.
- Fracture of fibularis malleolus.
Conclusion:
Fracture of fibularis malleolus and dislocation of the ankle joint.

Image original by: @anroja
References:
Kenhub - The Ankle Joint
Wikipedia - Soft Tissue Injury
Healthline - Dislocation
Thanks for visiting my blog
Regards @anroja