¡Hola querida comunidad científica de #Hive, reciban todos un cordial saludo!🖐
Hello dear #Hive scientific community, receive warm greetings from all of you!🖐
En las Ciencias Naturales el proceso de medición es fundamental, es por ello que cuando el individuo comienza su viaje a través de las ciencias lo primero que se le enseña es sobre las medidas y las unidades. Partiendo de la importancia de este hecho, me resulta pertinente que conozcamos un poco sobre la Historia del Sistema Internacional.
In the Natural Sciences the process of measurement is fundamental, that is why when the individual begins his journey through the sciences the first thing he is taught is about measurements and units. Given the importance of this fact, it is pertinent that we know a little about the history of the International System.

Imagen realizada con la página web de diseño gráfico y composición de imágenes Canva // Image made with the graphic design and image composition website Canva.
Antes de comenzar, no podemos dejar de mencionar a mis amigos griegos, quienes en sus comienzos realizaron importantes contribuciones a la metrología y gracias a ellos hoy podemos dar un paseo por la evolución de dicho sistema, reconociendo que ellos son pioneros en el mundo de la ciencia. Sin embargo, este paseo por la historia empieza a finales del siglo XVIII en Francia en plena época de revolución. Primero es relevante mencionar a Antoine Lavoisier un brillante científico que perdió la cabeza en la guillotina por una disputa científica y que además fue miembro de la Comisión de Pesos y Medidas quienes fueron los encargados de definir las bases del sistema métrico. Otros científicos de renombre como Laplace, Coulomb y Lagrage también se unieron a esta comisión.
No obstante, en 1970 la Academia de Ciencia decide tomar una unidad para medir la longitud, para ello establece el metro resaltando de que debería estar basado en algún hecho de la naturaleza. Partiendo de esta condición se decidió que fuera la diezmillonesima parte del cuadrante del meridiano terrestre, para esto los astrónomos franceses Jean-Baptiste Joseph Delambre y Pierre Méchain, fueron los encargados de realizar los cálculos correspondientes; ellos midieron la longitud de arco del meridiano que va desde Dunkerque a Barcelona. El resultado de estas mediciones y los respectivos cálculos fueron materializados en el año de 1799, en un metro patrón conformado por una barra de platino, para esa época se grabaron en mármol varios patrones de metro con la finalidad de que todos se familiarizaran con la nueva medida.
Before we begin, we cannot fail to mention my Greek friends, who in their beginnings made important contributions to metrology and thanks to them today we can take a walk through the evolution of this system, recognizing that they are pioneers in the world of science. However, this walk through history begins at the end of the eighteenth century in France at the height of the revolution. First it is relevant to mention Antoine Lavoisier, a brilliant scientist who lost his head in the guillotine for a scientific dispute and who was also a member of the Commission of Weights and Measures who were in charge of defining the basis of the metric system. Other renowned scientists such as Laplace, Coulomb and Lagrage also joined this commission.
However, in 1970 the Academy of Science decided to take a unit to measure the length, for it establishes the meter highlighting that it should be based on some fact of nature. Based on this condition it was decided that it should be the ten-millionth part of the quadrant of the terrestrial meridian, for this the French astronomers Jean-Baptiste Joseph Delambre and Pierre Méchain, were in charge of making the corresponding calculations; they measured the arc length of the meridian that goes from Dunkerque to Barcelona. The result of these measurements and the respective calculations were materialized in the year 1799, in a standard meter formed by a platinum bar, for that time were engraved in marble several meter patterns in order that everyone was familiar with the new measure.

Source
Ahora bien, para el año de 1793 la asamblea francesa establece como unidad de masa, el grave, la de un decímetro cúbico de agua destilada a una atmósfera de presión y a una temperatura de 4°C, cuya temperatura resulta ser a la que el agua tiene la mayor densidad a presión atmosférica, pero fue en 1799 cuando se le coloca la denominación de kilogramo a la masa de un cilindro de platino. Sin embargo, en 1884 se preparó un nuevo prototipo internacional, algo más resistente, fabricado con una aleación de platino iridiado en forma cilíndrica, el cual se encuentra resguardado en la Oficina Internacional de Pesas y Medidas de Sévres, en las adyacencias de París.
Por otra parte, también se colocaron medidas de tiempo las cuales se han basado en el movimiento del Sol y la Luna, la cual fue denominado como segundo y fue introducido por Al-Biruni como 1/86400 del día solar medio.
Now, in 1793 the French assembly established as a unit of mass, the grave, that of a cubic decimeter of distilled water at one atmosphere of pressure and at a temperature of 4°C, which is the temperature at which water has the highest density at atmospheric pressure, but it was in 1799 when the denomination of kilogram was given to the mass of a platinum cylinder. However, in 1884 a new international prototype was prepared, somewhat more resistant, made of an iridized platinum alloy in cylindrical form, which is kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Sévres, near Paris.
On the other hand, time measures were also placed which were based on the movement of the Sun and the Moon, which was denominated as second and was introduced by Al-Biruni as 1/86400 of the average solar day.

Source
Para 1832 comenzaron las mediciones de las Fuerzas Magnéticas Terrestres, estas a cargo de los científicos Gauss y Weber quienes utilizaron unidades básicas como milimetros, gramos y segundos para ser extendidas a los fenómenos eléctricos. En 1860 los físicos Maxwell y Thomson, mediante la Asociación Británica para el Avance de la Ciencia, llevaron estas unidades a la electricidad y el magnetismo e insistieron que debía establecerse un sistema claro y coherente, es allí donde se establece el Sistema CGS (centímetros, gramos y segundos).
No obstante, en 1875 se reunieron diecisiete países en los que se dio a conocer como Convención del Metro y donde se procedió a firmar el Tratado del Metro por el cual se procedieron a establecer algunos organismos quienes serían los encargados de asesorar y revisar periódicamente este tratado. Los organismos son:
- La Conferencia General de Pesos y Medidas (CGPM)
- El Comité Internacional de Pesas y Medidas (CIPM)
- La Oficina Internacional de Pesos y Medidas (BIPM)
By 1832, measurements of terrestrial magnetic forces began to be made by the scientists Gauss and Weber, who used basic units such as millimeters, grams and seconds to be extended to electrical phenomena. In 1860 physicists Maxwell and Thomson, through the British Association for the Advancement of Science, took these units to electricity and magnetism and insisted that a clear and coherent system should be established, and it is there where the CGS System (centimeters, grams and seconds) was established.
However, in 1875 seventeen countries met in which became known as the Convention of the Meter and where they proceeded to sign the Treaty of the Meter by which they proceeded to establish some agencies who would be responsible for advising and periodically review this treaty. These bodies are:
- The General Conference of Weights and Measures (CGPM).
- The International Committee of Weights and Measures (CIPM).
- The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM).
 Source
SourceEso se mantuvo de esta forma durante algún tiempo, pero justamente en septiembre del año 1899 se sancionaron los prototipos existentes de metro y kilogramo. Entonces, en 1901 Giovanni Giordi propone realizar una combinación de las unidades de electricidad en la cual las unidades básicas sean kilogramo, metro y segundo. Giovanni apostando por sus ideas y después de haber realizado diferentes revisiones y estudios, tomaron decisiones conjuntamente con otros organismos, uno de ellos la International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) se procedió a la aprobación del sistema denominado MKSA cuyas unidades fundamentales eran el metro, kilogramo, segundo y amperio, luego en el año 1954 se introducen dos unidades más, las cuales son la candela y el kelvin.
Pero no fue sino hasta 1960 cuando el sistema adopta el nombre de SI, que son las siglas de Systéme International, para ese año se definió al metro partiendo de una longitud de onda de la transición entre dos niveles de energía del kriptón-86, pero esta definición cambió nuevamente en el año 1983 cuando se tomó como base la velocidad de la luz en el vacío. Para 1967, se define el segundo como 9192631770 períodos de la radiación correspondiente a la transición entre dos niveles hiperfinos del estado fundamental de cesio-133.
En 1971 se incorpora también como unidad básica el mol, es cual se utiliza para medir cantidad de materia. Es así, como el Sistema Internacional tiene siete unidades fundamentales que la podemos ver resumidas en la siguiente tabla:
This was maintained in this form for some time, but just in September 1899 the existing prototypes of meter and kilogram were sanctioned. Then, in 1901 Giovanni Giordi proposed to make a combination of the units of electricity in which the basic units would be kilogram, meter and second. Giovanni betting for his ideas and after having made different reviews and studies, took decisions together with other organizations, one of them the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) proceeded to the approval of the system called MKSA whose fundamental units were the meter, kilogram, second and ampere, then in 1954 two more units are introduced, which are the candela and kelvin.
But it was not until 1960 when the system adopted the name SI, which stands for Systéme International, for that year the meter was defined based on a wavelength of the transition between two energy levels of krypton-86, but this definition changed again in 1983 when the speed of light in vacuum was taken as a basis. By 1967, the second was defined as 9192631770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between two hyperfine levels of the fundamental state of cesium-133.
In 1971, the mole is also incorporated as a basic unit, which is used to measure the quantity of matter. Thus, the International System has seven fundamental units that we can see summarized in the following table:
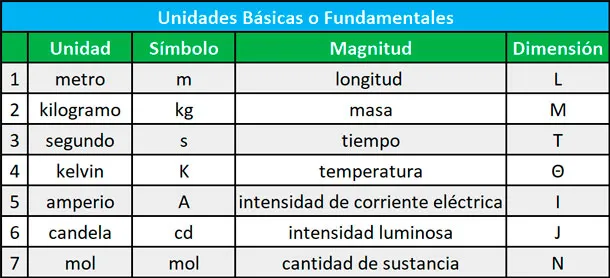
Source
Ya para despedirme, agradezco a quienes se tomarnos unos minutos de su tiempo para leer mi publicación y me encantaría poder leer en los comentarios sus opiniones e impresiones sobre el tema.
In closing, I would like to thank those of you who took a few minutes of your time to read my publication and I would love to read in the comments your opinions and impressions on the subject.
Referencias
Baldor, A. (1941). Algebra. México, Publicaciones Cultural.
Pinto,G; Martín, Manuela; Martín,María. (2012). Sistema Internacional de Unidades: resumen histórico y últimas propuestas. [Documento en línea] [Disponible en:](file:///C:/Users/Hanny/Downloads/Dialnet-SistemaInternacionalDeUnidadesResumenHistoricoYUlt-4042855%20(1).pdf)
References
Baldor, A. (1941). Algebra. Mexico, Cultural Publications.
Pinto,G; Martín, Manuela; Martín,María. (2012). International System of Units: historical summary and latest proposals.[Online document] [Available in:](file:///C:/Users/Hanny/Downloads/Dialnet-SistemaInternacionalDeUnidadesResumenHistoricoYUlt-4042855%20(1).pdf)
Translator Deepl

