Gallbladder Carcinoma
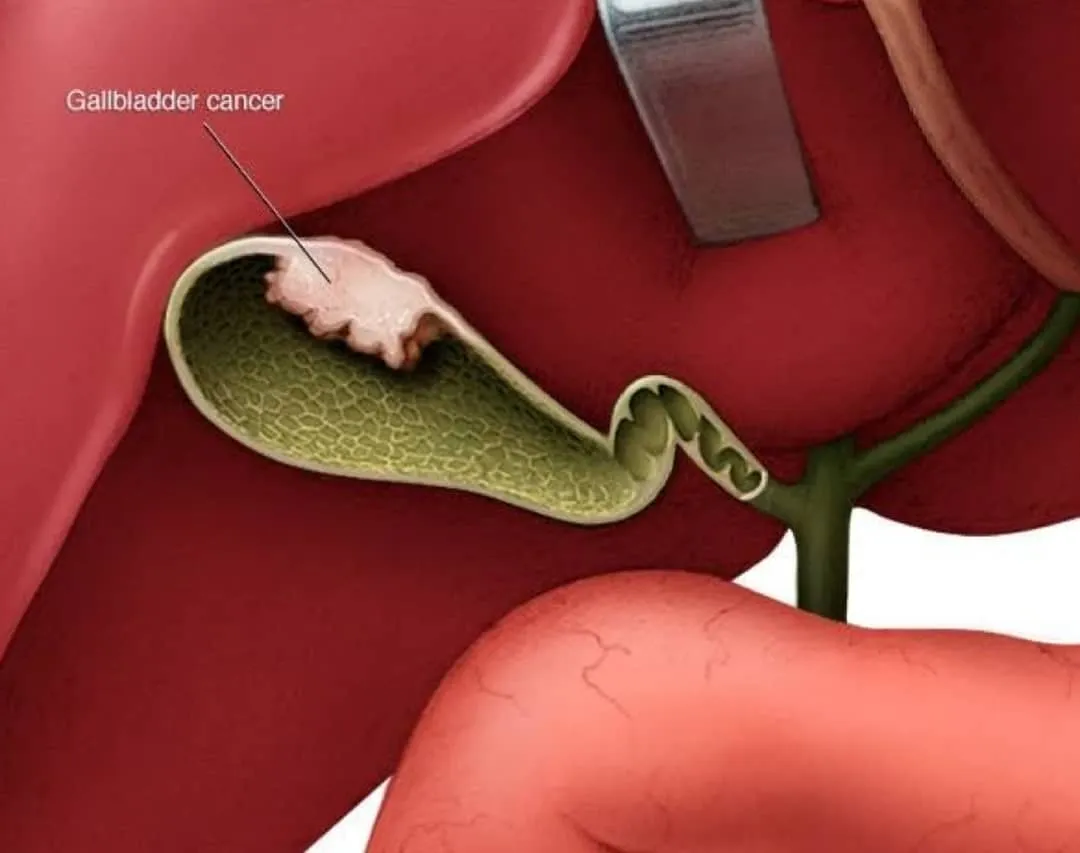
Definition: Malignant Epithelial neoplasm arising from gallbladder mucosa.
Epidemiology: Though uncommon, GB carcinoma is the 5th most common GI cancer, and the most common primary biliary cancer. 75% of the population affected are older women >60 years of age with long standing cholecystolithiasis. F:M ratio=4:1.
Etiology: Porcelain gallbladder, chronic cholecystitis, and long standing cholelithiasis predisposes to GB carcinoma.
Pathology: 90% of GB carcinoma are adenocarcinoma and the rest 10% are squamous cell carcinoma.
..
Early stage :Polypoid mucosal mass.
..
Late stage : Mass infiltrating GB fossa.
Staging or Grading Criteria.
....
Stage 1: Carcinoma confined to mucosa.
.....
Stage 2: Carcinoma involves mucosa and muscularis.
.....
Stage 3: Carcinoma extends to serosa.
.......
Stage 4: Transmural involvement with positive nodes.
........
Stage 5: Liver or distant metastasis.
Clinical Signs & Symptoms.
RUQ pain, Weight loss, Jaundice, elevated bilirubin levels and alkaline phosphatase, biliary obstruction.
Ultrasound Findings.
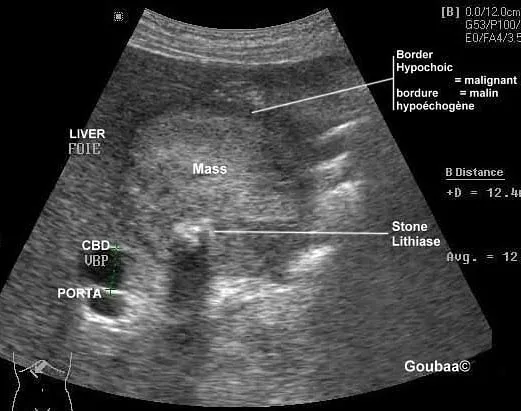
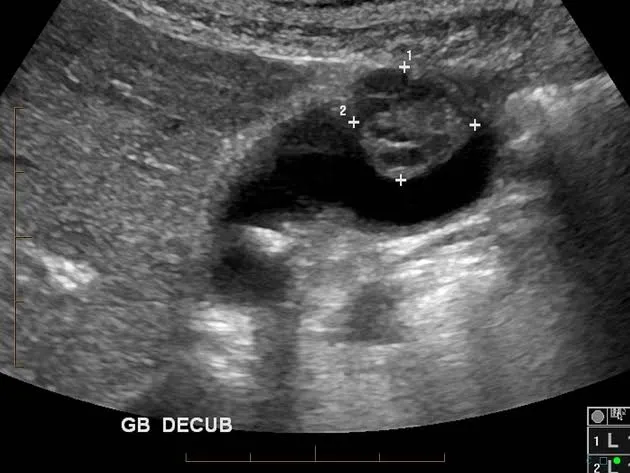
- Intraluminal moderately echogenic gallbladder mass >1cm.
...... - Asymmetric GB wall thickening and/or destruction of GB wall.
....... - Mass infiltrating GB fossa.
....... - Presence of Gall stones 70-90% in GB carcinoma cases.
....... - Regional metastatic lymphadenopathy (early stage of disease).
....... - Liver metastasis.
....... - Biliary obstruction /dilatation, tumour extension to hepatic confluence, extrinsic compression by enlarged regional lymph nodes.
........ - Color Doppler will show hyper-vascularity within the mass.
Differential Diagnosis.
- GB polyps, GB Adenomyomatosis, Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis, Chronic cholecystitis, and metastatic disease to GB fossa.
Treatment and Prognosis.
......
Unfortunately most of the patients already have metastasis at point of diagnosis, so prognosis is very poor.
.......
1--year survival : 80%
5--year survival :1-5%.
Some common treatment includes but not limited to; Radical cholecystectomy and/or partial hepatectomy.