There’s no denying that email has become an incredibly important part of our daily digital lives. We read and write emails every day without really thinking about it, but it’s interesting to see how the email process actually works and brings your digital letters from Point A to Point B.
What exactly is email?
As you might expect, email is short for electronic mail and was first used in 1971 on the ARPANET computer network, the predecessor of the internet we all know and adore today. Raymond Tomlinson is known as the inventor of the electronic mail. Tomlinson worked as a software developer for the American Department of Defense. [1][2]

Image source: Pixabay
It was new to send messages between the different terminals that were connected to the same ARPANET mainframe, but Tomlinson did introduce the key element that is used in emails today: the @-symbol. He was the first to use this symbol as a means to address a message to another system.
Fun fact: Ray Tomlinson was rewarded with a prestigious Princess of Asturias Award in 2009 for the introduction of the @-symbol. The man was also inducted into the Internet Hall of Fame by the Internet Society in 2012. [3][4]

Image source: BBC
The email didn’t become popular until 1995 when the internet gained popularity as well and started to become accessible to users and the big audience. Email became a major hit and for all the right reasons: it’s an instantaneous and completely free alternative to regular letters, and its simplicity was another major benefit.
From Point A to Point B
Just like with regular mail, you need to have the address of the recipient before you can send an email. Those addresses always have the form of [user]@[domain]. If you’d like to send me an email, for example, an example email address would be hello@rebelheart.com. It’s incredibly simple from the user’s point of view, but what exactly happens when you press that ‘Send’ button?

Image source: Pexels
Your digital mail will be sent to an outgoing mail server via SMTP, short for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. You can compare SMTP to a local post office, for example. This protocol ensures that your email is able to send to the correct email address and will check if the address given is valid. [5]
The mail server that works via SMTP will communicate with a DNS server, short for Domain Name System. The DNS provides data for domain names used (such as @gmail.com, or a custom domain such as in the example above). Domain names are linked to an IP-address (172.16.254.1, for example). Because it would be hard for us humans to remember those digits, the DNS system takes care of that for us. Think of the DNS as a sort of major telephone book for the internet, only for web and email addresses. [6]
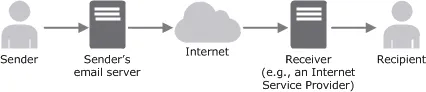
Image source: Amazon AWS Documentation
When looking up DNS records of an address, you’ll also be able to see where the mail server is in that domain thanks to Mail Exchange (MX) records.
Once the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol has extracted all the necessary information of the DNS and MX records, the server will send your email across the internet to the domain of your recipient. The recipients Mail Transfer Agent will then take control of the email and ensure a good delivery of your message.
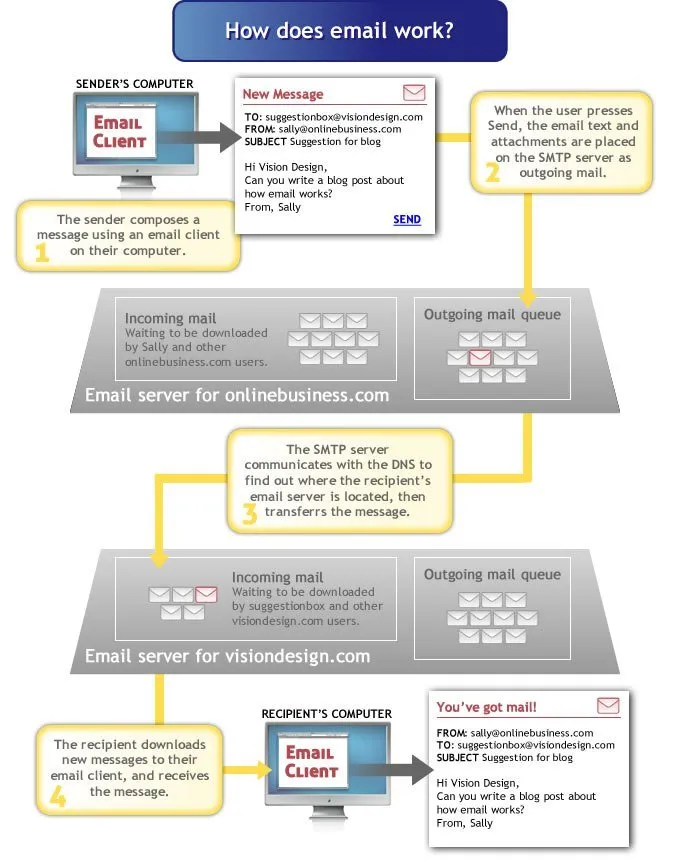
Image source: Vision Design
A little bit confused? Here’s an analogy with regular mail. Think of the SMTP-server as the Post Office, and the internet as the means of transportation. Your email will be delivered to your recipient’s MTA-server, which is the mailman. The mailman then puts your mail into your (digital) mailbox for you to open and read.

Image source: Pixabay
The difference between POP and IMAP
There are plenty of ways to read your emails, although most people just use a web client such as the one given by your internet provider, or popular email providers such as Gmail or Outlook. You can check your emails on every device with access to the internet.
There’s also a possibility to check your emails offline, which means you’ll have to download the emails in their entirety instead of viewing them online. There are a lot of examples of offline mail clients, such as the offline version of Outlook and Mozilla Thunderbird. Mail apps on mobile devices also download your emails for offline viewing.
Image source: Office Blogs
You’ve probably already heard of the terms POP and IMAP if you’ve worked with an offline mail client before. Both are email protocols that are used to ensure you can read and send emails instantaneously. POP and IMAP are used to download your emails stored on the mail server to your email client. In other words, these protocols are responsible for you being able to read your emails.
POP, short for Post Office Protocol, is the simplest protocol of the two. Compare it to checking your virtual mailbox and emptying it. POP downloads all the new emails that you have received and saves them for offline viewing. After the Post Office Protocol is finished downloading your emails, they will be deleted from the mail server in order to reserve space for other emails. [7]

Image source: Pexels
This protocol has a heavy focus on offline viewing because it only works in one direction. If you use POP with your email client, there will be no further communication to the mail server after retrieving your messages. That doesn’t really sound like a major issue, but can be a serious inconvenience for some. If you check your emails on a number of different devices, for example, the lack of communication will result in annoyances. If you’ve read an email on your smartphone, for example, that same email will still be marked as ‘unread’ on your computer because POP only controls your emails locally.
Luckily, an alternative for the Post Office Protocol was created in the form of IMAP. The acronym stands for Internet Message Access Protocol and in contrary to POP, this protocol does offer a two-way communication line between the email client and the mail server. Everything is completely synchronized and emails will also be kept on the mail server itself after downloading them. That means that your emails on all your devices will be perfectly synchronized. [8]
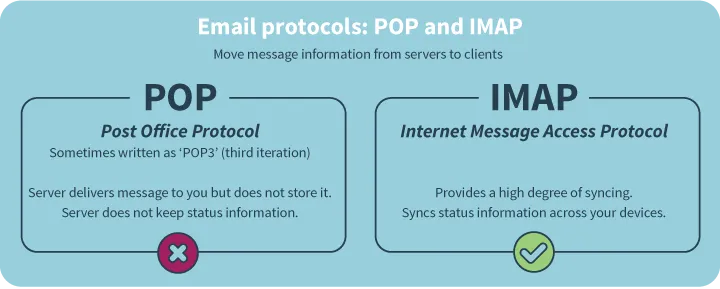
Image source: Quest Technologies
Of course, you’ll need to have internet access in order for the IMAP synchronization to work. Luckily, you don’t have to worry in case there’s no internet – you’re still able to access your emails because IMAP also downloads them locally. Any changes in your emails that you might make, will be sent back to the mail server once your internet connection restores.
With IMAP, your emails are both stored locally (if wanted) and in the cloud of your email client. Storage space is not unlimited, so keep that in mind if your mailbox is getting full. When you’re out of storage space, emails will be returned to sender and can’t be delivered. Luckily, emails that only contain text are extremely lightweight, so you likely won’t have to worry about running out of storage space anytime soon.
- [1] The History of Electronic Mail, Tom Van Vleck
- [2] Computing History
- [3] Fundación Príncipe de Asturias
- [4] Official Biography: Raymond Tomlinson
- [5] Basic Structure SMTP, John Klensin
- [6] How DNS Works, Verisign
- [7] Google Support
- [8] How Does POP Differ From IMAP, Stanford University
- The Processor Bug: Everything You Need To Know About The Massive Meltdown And Spectre Leaks And How It Affects Your Computer
- A Detailed Look at the Rise and Fall of Fingerprint Scanners in Smartphones and the Future of Biometric Identification

