What is heat :- The quality of been hot
The word thermal is also the same as the term heat
Therefore the word dynamic can be describe as motion, that is changing of states of particle
Thermodynamics is a part of science that deals with the relationship between between heat and other forms of energy also the change of heat and also the movement or motion of it.
ZEROTH LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
It states that when two bodies are at thermal equilibrium with a third body, then they are said to be at thermal equilibrium with each other.
i.e
A and B = C then A= B also
FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS :- It can be mathematical written as
dQ = dU + dW
i.e dQ - change in heat
dU - change in internal energy. ( temperature)
dW - work done
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Second law of thermodynamics can be stated in two forms, namely:
Kelvin planks statement and Clausius statement
Kelvin Planck statement of second law of thermodynamics states that an engine moving in a cyclic process cannot convert all heat energy to mechanical works. That is it can never be 100% efficient
Clausius statement of second law of thermodynamics states that it is impossible for a self acting machine moving in a cyclic motion to move all heat at lower temperature to higher temperature except with an external agent
Moreover there is machine that violates this statement it is called PERPETUAL MOTION MACHINE OF ITS SECOND KIND (PMM 2)
Third law of thermodynamics :- it state that when a pure entropy approaches zero and absolute zero temperate.
dS = 0
T = 0
Entropy :- it is the degree of disorderliness in a system
Clausius inequality :- it states that when close system undergoes a cyclic process, the integral equation is shown below :
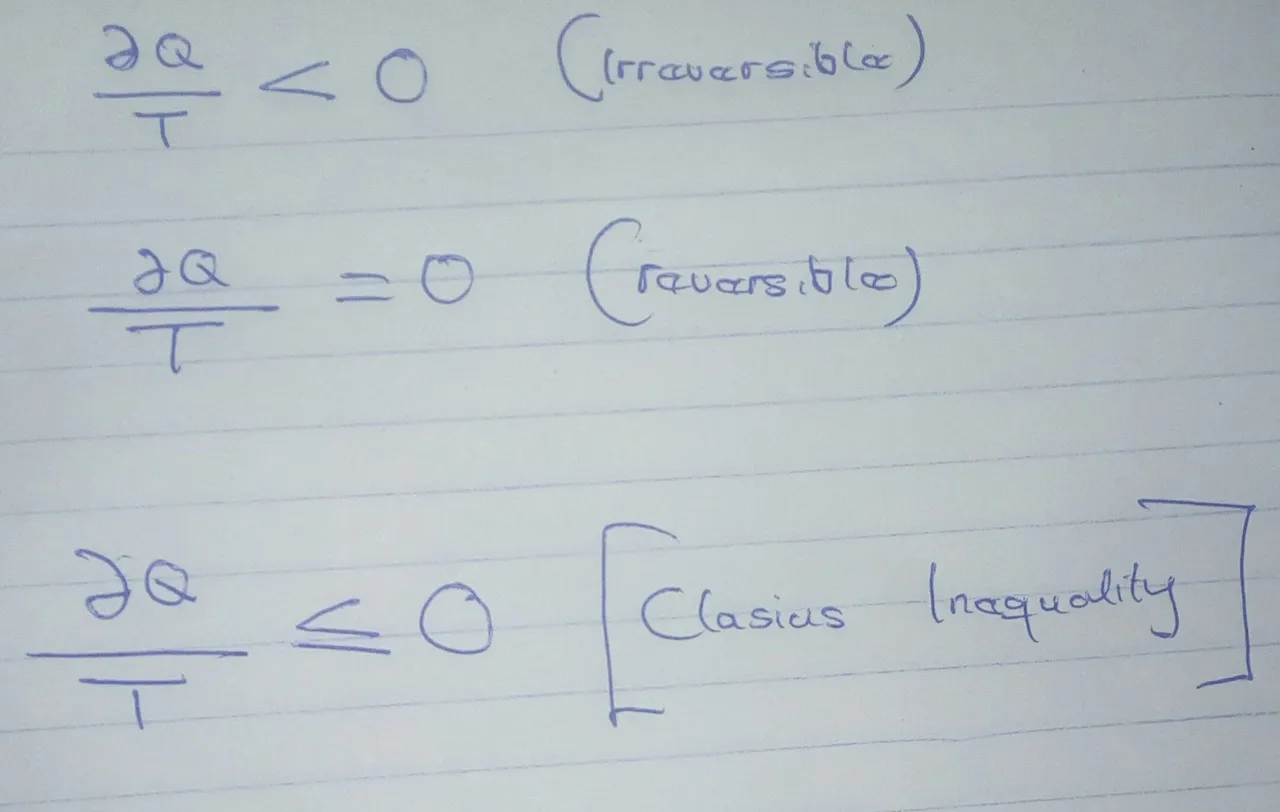
[Source](from gallery)
More so there are some definitions that needed to be take into full consideration when studying heat and thermodynamics as a course of study:
Thermal Reservoir :- This is a system with infinite capacity of absorbing or releasing unlimited amount of heat with altering the temperature
Heat Engine : - This is a device that is used to convert heart energy into mechanical works
Quasi - static process :- This is a process whereby a system is infinitesimally close to the equilibrium
EPISODE 1 (INTRODUCTION ON HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS)