Part I. Gravitational field
1- Field of forces.
When a physical agent A exerts a force of action at a distance on another B, instead of considering that this takes place by mutual action between both bodies, it is more convenient to proceed as if agent A had the property to modify the characteristics of the space that it surrounds him, creating a field of forces, which is the cause of the appearance of a force on B.
There are different kinds of force fields, each of which is characterized by the type of agent that creates it and by the type of agent on which it acts. Among them, the main ones are three: gravitational, electric and magnetic.
When the presence of a mass originates a field of forces, whose action is manifested on another mass, the field of forces is called the gravitational field.
"Gravitational field is a region in which all mass is subjected to the action of a force."
The force that acts on a mass m, located in a gravitational field, depends on the own value of the mass and a specific characteristic of the field, which is called intensity of the gravitational field, and is defined as follows: «Intensity of a field gravitational at a point of it is the force acting on a unit of mass placed at that point. »It is represented by I. To determine the intensity of a gravitational field, it is considered that if on a mass m placed at a point of it, a force F acts, the force acting on each unit of mass, that is, the intensity of the field is:
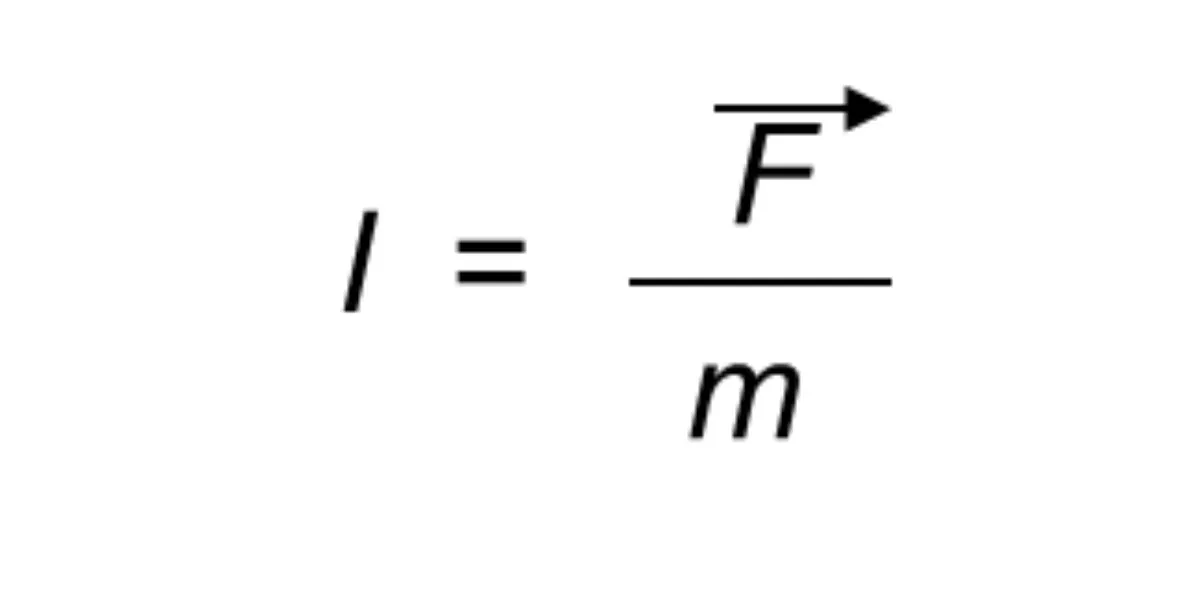
Because of the quotient between a vector magnitude - the force - and a scalar quantity - the mass - the field strength is a vector quantity; its direction and sense of the force that acts on a mass placed at said point. The dimensional formula of the field strength is equal to that of the acceleration, since:
![3.2- ejemplo 2 campo gravitatorio[526].jpg](https://images.ecency.com/p/BgxWBRxjvNhppUjpaAaBDXJRZLu3AdaGMqihzn3oYtZG2GmYjXc9ag1uQvfesGtp7JiRzkvDAdKpMar7aN5Cfx874q3bE7RUfbymi84tS7E99Jf1nvYcqysa7ixDqgyeKi4Kb77WDbZLhfJAtkYFPLWtMGQ49rCKakpozJLAKnkCuVx.png?format=match&mode=fit)
By coinciding with its dimensional formula with that of acceleration, the field intensity units in the different systems are equal to the corresponding acceleration units. - International and technical system: m / s2 - Cegesimal system: cm / s2 And this is so, because - as is evident - the intensity of a gravitational field at a point is nothing but the acceleration that a mass placed at that point would acquire.
Gravity is the force with which we are not familiar because it governs both the movement of the planets of the solar system (to the left) and the fall of bodies on Earth. The law to which all these phenomena fit is illustrated in the image under these lines, where it is indicated by arrows of different width that it is not only the Earth that attracts the apple, but the apple also attracts Earth.
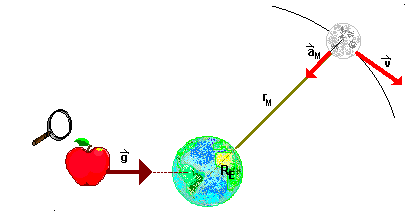
source
2- Potential of a gravitational field.
It is considered that a gravitational field created by a mass M, and at it point A. Supposed, likewise, a mass m that initially is in an arbitrary point O, we want to move it to the point A.
Since the mass m is subject to the action of a force, that of the field created by M, which must be overcome, it is clear that a work will have to be performed, which will be greater the higher the value of the mass m. Well, when this mass is the unit (m = 1), the work is called the potential of the gravitational field. «Potential of a gravitational field in a point of the same one is the work that is necessary to realize to transport a unit of mass from an arbitrary point, that is taken like origin, until the considered point. »
![3.3- ejemplo 3 campo gravitatorio[527].jpg](https://images.ecency.com/p/BgxWBRxjvNhppUjpaAaBDXJRZLu3AdaGMqihzn3obujdKzYHNgkEDVSTVnKhdcoMt5zdQnDR8NLbPGA7GuSWXoU1KP5RK9SprZMqzfDWpprZawWJfTdJdsAHRYjq3F1G3eUDKcWdrcXuBpLVo7JNVtt4EgbPU7bCAS7h2vnYShzcvUE.png?format=match&mode=fit)
For more information visit the following links.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitational_field
- https://isaacphysics.org/concepts/cp_gravitational_field
- http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/152.mf1i.spring02/GravField.htm