
Welcome...
Hello and welcome to another #steemitschool blog. Today we shall be learning about respiration. I hope you find this post useful and learn something new.
What is 'respiration'?
People are lead to believe that 'respiration' means simply breathing in and out. However, this isn't the case.
Respiration is defined as the process of transferring energy from glucose, which occurs in every cell in your body constantly.
You might think that only humans have the capability to respire, but that is untrue. Plants can do it too!
In fact, all living things are able to respire. It's this way that energy can be transported from their food into their cells. The cells can then use this energy to carry out all the living processes.
What sort of reaction is respiration?
Respiration = exothermic reaction.
This is due to energy being transferred into the environment.
So how is the energy transferred in respiration helpful?
- For the building of large molecules from tinier ones. (e.g Formation of proteins from amino acids)
- To permit the contraction of the muscles in animals. This allowing free range of movement.
- Within some birds and mammals, the energy is utilised by keeping their body temperature stable in much colder climates. This is different when compared to other animals, birds and mammals that sustain warm body temperatures.
The 2 different types of respiration... Aerobic and Anaerobic
Aerobic respiration
- Aerobic respiration = respiration that uses oxygen.
- It is the most effective method to transfer energy from glucose.
- This form of respiration is occurring constantly in both plants and animals (usually inside the mitochondria cells)
Word equation for aerobic respiration:
glucose + oxygen (produces) carbon dioxide + water
Here is this equation in symbol form.
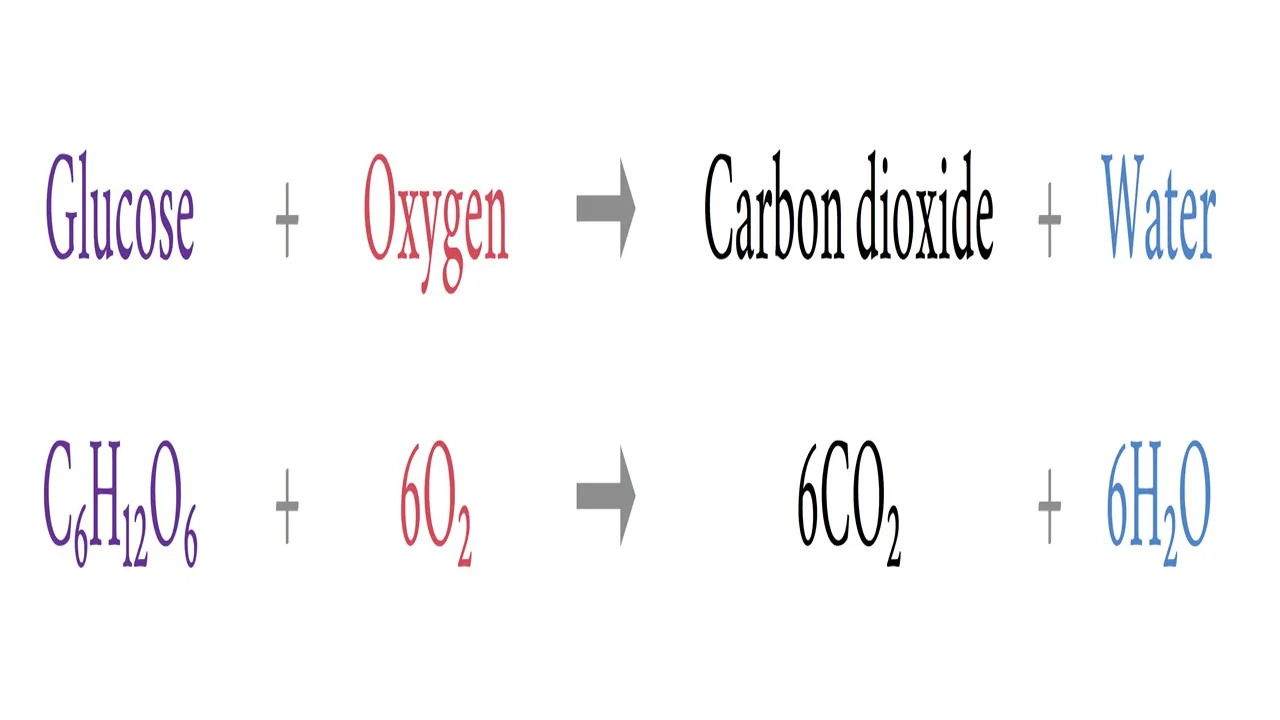
(credit: https://examhints.wordpress.com/2014/09/21/how-to-answer-respiration-questions/ )
Anaerobic respiration
- Anaerobic respiration = Respiration without oxygen.
- During anaerobic respiration, glucose is not broken down completely. This causes lactic acid to be produced. Lactic acid then accumulates in the muscles, which can cause you to feel much pain!
- This type of respiration occurs when the body is incapable to supply a sufficient amount of oxygen to the working muscles. For example, when you take part in physically intensive activity.
- It is because of this that anaerobic respiration is only useful in extreme circumstances - like getting your muscles to work at a higher intensity for a longer duration.
- In comparison to aerobic respiration, anaerobic does not transfer anywhere near as much energy! This is down to the glucose not being oxidised entirely.
Word equation for anaerobic respiration:
Glucose (produces) Lactic acid
Here is the symbol equation for this reaction.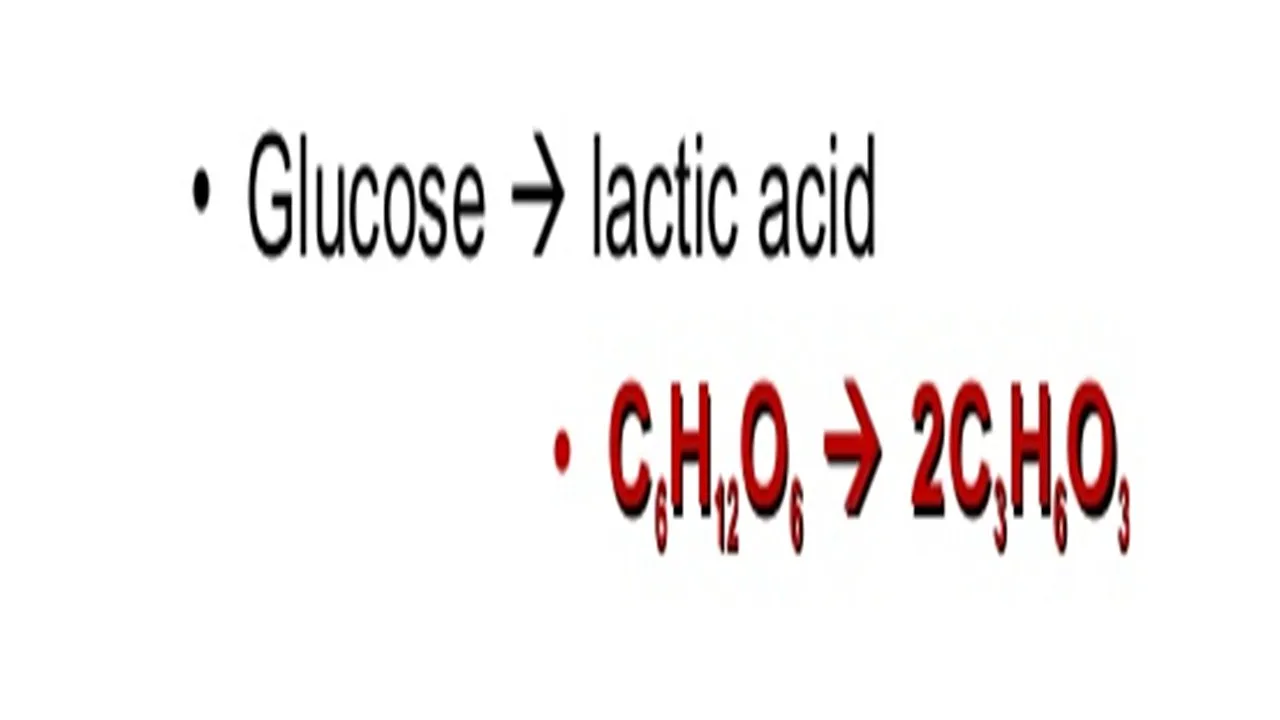
(Credit: https://www.slideshare.net/Kshirja2002/respiration-gas-exchange-41949409 )
Exercise - how does respiration work here?
During exercise, some muscles will be contracting more than usual. Therefore, more energy is required to help this process happen. This energy is sourced from an increase in respiration.
A rise in respiration allows more oxygen to be obtained by the cells. Furthermore, more oxygen can be transported into the blood from a greater breathing rate and breath volume. Through the increase in our heart rate, the flow of oxygenated blood around the body will be at a greater pace.
As a result of this occurring, carbon dioxide can be removed from the cells at a quicker rate and simultaneously to the above processes.
Oxygen debt
oxygen debt = the quantity of oxygen needed to oxidise/breakdown lactic acid to produce carbon dioxide + water.
This means, essentially, that you are required to "pay back" your body with the oxygen that could not be provided to your muscles earlier as the heart, lungs and blood were unable to maintain the constant need for it.
This is the reason that you breath much heavier after you stop intense exercise - your body requires more oxygen to be transported to the cells that are in the muscles.
During times when high levels of carbon dioxide and lactic acid are within the body, the breathing rate and pulse remain high in order to remove it.
However, this isn't the body's only way of dealing with such high levels of lactic acid. The blood that accesses your muscles can take the lactic acid to your liver where it is then changed back to glucose.
Thanks for reading. I hope you've learnt something new today!
Hope everyone's having a good week.
Jonathan.