Plant Cells With Organelles and Their Functions
Basically Organel Types Plant cells are cell walls and plastids. Cell walls function for protection and plastids (chlorophyll) function for photosynthesis. Here's the full discussion.
this will explain about plant cells, plant cell structure, plant cell organelles, organelle function, and plant cell components.
Plant Cells
Cells are the smallest unit of life. Every living thing is made up of many cells (multicellular), but some are composed of only one cell (unicellular). Plants include multicellular living beings.
Plant cells also belong to eukaryotic organisms, not prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic organisms have a true nucleus that is bounded by the membrane (the nuclear membrane). Eu means true and karyon means core. The cell size is relatively large (10-100 μm) and has membrane-bound organelles such as RE, Golgi, mitochondrial, and lysosomal bodies.
The eukaryotic cells also have unrestricted organelles such as ribosomes, microtubules, centrioles and cytoskeleton. Examples of eukaryotic organisms are animals and plants. Others with prokaryotic organisms. Prokaryotic organisms are living things whose nuclei have no membranes or membranes. Pro means primitive and karyon means core. They are small (0.5-1 μm) and do not have organelles with endomembranous systems (nuclei, mitochondria, plastids). Examples of prokaryotic organisms are in the monera kingdom (bacteria and blue algae).
In addition to belonging to eukaryotic organisms, plants also include autototropic organisms. Autotrophs are organisms capable of converting inorganic substances into organic substances. We often refer to it as organisms that are capable of making their own food.
Plants include autotrophic organisms because they have chlorophyll that serves to perform photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is a green leaf substance produced by chloroplast organelles.
In addition to chloroplasts, plant cells also have other organelles. The organelle exists only in plant cells and there are also found in other cells.
Typical Structure of Plant Cells
The typical structure of plant cells is as follows:
- Vakuola, actually other cells also have vacuoles, but very rare and if any size is very small.
- Plastida, one of the plastid types that you must know is chloroplasts. In addition to chloroplasts, there are also other types of plastids that will be watched below.
- Cell wall, this is the structure that makes the plant body becomes stiff.
Plant Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Here are the organelles in plant cells and their functions:
1. Nucleus (Cell Core)
The nucleus is the nuclear organelle of a cell. The organelle is composed of four parts, namely the Core (Karioteka), nucleoplasm (Kariolimfa), chromatin or chromosome (genetic material) and nucleolus (the nucleus). The function of the cell nucleus is to regulate all cell activity because it contains genetic material (DNA and RNA) that serves to print proteins. Of course you know that protein functions as our body builder.
2. Endoplasmic Reticulum (RE)
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle consisting of two layers of membrane, a sisterna and a tube. If we look at the cell picture, this RE is like a sheet attached to the cell nucleus.
The function of RE is as follows:
- Intracellular transport of materials to be secreted
- The transport of substances within the cell itself
- Involved in the formation of vacuoles
- Establish membrane on Golgi body
By the way, RE is divided into two types, namely RE fine and rough RE. The fine RE is not attached by the ribosome. While the rough RE ribosome plastered so it looks like it has a rough surface.
3. Ribosome
Ribosomes are round organelles, their size very small when compared to other organelles. The structure of the ribosome consists of two parts, namely large and small parts. Large sections are called large subunits and small parts are called small subunits. Ribosomes are composed of proteins and RNA, some are attached along the RE and some are solitary or dispersed freely within the cell. The function of the ribosome is as a place of protein synthesis.
4. Mitochondria
The oval-shaped structure of mitochondria has two layers of membrane (double membrane), the inner layer is grooved and is called Krista. Inside mitochondria there is also DNA. Mitochondrial function is the center of cellular respiration that produces a lot of ATP (energy).
5. Golgi Agency (Diktiosom)
Golgi's body or Golgi apparatus consists of a group of sisterna that is flat and arranged in parallel. The function of the Golgi body is related to the cell excretion function.
6. Plastids
Plastids are divided into three types, namely:
- Leukoplas, which is white plastida serves as a food store. Leukoplas consists of:
• Amyloplast (untill store starch)
• Elaioplas (Lipidoplas) (to store fat / oil)
• Proteoplasts (for storing proteins) - Chloroplast, the plastida is green. This plastida serves to produce chlorophyll and as a place of photosynthesis.
- Chromoplast, ie plastids containing pigment. The chromoplast consists of:
• Carotene (yellow)
• Fikodanin (blue)
• Fikosantin (yellow)
• Ficoeritrin (red)
7. Vakuola
Vakuola is a sac surrounded by a fluid / water-filled membrane. The membrane or membrane between the vacuole and the cytoplasm is called a tonoplast. Vakuola functions are as follows:
- Storage water, food reserves, oils, enzymes, pigments, toxic compounds and metabolic by-products.
- Helps maintain turgor pressure in cells.
- Vakuola has an important role as a shelter of secondary products in the form of liquid, so-called 'liquid cell'.
- Some experts have called vacuoles not organelles (but nonprotoplasma components).
- In cells that are still young / meristematic, vacuoles are usually small and large.
- While in adult cells vakuolanya large.
- Plants have no excretory system as in animals, therefore vakuola serves to store the waste of metabolism.
- Place of destruction of certain compounds by hydrolas enzymes.
- Vacuoles with vesicles contribute to the storage of matter in the cell (vacuole size larger than vesicles).
8. Peroxisomes
Is a special organelle equipped with a single membrane. This organelle produces oxidative enzymes used in metabolic breakdown. The function of peroxisomes is to help chloroplasts during photorespiration and as an equal breaker of fat into sugars. Contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, which produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product.
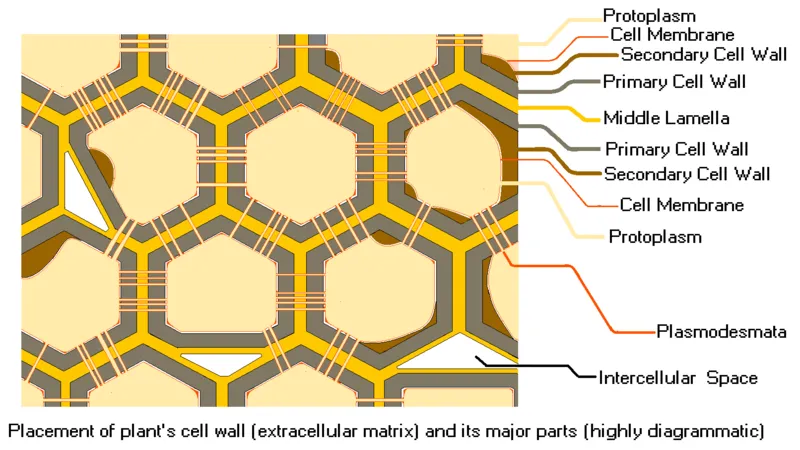
Plant cell components
Plant cell component consists of 2 main parts, namely cell wall and protoplas. Cell wall is divided into three parts, namely the primary wall, secondary wall and central lamela. While protoplas consists of protoplasm and non protoplasm. Protoplasm includes cytoplasm (cell fluid), nucleus (nucleus), and organelles. The protoplasts belonging to the non-protoplasm categories are vacuoles and ergastic substances. Thus the discussion of organelles of plant cells, their functions and their components. Hopefully useful and do not forget to follow our social media to get the latest updates about biology.