1.what is an information security assurance?
- Information systems play an important role in the infrastructure that supports commerce, banking, telecommunications, health care, and national security, driving the need for qualified information assurance and security specialists, Security professionals will be called on to solve security and data-retrieval issues, as well as help with computer system design and networking. They may be expected to maintain disaster-recovery plans, which copy data into storage backup files that are located outside the IT network.
2.Components information security assurance ?
- Integrity-Integrity involves assurance that all information systems are protected and not tampered with. IA aims to maintain integrity through means such as anti-virus software on all computer system
-Availability-Availability simply means those who need access to information, are allowed to access it. Information should be available to only those who are aware of the risks associated with information systems
-Authentication-Ways of improving authentication involve methods such as two-factor authentication, strong passwords, bio-metrics and other devices.
-Confidentiality-involves the confidentiality of information, meaning only those with authorization may view certain data.
-Nonrepudiation-The final pillar simply means someone with access to your organizations information system cannot deny having completed an action within the system, as there should be methods in place to prove that they did make said action.
3.Differentiate the certification programs to common body language?
-This course on 'Body Language' is designed to help you understand the different aspect of body language so that you are able to use the information to your personal and professional advantage.
4.Differentiate the governance and risk management ?
-The difference between Governance and Risk Management is that Governance is the creation of Theory and Risk Management is Applied Theory. The two go hand-in-hand. They really cannot exist exclusive of each other. The business framework "rules of engagement" are set out by the members of the board, stakeholders, and investors that drive business strategy, business value, corporate responsibility, and managed risk - ensuring that risks are identified, minimized, and controlled within acceptable "risk-appetite".
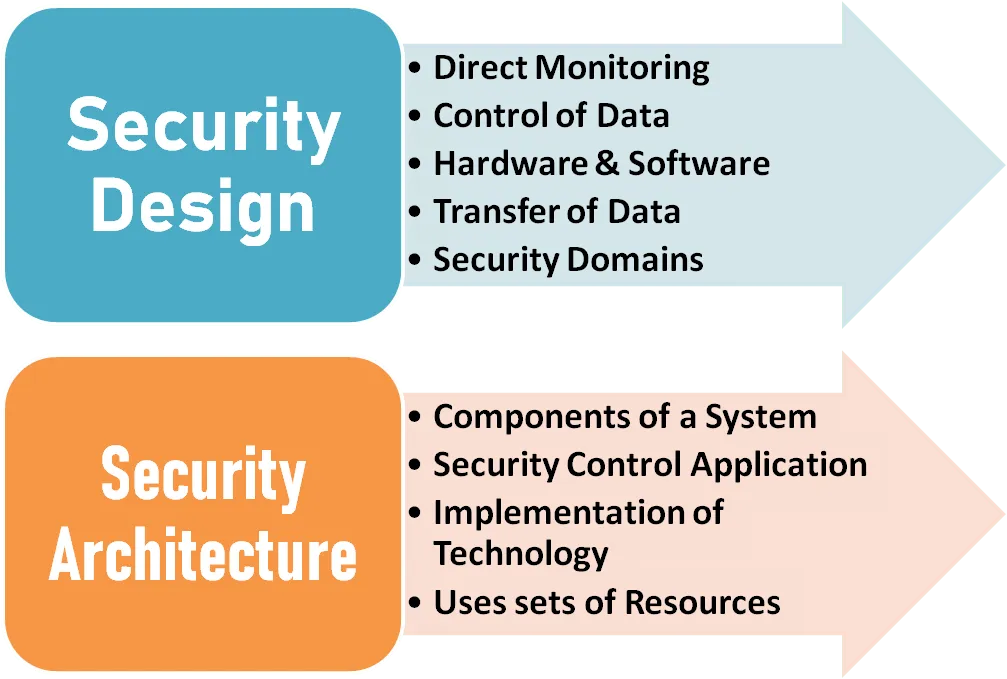
5.Different between security architecture to design ?
-Both security architecture and security design are elements of how IT professionals work to provide comprehensive security for systems. However, these two terms are a bit different.
Security architecture is the set of resources and components of a security system that allow it to function. Talking about security architecture means talking about how a security system is set up, and how all of its individual parts work, both individually and as a whole.
6.Different between business continuity planning to disaster recovery planning ?
-Two specific fields address potential business interruptions: business continuity and disaster recovery. These disciplines minimize the impact that a catastrophic event might have on a business’s ability to reliably deliver its products and services.
While both fields are important, and even similar in some aspects, they are not synonymous. There are important differences in business continuity vs. disaster recovery, and those in leadership or emergency preparedness roles can benefit from understanding the core distinctions.
7.what is physical security control?
-Physical control is the implementation of security measures in a defined structure used to deter or prevent unauthorized access to sensitive material. Examples of physical controls are: Closed-circuit surveillance cameras.
8.what is operation security ?
-is a security and risk management process that prevents sensitive information from getting into the wrong hands. It includes analytical activities and processes like behavior monitoring, social media monitoring, and security best practice.

9.What is law?
-Law is a set of rules created by state institutions which make laws through the authority of the state. The laws have sanctions which are recognized by the state and enforced by state-authorized bodies. only certain institutions can make law. the institutions that make law have been given the authority to do so.

10.What is investigation
-An examination is an orderly attempt to obtain information about or to make a test of something, often something presented for observation: a physical examination. An inquiry is an investigation made by asking questions rather than by inspection, or by study of available evidence: an inquiry into a proposed bond issue. Research is careful and sustained investigation.

11.what is ethics
-Ethics is based on well-founded standards of right and wrong that prescribe what humans ought to do, usually in terms of rights, obligations, benefits to society, fairness, or specific virtues. An example of ethics is a the code of conduct set by a business. The system or code of morals of a particular person, religion, group, profession, etc.
12.What is information Security ?
-Information security refers to the processes and methodologies which are designed and implemented to protect print, electronic, or any other form of confidential, private and sensitive information or data from unauthorized access, use, misuse, disclosure, destruction, modification, or disruption.