Before now I had thought this article to be where I introduce this plant and their cool survival system in the wild (being amongst the carnivorous and have their habitat to be aquatic) , then I came across their status as being endangered in the wild and extinct in some countries where they were earlier found, hence I decided to bring to the steemit community the awareness needed for the survival of this plant with the hopes that reading this not just a rethink of how our activities affect nature but more will be done to conserve them.
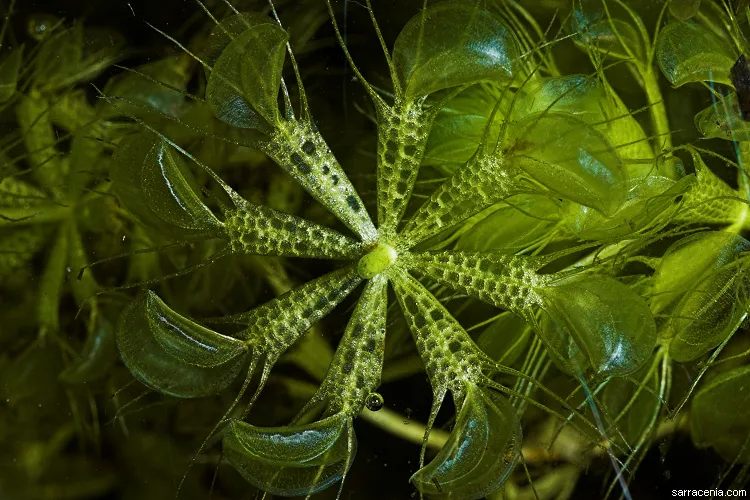

About The Waterwheel
They were discovered by Leonard Plukenet in the year 1699 in India. After a decade later, they got their name as Aldrovandia by a botanist from Italy named Gaetano Monti. He named them in honor of a naturalist from Italy by name Ulisse Aldrovandi but a misspelling occured by Carl Linnaeeus in his book tagged Species Plantarum in 1753 with the "i" missing to make them now go by Aldrovanda.
The snap behavior of the trap was observed in 1861 by De Sassus and later their carnivorous nature was observed by Darwin.
How You Recognize An Aldrovanda Visiculosa
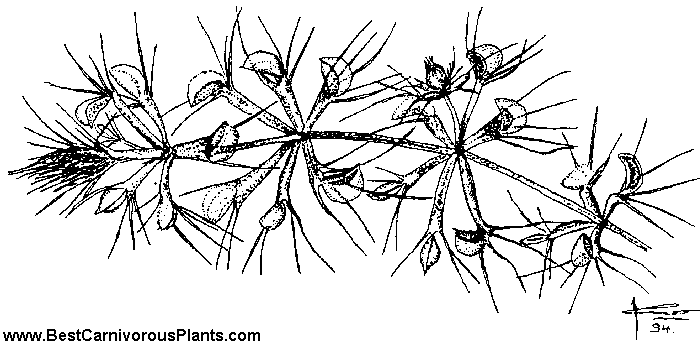
The water wheel is a floating carnivorous plant without root and normally found in waters rich in nutrients, their leaves are well arranged hence their name as the water wheel.
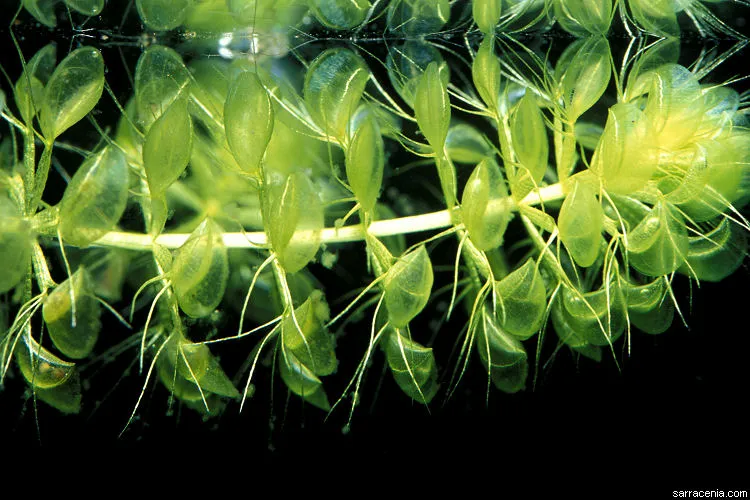

Water wheel normally measures a length less than 20 centimeters, their leaves are about 6-8 in arrangement and they have shoot of diameter ranging form 1-2 centimeter. Degeneration occurs in the base of this plant to its older whorls as new ones grow at the top and shoots are sometimes produced in the stem which spring up new plants.
The Eurasia water wheel have a colouration of a light green to yellow while the Australian specie of this plant have a red rose to a purple colouration.
Leaves
Their leaves is made of flattened petioles which are of length of about nine millimeter and they end at a trap with bristles which helps against trigger from items which are not prey to them.
Flower

They produce flowers which tend to shoot out of the water surface , this flower has about 5 pink tinged petals and also about 5 sepals.
Range Description
The water wheel plant have range throughout Europe from the west and South of France down to the central and northern part of Italy, they also have their rang in countries like Croatia, Poland, Austria, Germany, Volga, Romania, Hungary, Ukraine, Lichtenstein, Russia, Lithuania Amur, Slovakia, Belarus, Serbia, Lipetsk, Caucasus and Turkey
Their range also covers some part of Asia in China, Japan, India, South and North Korea and they also cover parts of Australia. Their population have been recorded too in some part of Africa which include South Africa, Togo, Zambia, Tanzania , Botswana, Uganda, Burundi, Chad Cameroon South Sudan and Ghana.
Some locations have not been verified, but they are recorded to be scares in some part of Europe. generally they have their system to be of freshwater habitats.
They have quite a wild geographical range but though they cover a very wide range they have been notice to be of a decline in the wild with estimation of extinction in about 11 countries where they were found earlier in the last century and they are now listed as endangered according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature, (IUCN)
Behavior In The Wild
The waterwheel plant is known to occur in varieties of habitat including lagoons, river delta, small fans lakes and billabong. Their growth season are known to extend mid spring to the early parts of the autumn and they have their flowers in the summer when growing conditions are good. In late autumn as the length of day begins to decrease, the temperature of the water is noticed to drop and this period sees this plant producing dormant buds which are referred to as turions.
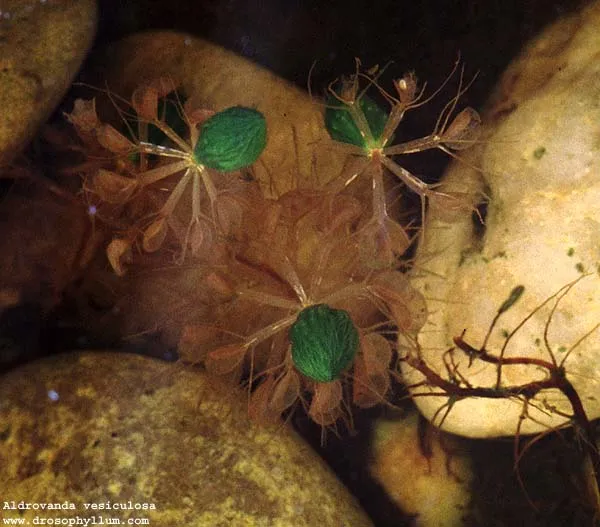

From a mature turions stem and some vegetative material tend to break off and sink down the water to a stable temperature during winter, it has been known that an overwinter will lead to quite a loss in population of this specie as their survival of winter only ranges from twenty to thirty percent of the total population
Turions which do not sink are washed to the shores and when temperature begins to increase in the spring these surviving turions tend to recommence growth. At areas which are known for mild winter they may grow through the year without any form of over wintering and they are known for extreme rapid growth when the habitat condition is favorable to their growth.
Flowers in this plant do not occur often and when they do they are normally of low numbers, unlike other flowers which bloom in their season, their flowers only tend to open for only a short period of time and most times do not develop any fruit producing less seed even in very good conditions through self pollination.
Their main system of distribution in the wild is vegetative propagating like turions or stem fragments which might be transported by bird from one suitable habitat to another, and they are known to not tolerate any form of degradation of habitat as a slight change in the water will lead to an extinction in that area.
Their Trapping System
When seen, their trap is small in nature, it us surrounded with bristles which are hair-like and this bristle functions as that which tend to block this plant other aquatic plants from getting in and getting them damaged of inducing a false trigger on them.

The outer edges of this trap is seen to have lobes which consists of teeth which are hook-like just like that in the Venus flytrap and these teeth interlock between we each other when a prey is caught.
The mechanism of Trapping works with trigger hairs which is about forty, now you can imagine how efficient this trap is as a trap as effective like the Venus flytrap has about six to eight hair trigger. When these hairs are triggered about one or more times, they snap shut leaving the the prey helpless.
The waterwheel plant is known to be among the fastest movement in the plant world as their trap take about 10-20 milliseconds to snap shut on their prey and their carnivorous nature sees them trapping marine invertebrates. This trap consist of glands which help in the digestion by first breaking down soft tissues and absorption of Nutrients from them.
Sealing in this trap is achieved by the teeth which interlock on prey and a mucus type sealant which hold this prey in captivity and force it down to the base and doing this they force out much of the water in this trap replacing them with digestive enzymes for the digestion of their prey. They have no means for luring prey unlike the Venus flytrap.
Threats To The Survival Of Water Wheel Plant
With respect to review on the threat on this plant, their primary threat is the increase in commercial development and also the need for residential areas due to increase in human population, aquaculture and agricultural purposes, pollution and the modification of their natural habitat have also been seen to contribute to their decline.
According to the Commission of the European Union threat on this plant species was also recorded as canalization, acidification, drainage, forest clearance, mining, process of gravel extraction, desilting, limited dispersion and hydrologic modification was noted as threat on the survival of this plant across the European region.
It is also believed that illegal trade occurs in some areas. Mainly, the degradation of the habitat of this plant is noticed to be common through their range of occurrence that also includes those in areas in conservation reserves.
Conservation According To IUCN
According to the IUCN conservation status, this plant is currently receiving protection in almost all countries where they now exist. Areas where it receives less protection like Asia, Australia and Africa is due to insufficient data as at their number of occurrence in those places have not been determined, but across the range of Europe, the water wheel plant is at a decline and now is treated as a critically endangered plant specie and now included in the Annex 1 with respect to Bern Convection to focus on the conservation of their habitat.
Conservation of this plant have seen to it that a number of them be located in various conservation sites such as nature reserves monitored parkland and other biosphere reserve areas and this has over some years provide habitat security for this plant.
Some protected areas of this plant include the Astrakhan reserve, New England Table and Endangered Ecological Community in Australia , Srebarna managed nature Reserve but these areas have been seen to have their major challenge of conservation of this plant to be the change in the landscape caused by Biotic linkages and hydrology. But though the conservative measures now put in place for this plant species, their habit degradation can not be avoided entirely.
What I Think Should Be Done
When I came across this plant It actually did took the breath away as I was stunned with how they existed in the wild, unknown of the fact of their conservative status, endangered it says.

Though as seen above, many factors contributed to their current status which include degradation of their habitat in the wild by some factors of which are caused by human activities, hence a rethink should be done on our activities as at how they affect the aquatic world negatively with the sole aim to conserve it.
As have been seen with respect to what is being done to conserve this plant species I strongly feel that a lot still needs to be done, according to the IUCN data which I came across, I was shocked that though this plant was listed as endangered some countries around the world have not seen the need to put them in their redlist of threatened species with the reason of no sufficient data most especially in parts of Africa and Australia where they occur.
It's important to know that we only have one earth to conserve and as a specie of plant is known to be of decline in one part of the world it is necessary to conserve them in other parts, gathering information of their occurrence and putting in place conservative measures for continuity of this plant specie.