Sexually transmitted diseases or STDs are infections transmitted through sexual contact (normal, oral or anal) but can be transmitted in other ways.
Among the means of transmission of these diseases, apart from sexual intercourse, we can make contact with infected area, contact with infected objects (needles, etc.) or from mother to fetus, etc.
These diseases can be classified into two main categories:
Major STDs, which include:
- syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- Chancroid
- Granuloma inguinal
- Limfogranulomatoza groin
STDs minor, which includes:
- Nongonococcal urethritis (the most common diseases in this category are caused by Chlamydia, mycoplasma, candida albicans , trichomonas vaginalis)
- Trichomoniasis urogenital
- Urogenital candidiasis
- Genital herpes
- Warts
- Molluscum contagiosum
- scabies
- pediculosis
- Some forms of hepatitis.
In the past decade, HIV infection, the most dangerous infection, with syphilis, caused unprecedented epidemic. Clinical expressions of sexually transmitted diseases occur mostly in the genital region, but may be evident in the mouth, on the skin or in the eyes - conjunctival.
In the genital area, the symptoms manifested by unusual discharge, pelvic pain, burning, itching, irritation, pain during intercourse (dyspareunia) or urinating ( dysuria ). The presence of all these symptoms is not mandatory - some of them disappearing by itself, although infection remains in the body to treatment or chronic.
The first step in treating STDs is the medical advice and correct diagnosis . Not recommended empirical treatment or following informal consultation of other information sources often incorrect. The doctor may be a family in the first phase that will send you to a specialist in dermatology diseases - venereal that will make analysis and apply the proper treatment.
This treatment should be continued for the duration recommended, even if symptoms disappear, and intercourse may be resumed after 3 days after cessation of treatment in accordance with the recommendations of the specialist physician. Risk of getting these diseases is higher in sex with multiple partners when not in use condoms as a means of protection and use drugs when they are injecting drug users or your partner has in turn more sexual partners.
Overview
pox
gonorrhea
Chlamydia
Scabies
AIDS
To remember!
1.POX
Syphilis occurs after infection with T. Pallidum. It may be primary, secondary, tertiary, may have congenital forms ( congenital syphilis - the child is infected by sick mother at birth) and other not very well defined: - Latent - without symptoms but with positive test results - Forms crossing between secondary and tertiary, etc. The first symptom if primary syphilis is the appearance of a red (erythematous macula) becomes eroded, deep into, and then an ulcer that hurts only if traumatisation or superinfection. Women may be affected labia, vagina, urethra and perineum. Both sexes can be affected anorectal region, nipple, lips, tongue, tonsils, etc. Complications that can occur are phimosis , paraphimosis , superinfection of the lesion, blocking the lymph vessels ( lymphoedema ) with swelling of the penis and scrotum or labia. Secondary syphilis is considered a sepsis with Treponema - symptoms can occur in 3-6 weeks, causing the appearance of siphilides. They are spotted, pink - pale, not out in relief and cause rozeola silifica or leaving little relief on the skin (hives). There may be states like influenza (lack of appetite,headache (headache) and muscles, joints that hurt, runny nose , etc.). You can install latent or tertiary syphilis, but lately they occur less frequently due to treatment on time and in mass media.
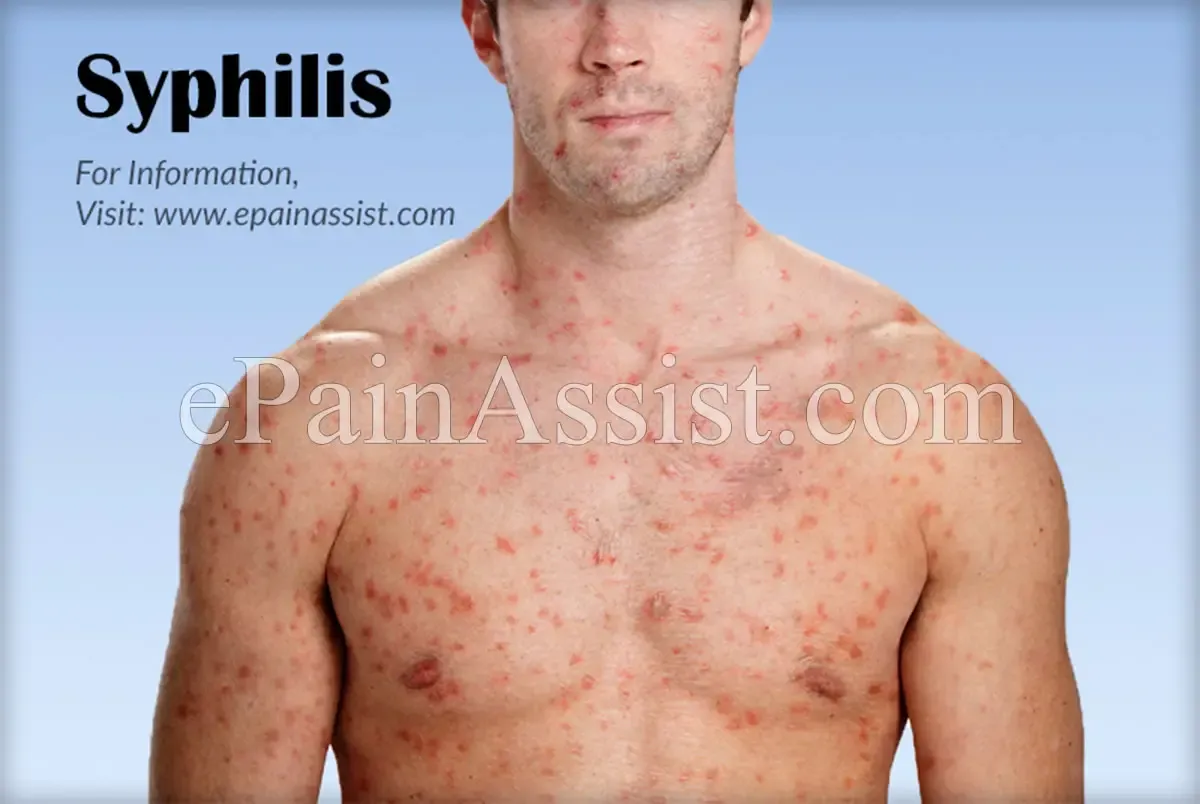
source:epainassist.com
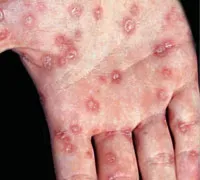
source:webmd.com/
2.Gonorrhea
In this infection, the first symptoms occur 2-3 days after intercourse: abundant secretions yellow - green, stinging and burning sensations, congested mucosa, red, swollen urethra, etc. These symptoms may disappear after 8 weeks - but not disappearance marks the end of the disease, but chronic her. Complications that arise are phimoshes, prostatitis , urethral strictures, etc. Gonorrhea is spread through direct contact with mucous membranes or fluids and rarely infected by sharing of sanitary towels, sponges, etc. It can be treated with antibiotics recommended by the doctor in case of early diagnosis and disease situation which is uncomplicated treatment is short. Gonorrhea has a higher frequency in developing countries, presenting a high risk of contamination.
3.Chlamydia
Chlamydia is Chlamydia trachomatis infection by bacteria and is the most common sexually transmitted disease in developed countries. This bacterium lives only within cells and is difficult to detect because it often arise without symptoms (pain with intercourse, vaginal discharge not very abundant, pins, irregular menstruation, burning during urination, etc.). Like gonorrhea, chlamydia is spread by direct contact with infectious fluids or mucous membranes. Regarding treatment, it must be followed by both partners (regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms) and lasts 14 to 21 days, consisting of antibiotics targeted.
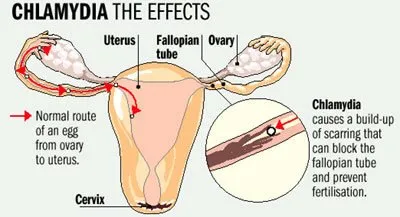
source: athomestdtests.com
4.Scabies
The appearance of scabies involves the presence of a parasite female digging a channel into the skin in submitting 2-3 eggs a day for a month, causing itching and irritation of skin - scratching lesions. The transmission of this parasite is so sexually, and through ongoing contact - like sharing in lingerie and clothes. Symptoms include itching (pruritus localized) on the inner face of hands, between fingers, in the region of the breasts and genitals. Regarding treatment, it applies to both sexual partners, persons cohabiting with those infected with scabies. Linens and personal items used by infected persons require disinfection.
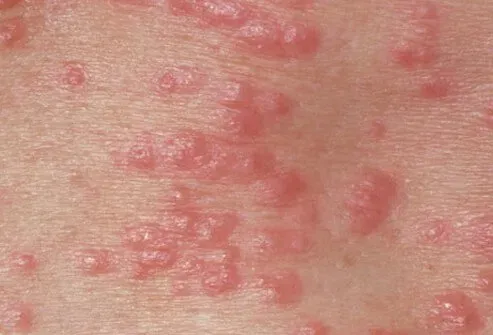
source:medicinenet.com
5.AIDS
AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome and marks an acquired deficiency of the immune system due to HIV infection. AIDS predisposes you to disease typically affecting people infected with HIV and that the body would normally be able to disprove. Like all viruses, HIV, and its metabolism does not require a host cell in order to multiply. Such host cells are, among others, immune system cells, lymphocytes, white blood cells, cells of the nervous system. Researchers classify different stages of HIV infection. By AIDS status means the immune system is very weak and can occur in various diseases and tumors - forms of cancer . Evolution of an HIV infection vary from one person to another. Soon after HIV infection, it begins to multiply very quickly, so in the first weeks symptoms usually do not appear (at first, any state influenza).After 12 weeks of contamination by assay antibodies, antibodies manufactured by the virus can be found. Infections, opportunistic in the case of AIDS, a healthy body sometimes does not manifest or can be tackled with relative ease. Not too dangerous viruses such as herpes simplex or herpes zoster can lead to serious illness. Toxoplasmosis , tuberculosis , cytomegalovirus, CFP - a form of pneumonia and fungus Candida albicans are also characteristic stage disease AIDS. Entrance gates in the body of this virus are open wounds, irritated surfaces, scratched or inflamed skin and vaginal mucosa gender sensitive tissues. Infectious fluids that transmit it are blood, semen, breast milk, etc. and not the saliva, urine, sweat or tears.

source: wikimedia.org
6 To remember!
In recent years, STDs have increased in number and will increase further unless drastic measures are taken to combat mechanism that allows the propagation of these diseases in the population. Although measures have been taken to combat these diseases and there are new drugs and effective treatment of these diseases is soaring and the number of new cases occurring in a part of the population, which is a sign of alarm for the future. Perhaps the social factor - economic where we are at present, the existence of clandestine prostitution and a "loitering" sexual allow greater proliferation of these disorders with serious consequences for the population and health. Especially occasional sexual contacts with strangers, hampers proper conduct an epidemiological survey, making the source of infection is not found, this is essential in stopping the phenomenon of rapid expansion sexually transmitted diseases . Health education currently lacking is one of the most effective methods to prevent and combat these diseases,but it is not applied properly with negative results visible.
Bibliography:
Sharp, P. M.; Bailes, E.; Chaudhuri, R. R.; Rodenburg, C. M.; Santiago, M. O.; Hahn, B. H. (2001). "The origins of acquired immune deficiency syndrome viruses: where and when?
Eaton, L; Kalichman, SC (November 2009). "Behavioral aspects of male circumcision for the prevention of HIV infection"
Kurth, AE; Celum, C; Baeten, JM; Vermund, SH; Wasserheit, JN (March 2011)."Combination HIV prevention: significance, challenges, and opportunities"
Trebach, Joshua D.; Chaulk, C. Patrick; Page, Kathleen R.; Tuddenham, Susan; Ghanem, Khalil G. (2015). "Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis Among Women Reporting Extragenital Exposures". Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
Groopman, Jerome (2012-10-01). "Sex and the Superbug". The New Yorker.
Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Pfaller MA (2013). Medical microbiology