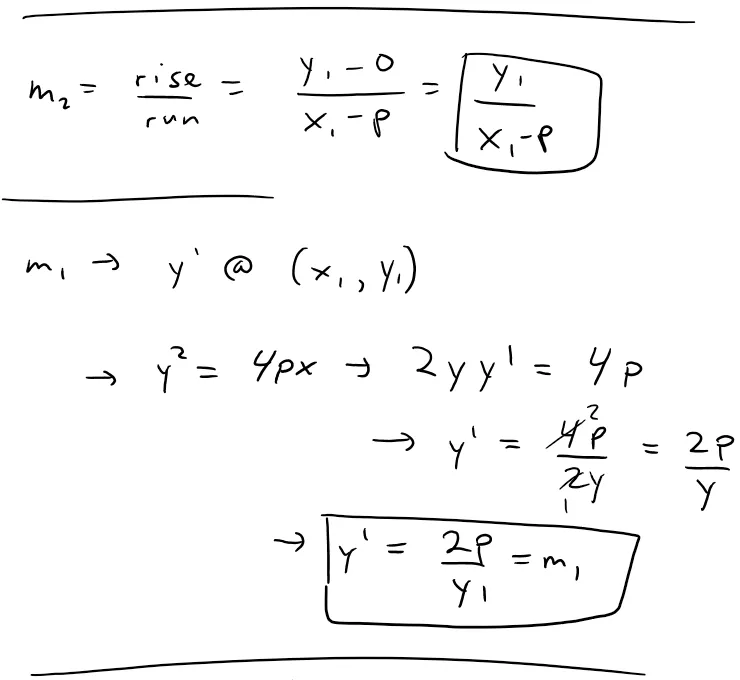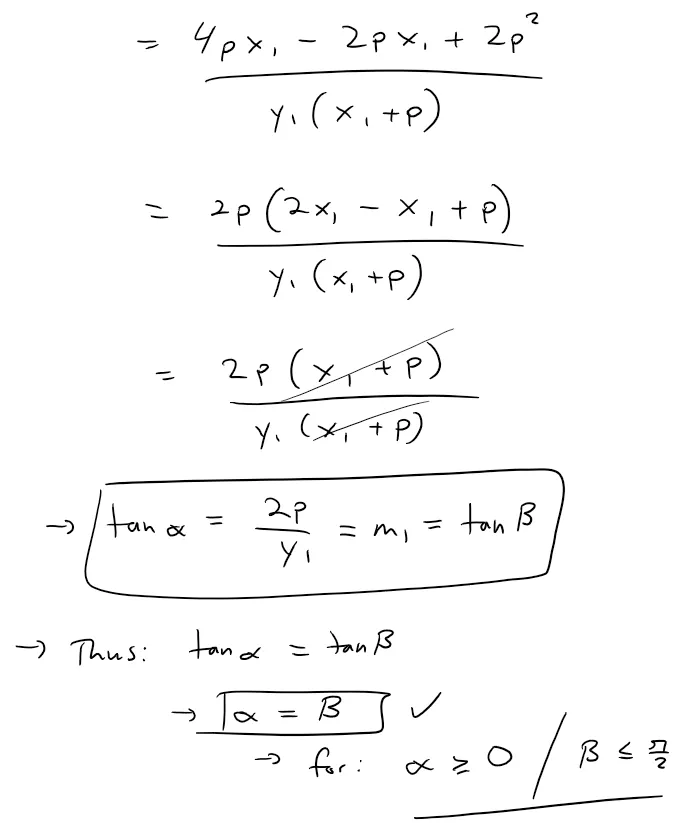In this video I go over another example on parabolas, and this time go over a very useful application of parabolas, which is the property that lines extending from the focus of a parabola to a point on the parabola get protruded in a horizontal line. This property makes it very useful to design headlights and telescopes in a paraboloid shape; which is a 3D parabola formed by rotating a parabola about its central axis. In this particular video I prove that this is the case by proving the angle between a line tangent to point on the parabola and a line extending to that point from the focus is equivalent to the angle between the tangent line and a horizontal line protruding from that point on the parabola. Many cars and large-scale mirror telescopes use this design property of the parabola, and thus it is pretty cool to see the math behind just why it works! This is a very interesting video in it is a more advanced example, part of the Problems Plus section of my Calculus book, as well as its real world applications so make sure to watch this video!
Watch Video On:
Download PDF Notes: https://1drv.ms/b/s!As32ynv0LoaIhvh4UkkM5vzwV2H3Yw
View Video Notes Below!
Download these notes: Link is in video description.
View these notes as an article: @mes
Subscribe via email: http://mes.fm/subscribe
Donate! :) https://mes.fm/donate
Buy MES merchandise! https://mes.fm/store
MORE links: https://linktr.ee/matheasyReuse of my videos:
- Feel free to make use of / re-upload / monetize my videos as long as you provide a link to the original video.
Fight back against censorship:
- Bookmark sites/channels/accounts and check periodically
- Remember to always archive website pages in case they get deleted/changed.
Buy "Where Did The Towers Go?" by Dr. Judy Wood: https://mes.fm/judywoodbook
Subscribe to MES Truth: https://mes.fm/truthJoin my forums!
- Hive community: created/hive-128780
- Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/AMAZINGMathStuff
- Discord: https://mes.fm/chatroom
Follow along my epic video series:
- #MESScience: https://mes.fm/science-playlist
- #MESExperiments: @mes/list
- #AntiGravity: @mes/series
-- See Part 6 for my Self Appointed PhD and #MESDuality breakthrough concept!- #FreeEnergy: https://mes.fm/freeenergy-playlist
- #PG (YouTube-deleted series): @mes/videos
NOTE #1: If you don't have time to watch this whole video:
- Skip to the end for Summary and Conclusions (if available)
- Play this video at a faster speed.
-- TOP SECRET LIFE HACK: Your brain gets used to faster speed!
-- Browser extension recommendation: https://mes.fm/videospeed-extension
-- See my tutorial to learn more: @mes/play-videos-at-faster-or-slower-speeds-on-any-website- Download and read video notes.
- Read notes on the Hive blockchain #Hive
- Watch the video in parts.
-- Timestamps of all parts are in the description.Browser extension recommendations:
- Increase video audio: https://mes.fm/volume-extension
- Text to speech: https://mes.fm/speech-extension
-- Android app: https://mes.fm/speech-android

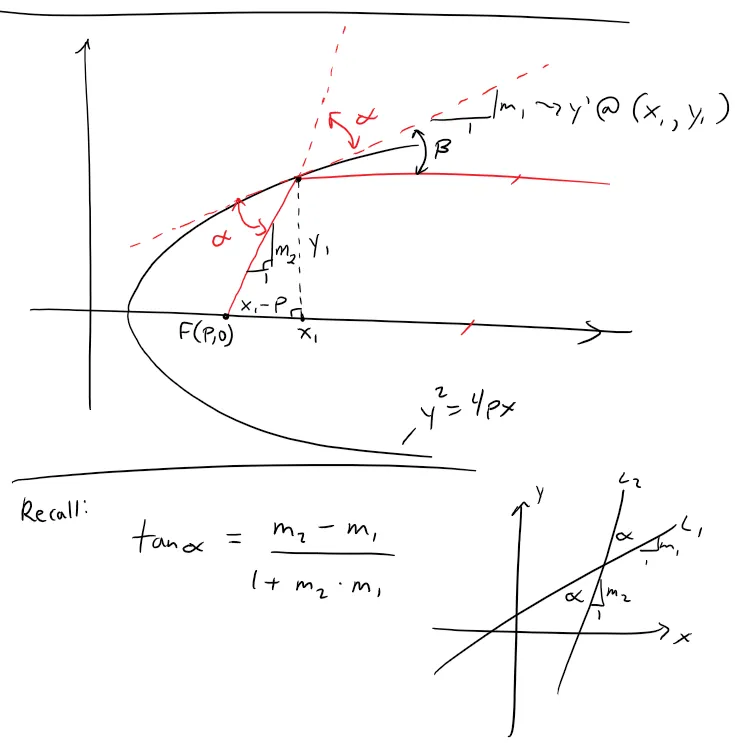
Example
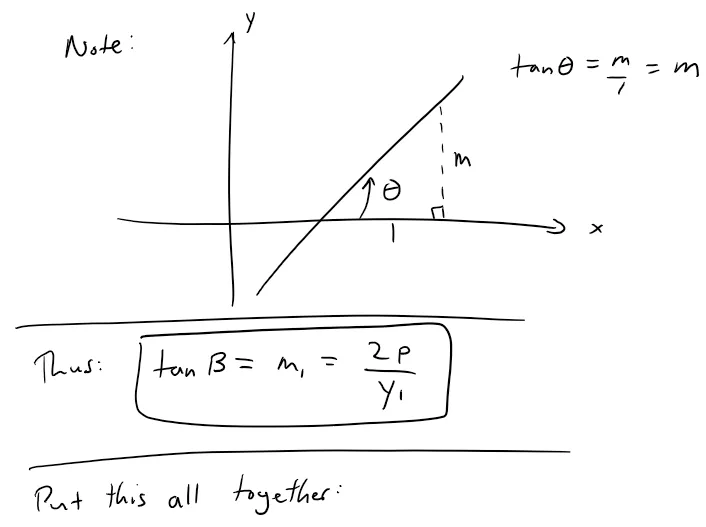
Let P(x1 , y1) be a point on the parabola y2 = 4px with focus F(p , 0).
Let α be the angle between the parabola and the line segment FP, and let β be the angle between the horizontal line y = y1 and the parabola as in the figure.
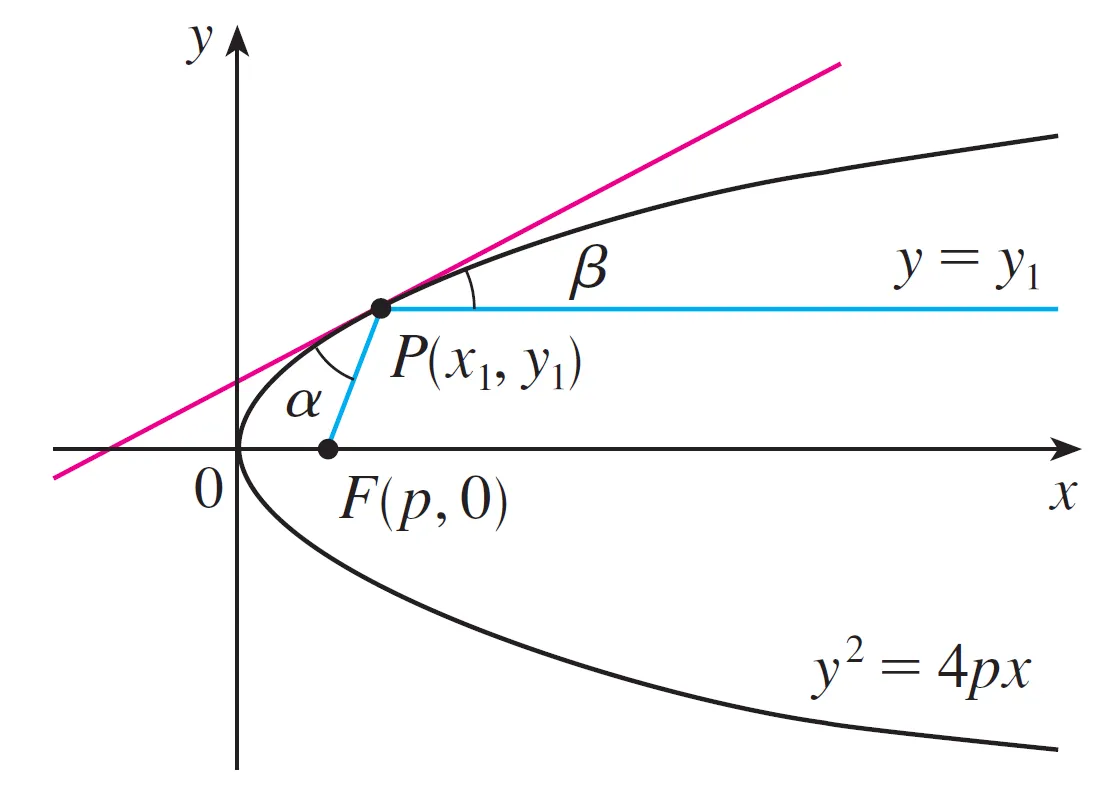
Prove that α = β.
Thus, by a principle of geometrical optics, light from a source placed at F will be reflected along a line parallel to the x-axis.
This explains why paraboloids, the surfaces obtained by rotating parabolas about their axes, are used as the shape of some automobile headlights and mirrors for telescopes.
https://www.hotrodhotline.com/headlights-part-2-lowhigh-beams#.WVNPoYjyvic
Retrieved: 27 June 2017
Archive: https://archive.is/05CmKHeadlights Part 2: Low/High Beams
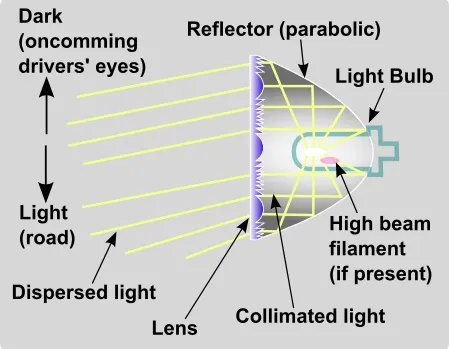
This is a side view of typical lens optics. Light is dispersed vertically (shown) and horizontally (not shown).
http://www.mathedpage.org/parabolas/geometry/
Retrieved: 28 June 2017
Archive: https://archive.is/8PsjAGeometry of the Parabola (2D)
Author: Henri Picciotto
This property is of course the basis of many applications (headlights, flashlights, satellite dishes, radar...) For example, here is a diagram of how this works in a reflector telescope:
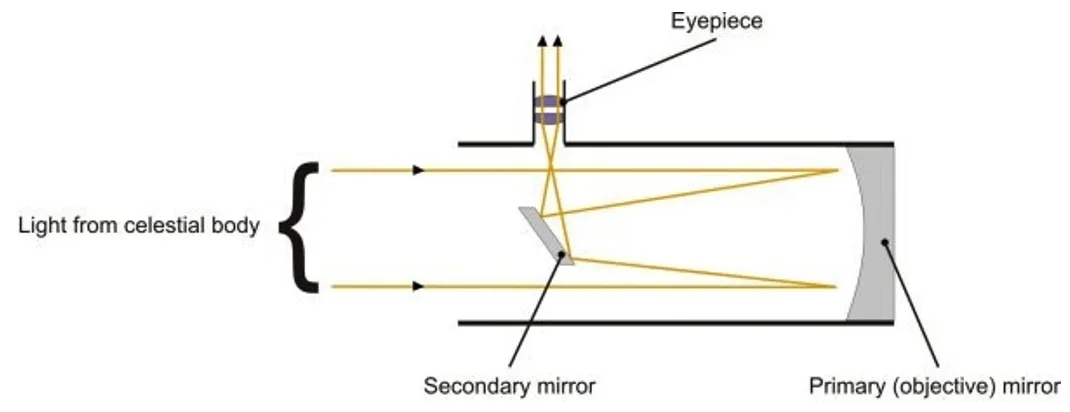
The primary mirror is parabolic, reflecting the parallel rays to the focus. The secondary (flat) mirror redirects this towards the eyepiece.