SMART Valley is a decentralized valley of innovations that brings together investors, project, and experts in a closed ecosystem of professional community, where all members are united by the same purpose – to create advanced, high-potential technologies. The SMART Valley ecosystem gives its participants an opportunity to raise funds, hire team members, find business partners, and realize their ideas – no matter where they are in the world. Four key features of the platform allow the ecosystem members to interact in the most efficient way: a safe deal mechanism, an experts marketplace, a fundraising tool, and – most importantly – a unique decentralized scoring system that utilizes expert opinions, crowd wisdom, and mathematical algorithms to assess projects. Our project will give investors worldwide a chance to invest in high-potential projects safely and legally, while project developers will be able to raise funds and build strong teams, providing experts and service providers with interesting projects to work on and stable employment.
The ecosystem is being developed as an Ethereum-based decentralized application.
Mission
We aim to create a digital valley of innovations and help the most promising projects survive and realize their potential. To achieve that, we plan to use infrastructural advantages and growth points, as well as powerful tools to connect project, investors, experts, service providers, incubators, and other market participants.
Market overview
We are currently living through an incredible era in which new projects and ideas enter the market at an astounding rate, while the number of new businesses and services is growing exponentially. However, most of these new projects fail for a number reasons (more on that in the next chapter). Statistics provided by various funds and startup accelerators indicate that less than 1% of all projects and startups actually obtain financing. At this moment in time, two concurrent events are taking place: world trade growth rates are decreasing (in 2016, for instance, the global value of foreign direct investment reached around $1.52 trillion, 13% less than in 20151 ), and investors are showing a growing interest in developing countries. FDI into developing countries rose by 38% in 2016, reaching $58 billion. As for the worldwide investment climate, in 2016 the total value of investment in Europe fell by 22%, by 19% in Latin America and the Caribbean, and by 5% in Africa. The most attractive countries for investors are still the U.S. ($385 billion), the U.K. ($179 billion), and China ($139 billion). According to UNCTAD General Secretary Mukhisa Kituyi, there are still many obstacles on the road to recovery for high FDI values. One of the main causes for concern is a strong drop in investment in industry and manufacture—both essential fields for generating economic growth and a rise in productivity in developing countries. One of the most promising applications of blockchain technology is decentralized crowdfunding realized via the ICO mechanism. Numerous ICO success stories demonstrate that an ICO can help raise the necessary funds in just a few days—or even minutes—by attracting up to several thousand small investors. The ICO market is developing extremely fast—hundreds of projects launch their ICOs each month. For instance, as of the end of November 2017, the total cryptocurrency market capitalization exceeded $313.6 billion.
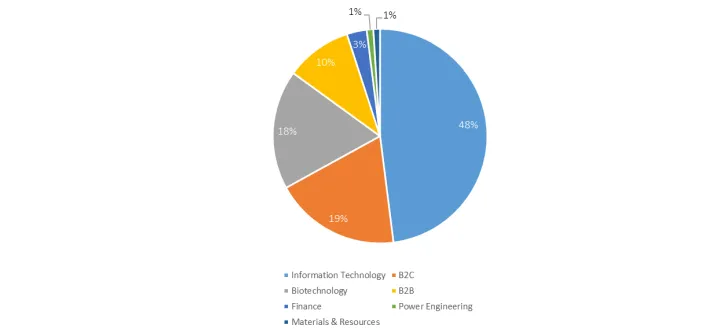
It is worth pointing out that venture financing is simply not an option for most high-potential technological startups due to its centralized nature and high costs. As for the venture market structure, investors’ interest in the B2C segment has grown from 13.7% to 18.9% over the past year. Another trend is the decrease in the share of the segment leader: IT projects. The average deal value varies depending on both geographic factors and the deal stage. At the seed stage, for example, average deal values fall between $0.8 million (Europe) and $1.9 million (the U.S. and Canada). By contrast, the highest values during the startup stage are found in Asia, where they reach around $7 million.
ICO as a source of rapid returns for investors
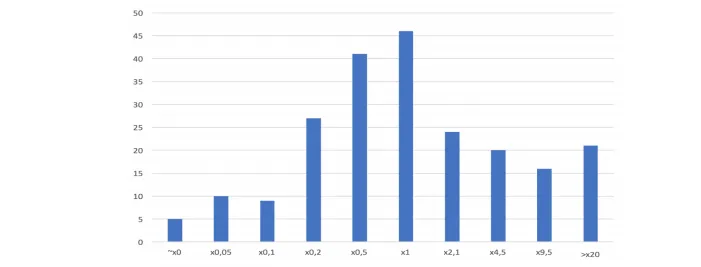
The above-mentioned Kama Flow study has determined that:
10% of tokens increased in value twentyfold or more;
37% of all tokens more than doubled in value;
58% of all tokens remained stable or showed a slight growth
Only 23% of all tokens decreased in value fivefold or more.
This return distribution outcomes are typical for venture business.
SMART Valley as a solution for project developers
A straightforward and convenient fundraising procedure;
Verified service providers;
A minimal number of intermediaries, competitive service rates on the platform, and a chance to reduce marketing budgets—all due to the closed and transparent character of the ecosystem and the presence of key business players who can directly influence the success of a project. Moreover, the SMART Valley ecosystem will allow project developers to:
Connect great technical or marketing ideas with interested investors;
Prepare high-tech projects for an ICO;
Develop efficient marketing strategies to launch projects;
Attract world-class ICO experts;
List tokens on international digital exchanges after the ICO.
Additional information on the advantages of DLT for the SMART Valley ecosystem
Secure encryption tools, anonymity, and confidentiality;
The mutual verification of data—the requirement for a broad agreement between all parties as a condition for any data alterations ensures that all database copies remain identical without any interference from a central regulating authority;
Smart contracts—unlike traditional data input methods, smart contracts consist of programs or bits of code stored on the ledger that can be programmed to generate instructions for the execution of various transactions, such as payment or the transfer of securities. Smart contracts allow the execution of transactions involving promissory notes, letters of credit, and other securities;
Universal data sources that are synchronized automatically between all participants;
More complete databases—for instance, it is possible to include data on property rights that reflect various levels of beneficial ownership;
The ability to make traditional centralized informational systems obsolete—centralized informational systems are currently used to track and register investment transactions and deals. There will be no longer be a need to send requests to centralized databases or to other participants in order to verify information, etc;
The use of up-to-date, transparent data can resolve disputes between counteragents, eliminate the need for a lengthy verification process, and allow for the complete control of transaction details. Moreover, participants will be able to choose to disclose additional data to their counteragents before concluding the deal, thus reducing credit risks, etc.;
Faster and more efficient transactions—all participants will have access to the same body of data, and any updates will spread quickly across the market. Cash transactions will be executed almost instantaneously, since a deal is considered concluded at the moment all participants agree to update the records on the ledger. This will remove the need for any post-deal confirmation and clearing at the end of a certain period.
Considering the fact that all participants will use the same set of data, the use of the blockchain will decrease the risk of errors, disputes, and delays due to the need to achieve consensus. All this will speed up most financial market processes.
SMART Valley Ecosystem
The SMART Valley ecosystem includes three key components: investors, projects, and experts and service providers. The creation of the ecosystem will be carried out in two stages, the first being the setting up of the key element of the framework—a decentralized scoring system—and the second, the realization of a set of three other SMART Valley services—the deal mechanism, the expert market service, and a fundraising tool.
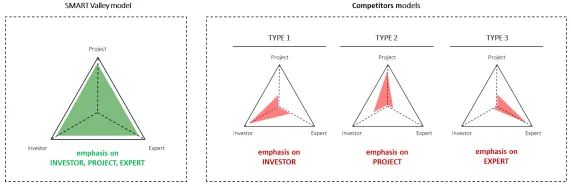
The main difference between the SMART Valley platform and its competitors is the emphasis it places on solving the problems of on the three key components. As our analysis of both direct and indirect competitors shows, three models dominate on the market, each of which focuses almost exclusively on the issues of one component, either investors, or projects, or experts. The SMART Valley model hypothesis states that it is impossible to resolve a complex issue by concentrating on just one of its aspects. The SMART Valley ecosystem approach ensures a unique synergy with emergent properties. The competitive advantage of the project’s ecosystem is driven by the very architecture of the system and four of its services, which provide solutions for the problems of each of the three project participant groups.
Decentralized project scoring by experts
Once again, the decentralized scoring tool acts as the principle and essential element of the SMART Valley scoring system. This service allows projects to receive feedback and evaluations from the SMART Valley expert community, while giving potential investors an opportunity to select projects with the best prospects. Moreover, the service secures the community against scams and fraud due to its decentralized nature and the practical impossibility of faking (or paying for) scoring results.
The experts market and the safe deal service
The safe deal mechanism plays a key role in the SMART Valley ecosystem, as it guarantees efficient transactions between clients and service providers. A more detailed description of the service—together with the service it self will be made available later. All projects (and companies) interact with experts and service providers by means of the experts market. In order to ensure the transparency and security of this system, all transactions are executed using the safe deal mechanism. Members of the experts market will include both professionals in traditional areas (such as front end developers, designers, HR specialists, etc.) and DLT experts (blockchain developers, smart contract designers, etc.). Thus, a project or company will be able to hire all the specialists or service providers it requires among the available experts, all of whom are members of the SMART Valley ecosystem. The transparency and security of transactions within the ecosystem is further guaranteed by a system of ratings, which allows users to verify the experience and qualifications of each platform member.
Training and education services and the social importance of SMART Valley
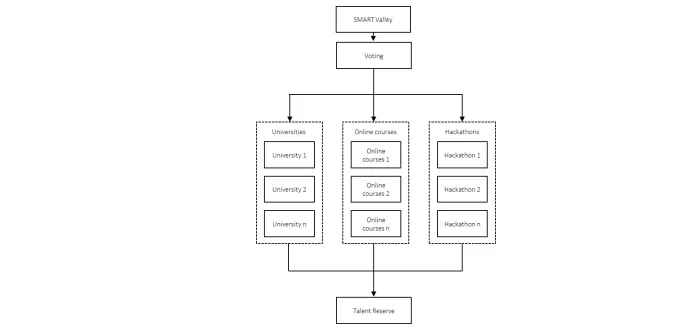
In the future, SMART Valley will finance employee training activities, the creation of new college and university study programs, raise the general qualification level among professionals, and in the long term help solve the issue of a lack of DLT specialists on the market. A special trust fund will be created to finance the professional development of industry specialist. The fund will be replenished using transaction fees paid by members of the ecosystem. Each ecosystem user with a high enough rating can submit an idea to a vote.
The time allocated for the voting is specified in advance; the decision is made based on a majority vote (at present set at 60%).
SMART Valley Tokens (SVT)
The SVT (SMART Valley Token) token is a utility-token, which can be used to purchase ICO-project tokens at a discounted rate using the SMART Valley platform. In addition, SVT will be charged for the use of key platform services (such as the scoring system, safe transaction mechanism, expert market, and fundraising service). General scheme SVT token circulation in SMART Valley ecosystem is shown below (Figure 20). As can be seen from this simplified scheme, there are several elements - Investors, Experts, Projects, Financial Center, Token Store, Core Services, and External Exchange. In order to use the services - you must have SVT tokens, which can be purchased on External Exchange. Projects can use the services both at their own expense, if they have the necessary amount of SVT, and at the expense of the ecosystem, by applying for financial assistance to the Financial Center. It is important to note that the Financial Center is formed once (during ICO) and it is not replenished by commissions that are collected from transactions within the ecosystem for the use of its services. Its initial goal is to create a stream of promising projects in the ecosystem, and form a primary community of experts and investors. In the future, the system will be supported and developed through commissions, as it was said earlier. After all the funds have been used up in the Financial Center, the possibility of the existence of this model, will be determined later, with the help of SMART Valley community.
Project risks
Anyone considering the purchase of SVT tokens is encouraged to examine and evaluate the risk factors described below, as well as other data contained in the White Paper, before making a decision.
Online vulnerability and the user’s dependence on technology
While the project developers will use all available methods to ensure the security of the network, the risk of viruses, hacking, and other security breaches by third parties still exist. Such breaches may lead to interruptions and delays in service and/or temporarily limit the use of SVT tokens.
Risk of the user’s login data being loss
Investors can access their accounts only by using their login and password details, which are known only to them. By using this service, you agree that nobody else will be allowed to gain access to your account and use it. Further, you agree to assume full liability for any actions performed by your account and not to transfer this liability to third parties, even if the loss of your login data results in the loss of your SVT tokens.
Personal information disclosure
Under certain circumstances, such as a court order or a subpoena, the Company will be obliged to disclose information on SVT holders. In this case, the Company will not be held liable for such disclosures. Risk of smart contract flaws While smart contracts possess significant advantages (including better security and lower contract costs), there are no guarantees that the smart contracts used in the system are flawless. Such flaws may lead to technical issues and, as a consequence, a loss of tokens.
Legal risks
Most countries have so far passed few laws regarding distributed ledger technology. Therefore, new laws and regulations pertaining to this technology may be introduced at any time. Such a change in the legislation may lead to limitations being imposed on the use or possession of SVT tokens, which may include the reduced functionality of the tokens and the impossibility to sell them in the future.
Risk on insufficient sales of SMART Valley services
The Company cannot guarantee that any specific volume of the SMART Valley services will be achieved after the launch of the system. There is the possibility that no sales will occur at all. Such an eventuality can negatively influence the price and liquidity of SVT tokens.
Force majeure
The Company may have to suspend or cease the performance of its activities and obligations in the event of certain unforeseeable circumstances outside of the Company’s control, including (but not limited to) natural disasters, war, terrorist attacks, outbreaks of violence, civil unrest, strikes, mass firings, or system failures.
Risk of token price volatility
The price of SVT tokens can change significantly for various reasons. The Company will not set any guaranteed token value and will not be held liable for any losses incurred by a decrease in the value of SVT tokens.
Risk of project failure
Though the project team has performed numerous market studies, tested consumer demand and obtained promising results, the Company cannot guarantee the commercial success of the project. The project may fail or be liquidated for various reasons, including the volatility of the Bitcoin and Ethereum exchange rates, interrupted or failed business partnerships, or the introduction of new state regulations incompatible with the work of the Company.
SVT tokens are not an investment tool
SVT do not represent a legally binding investment contract. The Company does intend to achieve all the goals outlined in the present document. However, by purchasing SVT tokens, you agree to accept the existence of inherent risks.
SVT tokens do not give their holders any property, distribution, control or management rights
The possession of SVT tokens does not invest the holder with either rights of property or distribution (including, but not limited to, the distribution of profits) or any share in the Company. Consequently, SVT holders do not possess any rights to control the Company’s operations or make any decisions relating to its activities.
The project team guarantees that all possible measures have been taken to provide factually correct information that corresponds to the exact state of the peer-to-peer business network at the moment of publication. However, the process of project development can result in further changes to the platform that will not be included in the present White Paper until its updated version is eventually published on the official website of the project. SVT holders, in their turn, are responsible for getting acquainted with and agreeing to the contents of any newly published edition of the White Paper.
Road Map
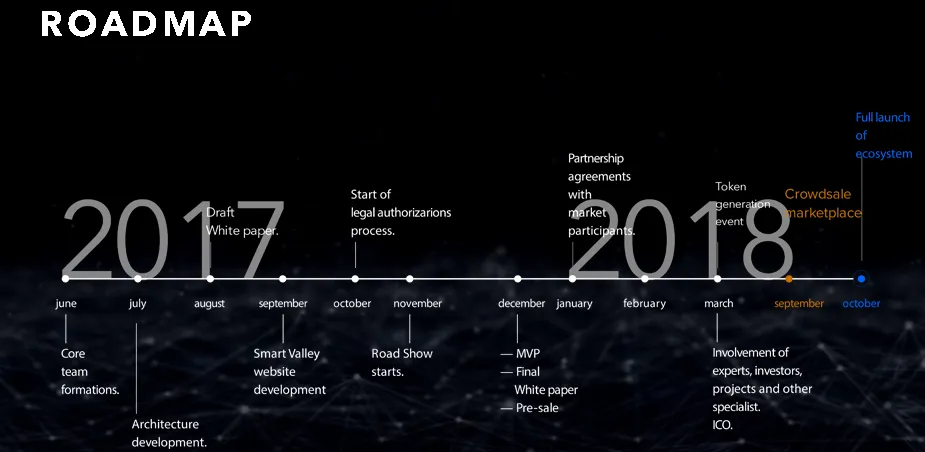
For more information, please go to the link provided below ..!
Website : https://smartvalley.io/
Whitepaper : https://smartvalley.io/files/WP_en.pdf
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/SmartValley.io/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ISmartvalley
Author: JigaMola
Bitcointalk profile: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1847143
