Surely many of you have wondered why a folio is DIN A4 size or what does that mean DIN A4.

They are so called because they are part of a series of sizes: A0, A1, A2 ... A8 and each one is half of the previous one.
DIN A0 paper measures 1 m2
DIN A1 paper measures half, that is, 1/2 m2
DIN A2 paper measures half of the previous 1/4 m2
And so on
These papers are designed to be able to increase and reduce their content without being deformed, that is, if you carry a drawing, for example, on a paper DIN A4, it can be increased without problems to size A3, A2 ... or reduce to size A5, A6 ... without it being deformed because the proportions are the same.
From the previous image, let's check it:
DIN A0 measures 1189 mm high by 841 mm wide.
If we divide 1189/841 = 1.41379310345
The DIN A1 measures 841 mm high by 594 mm wide.
If we divide 841/594 = 1.41582491582
...
The DIN A4 measures 297 mm high by 210 mm wide.
If we divide 297/210 = 1.41428571429
As you can see, the result is always the same, varying simply in thousandths, something despicable for this case. But does not the result of these proportions sound like something? Yes, it is equivalent to the √2.
√2 = 1.41421356237
This can be demonstrated in a very simple way. Consider the following drawing.
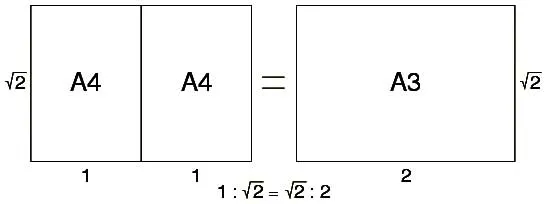
If we start from A3 with width A and height B, when creating an A4 what happens is that its width would be B and its height A / 2.
So, what we want is:
A/B = B/(A/2)
A/B = 2B/A
A*A/B*B = 2
A2/B2 = 2
Applying √ to both sides
A/B = √2
