
The star Betelgeuse, also known as Alpha Orionis, is a red giant star located in the right arm of the constellation Orion. Its remarkable brightness and prominence in the night sky have been observed for centuries and documented by various cultures and astronomers throughout history. It is one of the brightest stars in the sky in all hemispheres of the planet.
The earliest historical records of Betelgeuse date back to ancient Egypt and China, where it was given names such as "The Hunter's Leg" or "The Armpit" because of its position in the body of Orion. These civilisations reconstructed their agricultural and religious calendars using the movements of the stars, and Betelgeuse was an important reference for keeping track of time.
La estrella Betelgeuse, también conocida como Alpha Orionis, es una gigante roja ubicada en el brazo derecho de la Constelación de Orión. Su notable brillo y prominencia en el cielo nocturno han sido observados durante siglos y documentados por diversas culturas y astrónomos a lo largo de la historia. Es una de las estrellas más brillantes en el cielo de todos los hemisferios del planeta.
Los primeros registros históricos de Betelgeuse se remontan al antiguo Egipto y China, donde se le atribuían nombres como "La Pierna del cazador" o "La Armpit" debido a su posición en el cuerpo de Orión. Estas civilizaciones reconstruían sus calendarios agrícolas y religiosos utilizando los movimientos de los astros, y Betelgeuse era una referencia importante para el seguimiento del tiempo.

Later, as astronomy progressed, more detailed observations of Betelgeuse were obtained. In the 17th century, the German astronomer Johannes Bayer included the star in his famous celestial atlas "Uranometria", and later, the British astronomer John Herschel studied its spectrum in the 19th century, providing additional information about its chemical composition.
Recently, observations of Betelgeuse have again captured the attention of scientists. In late 2019 and early 2020, its brightness began to fade noticeably, prompting speculation that a supernova may be imminent. During this period, astronomers at Villanova University conducted a comprehensive study of the star, using ground-based and satellite telescopes to analyse its behaviour.
The results of these studies indicated that the change in Betelgeuse's brightness was related to the ejection of large amounts of material into the surrounding space. This led to a temporary reduction in its brightness, known as the "Grand Minimum" phase. This phenomenon is believed to be the result of stellar pulsations, which are common in stars of its type.
Posteriormente, a medida que la astronomía avanzaba, se obtuvieron observaciones más detalladas sobre Betelgeuse. En el siglo XVII, el astrónomo alemán Johannes Bayer incluyó a la estrella en su famoso atlas celestial "Uranometria", y más tarde, el astrónomo británico John Herschel estudió su espectro en el siglo XIX, proporcionando información adicional sobre su composición química.
Recientemente, las observaciones de Betelgeuse han captado nuevamente la atención de los científicos. A finales de 2019 y principios de 2020, su brillo comenzó a desvanecerse de manera notable, generando especulaciones sobre una posible supernova inminente. Durante este período, astrónomos de la Universidad de Villanova llevaron a cabo un estudio exhaustivo de la estrella, utilizando telescopios terrestres y satelitales para analizar su comportamiento.
Los resultados de estos estudios indicaron que el cambio en el brillo de Betelgeuse estaba relacionado con la expulsión de grandes cantidades de material al espacio circundante. Esto llevó a una reducción temporal de su brillo, conocida como fase de "Gran Mínimo". Se cree que este fenómeno es resultado de pulsaciones estelares, que son comunes en estrellas de su tipo.
Although Betelgeuse has partially recovered its original brightness, its life cycle is expected to culminate in a supernova explosion sometime in the next few hundred thousand years. This event will be visible from Earth and will leave behind a bright nebula and a neutron star or black hole.
Betelgeuse has been the subject of speculation and conjecture because of its unusual behaviour. During the period when it was dimming, several theories emerged about a possible impending supernova. However, it is important to note that predictions about when exactly Betelgeuse's death will occur are uncertain and subject to various interpretations.
Aunque Betelgeuse ha recuperado parcialmente su brillo original, se espera que su ciclo de vida culmine en una explosión supernova en algún momento de los próximos cientos de miles de años. Este evento será visible desde la Tierra y dejará tras de sí una nebulosa brillante y una estrella de neutrones o un agujero negro.
Betelgeuse ha sido objeto de especulaciones y conjeturas debido a su comportamiento inusual. Durante el período en el que disminuyó su brillo, surgieron varias teorías sobre una posible supernova inminente. Sin embargo, es importante señalar que las predicciones sobre cuándo ocurrirá exactamente la muerte de Betelgeuse son inciertas y sujetas a diversas interpretaciones.

One of the most interesting speculations is that the star may have already experienced an explosion, but the light from that event has not yet reached Earth. Betelgeuse's distance, approximately 650 light-years away, means that it would take centuries for the light from a supernova to reach us. It is therefore possible that Betelgeuse has gone through an explosion in the distant past, but we have not yet witnessed it.
As for when a supernova in Betelgeuse might be observed from Earth, astronomers cannot give a precise date. It is believed that Betelgeuse is in the final stage of its life and that its death as a supernova could occur any time within the next 100,000 years. Others estimate that the explosion could occur on a shorter timescale of decades or centuries. However, all of these estimates are approximate and based on our current understanding of stellar evolution.
Imagine what it would be like to witness a supernova in Betelgeuse from our planet. Once the star enters the explosion process, it would experience a sudden and dramatic increase in brightness, becoming brighter than the full Moon and easily visible even during the day. For several days or even weeks, Betelgeuse would be the brightest object in the night sky, emitting an intense reddish light.
Una de las especulaciones más interesantes es que la estrella ya podría haber experimentado una explosión, pero la luz de ese evento aún no ha alcanzado la Tierra. La distancia a la que se encuentra Betelgeuse, aproximadamente 650 años luz, significa que tardaría siglos para que la luz de una supernova llegue hasta nosotros. Por tanto, es posible que Betelgeuse haya pasado por una explosión en el pasado lejano, pero aún no lo hayamos presenciado.
En cuanto a cuándo podría observarse una supernova en Betelgeuse desde la Tierra, los astrónomos no pueden dar una fecha precisa. Se cree que Betelgeuse está en la etapa final de su vida y que su muerte como supernova podría ocurrir en cualquier momento dentro de los próximos 100,000 años. Otros estiman que la explosión podría ocurrir en una escala de tiempo más corta, de décadas o siglos. Sin embargo, todas estas estimaciones son aproximadas y basadas en nuestro entendimiento actual de la evolución estelar.
Imaginemos cómo sería presenciar una supernova en Betelgeuse desde nuestro planeta. Una vez que la estrella entra en el proceso de explosión, experimentaría un aumento repentino y dramático en su brillo, llegando a ser más luminosa que la Luna llena y fácilmente visible incluso durante el día. Durante varios días o incluso semanas, Betelgeuse sería el objeto más brillante en el cielo nocturno, emitiendo una intensa luz rojiza.
As the explosion unfolds, the star would hurl huge amounts of matter into space, generating a shock wave that would travel at high speed. This shock wave would expand and form a bright nebula, visible for several years or decades, depending on its distance and density.
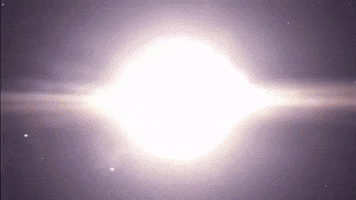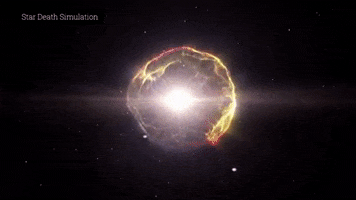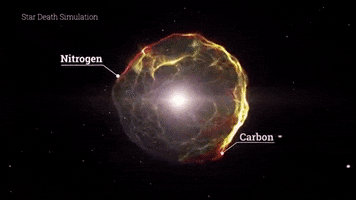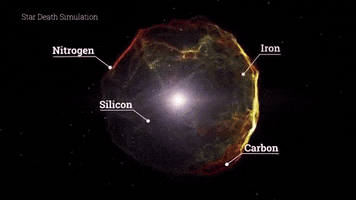
A supernova in Betelgeuse would be an extraordinary astronomical spectacle. The energy released during the explosion would be monumental, generating gravitational waves, the formation of heavy elements and sending a significant amount of radiation into space. In addition to the fascinating sight it would offer in the night sky, astronomers and scientists would be very interested in studying the astrophysical and cosmological implications of this explosion.
Speculation about the imminent death of Betelgeuse and its possible supernova has generated a great deal of interest. However, there is no precise date for this event and estimates vary widely. Imagining a supernova in Betelgeuse leads to a breathtaking celestial landscape, with a bright, reddish star slowly fading away and an expanding nebula as a witness to its glorious end.
A medida que se desarrolla la explosión, la estrella arrojaría enormes cantidades de materia al espacio, generando una onda de choque que viajaría a alta velocidad. Esta onda de choque iría expandiéndose y formaría una nebulosa brillante, visible durante varios años o décadas, dependiendo de su distancia y densidad.
Una supernova en Betelgeuse sería un espectáculo astronómico extraordinario. La energía liberada durante la explosión sería monumental, generando ondas gravitacionales, la formación de elementos pesados y enviando una cantidad significativa de radiación al espacio. Además de la fascinante visión que ofrecería en el cielo nocturno, los astrónomos y científicos estarían muy interesados en estudiar las implicaciones astrofísicas y cosmológicas de esta explosión.
Las especulaciones sobre la muerte inminente de Betelgeuse y su posible supernova han generado un gran interés. Sin embargo, no hay una fecha precisa para este evento y las estimaciones varían ampliamente. Imaginar una supernova en Betelgeuse nos lleva a un paisaje celestial impresionante, con una estrella brillante y rojiza que se desvanece lentamente y una nebulosa en expansión como testigo de su final glorioso.


