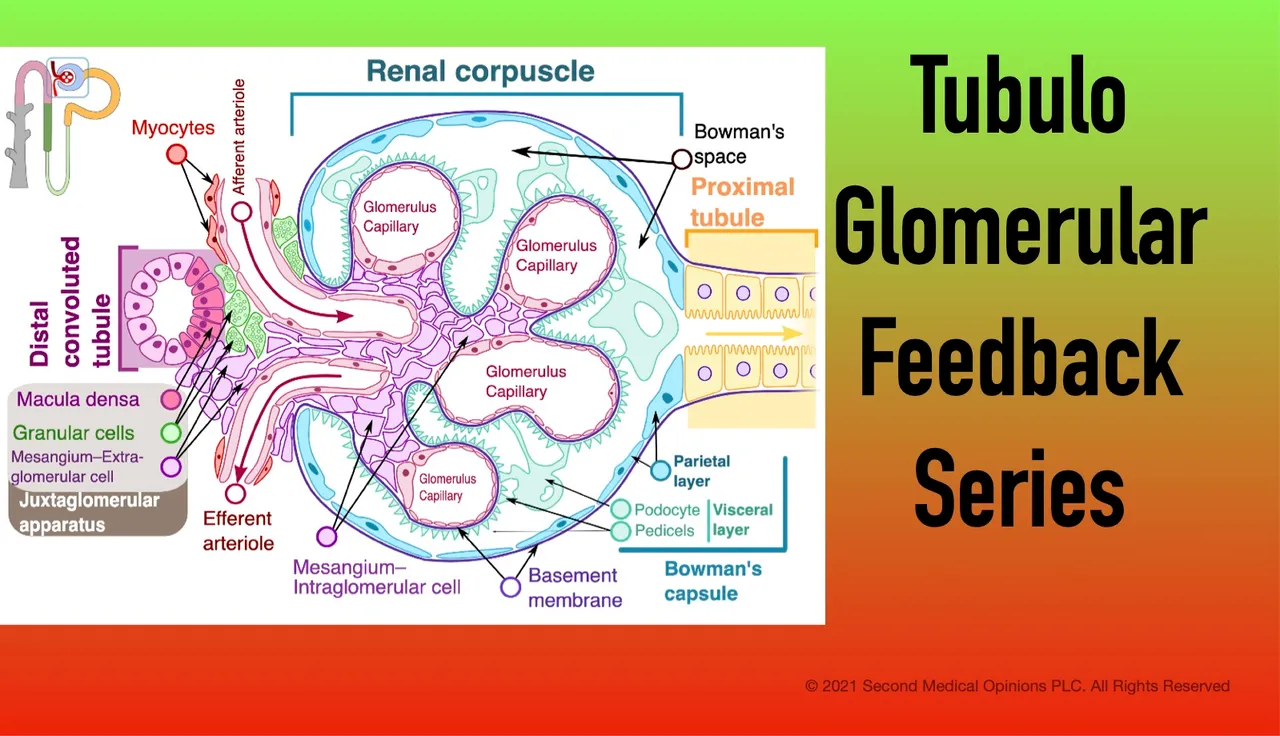
This article from 1989 demonstrates how the NKCC2 transporter in the macula densa (MD) cells involved in the sensing of the sodium and chloride concentrations in the tubule, the first action of the tubuloglomerular feedback
Adding furosemide, a specific inhibitor of the NKCC2 cotransporter in the thick ascending limb (TAL), to the lumen of the perfused TAL hyperpolarized the basolateral membrane voltage of the MD cell from -55 +/- 5 mV to -79 +/- 4 mV (n = 7). Reduction of NaCl in the lumen perfusate from 150 mmol/l to 30 mmol/l also hyperpolarized the basolateral membrane voltage of the MD cell from -48 +/- 3 mV to -66 +/- 5 mV (n = 4).
As we can see, the NHE3 (see previous post)and NKCC2 transporters in the apical membrane of the basolateral membrane of the MD cell are involved in the signaling of the changes in concentration of tubular sodium chloride, the first step of the tubuloglomerular feedback.
Credits
Renal Corpuscle Image. 2019. Downloaded under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License from Wikimedia Commons. Author: Shypoetess. No changes were made.
Posts in this series