~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
16-07-2024 - basic concepts of energy systems - Cycle Otto - M2T & M4T [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction regarding the technical topic mentioned in question
(code notes: 860-070)
real Otto cycle - ignition
In an internal combustion engine operating according to the real Otto cycle, the ignition advance occurs between 10° and 50° before the piston has reached TDC
NOTE:
In an internal combustion engine operating on the real Otto cycle, ignition advance typically occurs between 10° and 50° before the piston reaches top dead center (TDC).
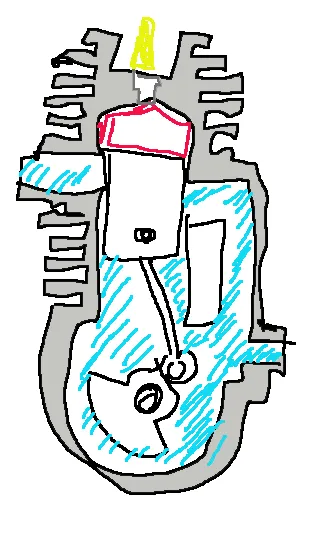
real Otto cycle - compression
In an internal combustion engine operating according to the ideal Otto cycle the compression phase occurs during the piston stroke from BDC to TDC
NOTE: In this phase the piston compresses the mixture inside the cylinder, while combustion takes place at top dead centre.
Royal Otto cycle - incorrect statement
It is a mistake to think that the ideal operating cycle of an internal combustion engine operating according to the Otto cycle considers the effect of the propagation of the flame front. In reality, for the perfect machine hypotheses one does not have to deal with the propagation of the flame front.
Note: In a real Otto cycle the following are considered:
-the variability of the specific heats of the fluid with the temperature and its composition
-the effects related to incomplete combustion
-the effects linked to the permanence in the dead space of a residual mass of fluid from
previous cycle
-irreversibility due to friction
- non-adiabatic compression and expansion transformations
Royal Otto cycle - composition
The Otto cycle is made up of 4 phases which occupy approximately half a turn of the crank in 4-stroke engines
NOTE: The stages are: Intake, Compression and Combustion, Expansion, Exhaust.
2T engine - incorrect statement
It is not exactly correct to think that in a 2-stroke engine the absence of valves allows a more efficient charge replacement process than that of a 4-stroke engine.
Instead, the absence of the valves, present in the 4-stroke models, replaced by the exhaust and wash ports, makes the 2-stroke engine simpler from a construction point of view.
NOTE 1:
In a 2T engine during the washing phase the fresh charge that is introduced into the cylinder helps to expel the burnt gases
NOTE 2:
-In a 2-stroke engine there are three ports: the exhaust port, the intake port and the intake port
NOTE 3:
In a 2T engine with the flush port closed, the exhaust port remains open for a small distance contributing to the escape of gas and fresh mixture
2T engine - first half
In the two-stroke engine during the first stroke the piston closes the wash ports and the pressure difference draws the fresh charge into the crankcase.
Conclusions
In conclusion we can say that the main differences between two-stroke and four-stroke engines focus on the duty cycle, the power produced, fuel efficiency, emissions and the specific applications for which they are designed
Request
Have you ever seen a 2-stroke engine?

[ITALIAN]
16-07-2024 - basic concepts of energy systems - Ciclo otto [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento tecnico citato in oggetto
(code notes: 860-070)
ciclo Otto reale - accensione
In un motore a combustione interna operante secondo ciclo Otto reale l'anticipo all'accensione avviene tra i 10° e i 50° prima che il pistone abbia raggiunto il PMS
NOTA:
In un motore a combustione interna operante secondo il ciclo Otto reale, l'anticipo all'accensione avviene tipicamente tra i 10° e i 50° prima che il pistone raggiunga il punto morto superiore (PMS).

ciclo Otto reale - compressione
In un motore a combustione interna operante secondo ciclo Otto ideale la fase di compressione avviene durante la corsa del pistone dal PMI al PMS
NOTA: In questa fase il pistone comprime la miscela all'interno del cilindro, mentre la combustione ha luogo in corrispondenza del punto morto superiore.
ciclo Otto reale - affermazione errata
Risulta un errore pensare che il ciclo di funzionamento ideale di un motore a combustione interna operante secondo ciclo Otto considera l'effetto della propagazione del fronte di fiamma. In realtà per le ipotesi di macchina perfetta non si ha che fare con la propagazione del fronte di fiamma.
Nota: In un ciclo Otto reale si considerano:
-la variabilità dei calori specifici del fluido con la temperatura e la sua composizione
-gli effetti legati alla combustione incompleta
-gli effetti legati alla permanenza nello spazio morto di una massa di fluido residua dal
ciclo precedente
-irreversibilità per attrito
-trasformazioni di compressione ed espansione non adiabatiche
ciclo Otto reale - composizione
Il ciclo Otto si compone di 4 fasi che occupano circa mezzo giro di manovella nei motori 4T
NOTA: Le fasi sono: Aspirazione, compressione e combustione, espansione, scarico.
motore 2T - affermazione errata
Non è propriamente corretto pensare che in un motore 2T l'assenza di valvole consente un processo di sostituzione della carica più efficiente rispetto a quello di un motore a 4T.
Invece, l’assenza delle valvole, presenti invece nei 4T, sostituite dalle luci di scarico e di lavaggio, rende il motore 2T più semplice dal punto di vista costruttivo.
NOTA 1:
In un motore 2T durante la fase di lavaggio la carica fresca che si immette nel cilindro contribuisce ad espellere i gas combusti
NOTA 2:
-In un motore 2T si hanno tre luci quella di scarico, quella di aspirazione e quella di ammissione
NOTA 3:
In un motore 2T chiusa la luce di lavaggio la luce di scarico rimane aperta per un piccolo tratto contribuendo alla fuoriuscita di gas e miscela fresca
motore 2T - primo tempo
Nel motore a due tempi durante il primo tempo il pistone chiude le luci di lavaggio e la differenza di pressione richiama la carica fresca nel basamento.
Conclusioni
In conclusione possiamo dire che le principali differenze tra i motori a due tempi e quattro tempi si concentrano sul ciclo di lavoro, la potenza prodotta, l'efficienza del combustibile, le emissioni e le applicazioni specifiche per cui sono progettati
Domanda
Avete mai visto un motore a 2 tempi?
THE END