Hello everyone and welcome back to my blog,
Last week we introduced the topic of the Mediterranean scrub: its definition, what plants it is made up of, where it is found in the world and why it is unique in its kind. If you missed this information you can find it from this post! Today we continue the scientific journey by talking about the main problems that afflict the Mediterranean scrub.
I live in Italy, so I mainly know the problems of my country, but I would be curious to know if there are other critical issues in your countries too.
Italy has always had to deal with problems of territorial degradation, but the phenomenon, in the most serious cases, was attributable to specific areas.
Since the 1950s, profound changes have occurred in rapid succession in the dynamics of the economy which have led to the abandonment of rural areas, changes in land use, an increase in water demand as well as the urbanization of rural and coastal areas without any territorial planning.
Ciao a tutti e bentornati sul mio Blog,
La scorsa settimana abbiamo introdotto il tema della macchia mediterranea: la sua definizione, da quali piante è composta, dove si trova nel mondo e per quali motivi è unica nel suo genere. Se vi siete persi queste informazioni potete recuperarle da questo post! Oggi continuiamo il viaggio scientifico parlando dei principali problemi che affliggono la macchia mediterranea.
Io abito in Italia, dunque conosco principalmente le problematiche del mio Paese, ma sarei curiosa di sapere se anche nei vostri Paesi vi sono altre criticità.
L'Italia ha avuto sempre a che fare con problemi di degrado territoriale, ma il fenomeno, nei casi più gravi, era riconducibile a zone specifiche.
A partire dagli anni '50 si sono verificati, in rapida successione, cambiamenti profondi nelle dinamiche dell'economia che hanno portato all'abbandono delle aree rurali, a mutamenti nell'uso del suolo, all'aumento della domanda idrica nonché all'urbanizzazione di aree rurali e costiere senza alcuna pianificazione territoriale.

Foto di Tapani Hellman da Pixabay
The two phenomena that immediately struck me are the following:
- Exploitation of the territory and degradation of the soil
One of the major causes of degradation of the Mediterranean vegetation is deforestation, which causes a strong reduction in the soil's water retention capacity and can therefore be considered the main anthropic cause of depletion of aquifer resources. Another aspect of the problem in Italy is the growing privatization of mineral water sources, often located in forested areas, and the widespread lack of attention to the rules that prescribe forest cover in the vicinity of the sources;
I due fenomeni che mi hanno subito colpito sono i seguenti:
- Sfruttamento del territorio e degrado del suolo
Una delle maggiori cause di degrado della vegetazione mediterranea è il disboscamento, che provoca una forte riduzione della capacità di ritenzione dell'acqua da parte del suolo e può essere considerato, quindi, la principale causa antropica di esaurimento delle risorse acquifere. Un altro aspetto del problema in Italia è la crescente privatizzazione delle fonti di acqua minerale, ubicate spesso in zone a vocazione boschiva, e la diffusa disattenzione delle norme che prescrivono la copertura forestale nelle vicinanze delle sorgenti;
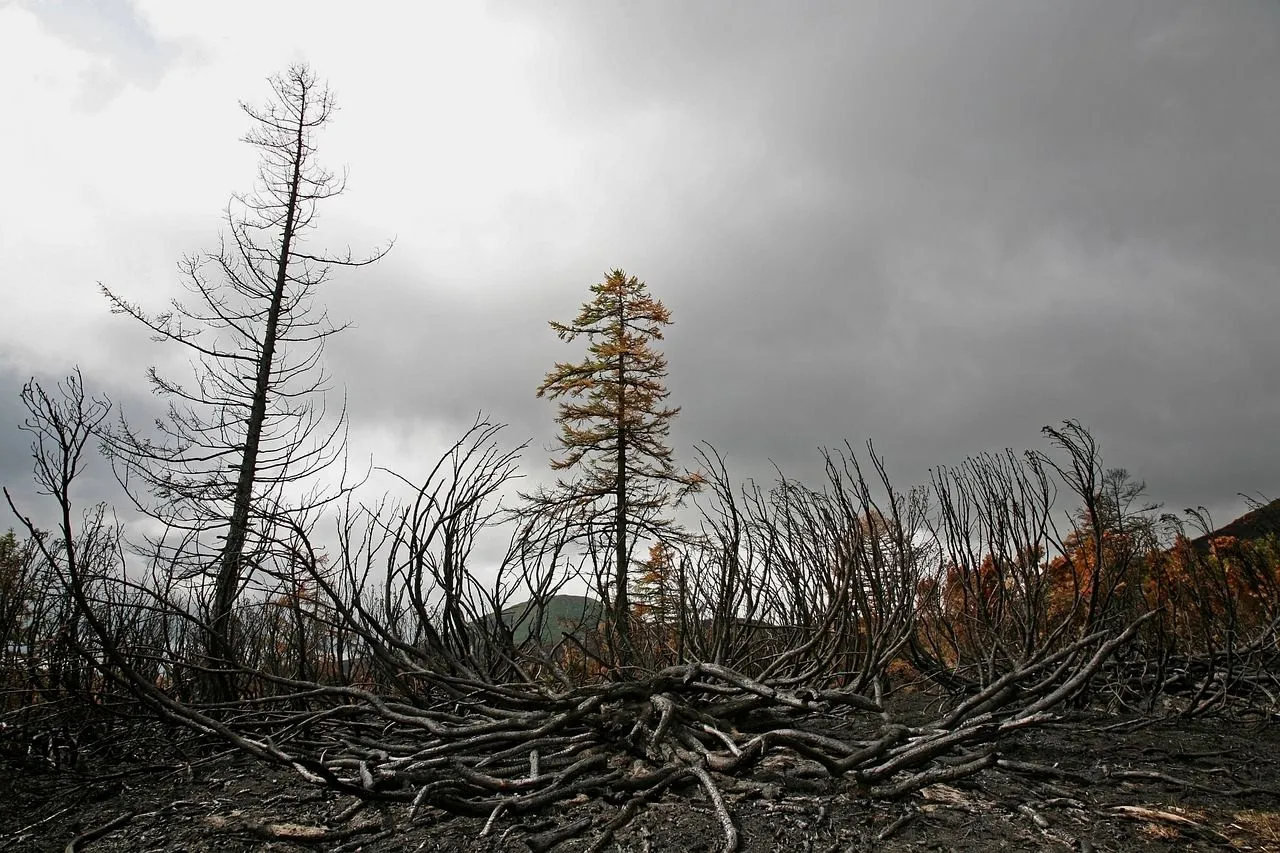

Foto di Наталья Коллегова da Pixabay
- Fires
The Mediterranean Region is particularly affected by fires, with an average of 600,000 to 800,000 hectares being burned every year. While small fires were part of natural dynamics, larger fires have increased sharply in recent decades. The intensity and danger of fires are closely linked to the type of vegetation and increase with the increase in the participation of shrubs. Fire can influence the composition and structure of plant and animal communities, influencing their evolution and perpetuation. Furthermore, the high temperatures of the fire can have negative effects on the physical-chemical properties of the soil: in certain cases they change the structure of the soil, making it less permeable and, therefore, more exposed to erosive processes.
- Incendi
La Regione Mediterranea è particolarmente colpita dagli incendi, venendo bruciati in media ogni anno da 600.00 a 800.000 ettari. Mentre gli incendi di piccola entità facevano parte delle dinamiche naturali, quelli di più ampia portata sono fortemente aumentati negli ultimi decenni. L’intensità e pericolosità degli incendi sono strettamente collegate al tipo di vegetazione ed aumentano con l’incremento della partecipazione di arbusti. Il fuoco può influire sulla composizione e sulla struttura delle comunità vegetali ed animali, condizionando la loro evoluzione e la loro perpetuazione. Inoltre, le alte temperature del fuoco possono avere effetti negativi sulle proprietà fisico-chimiche del suolo: in certi casi arrivano a cambiare la struttura del terreno rendendolo meno permeabile e, quindi, più esposto a processi erosivi.
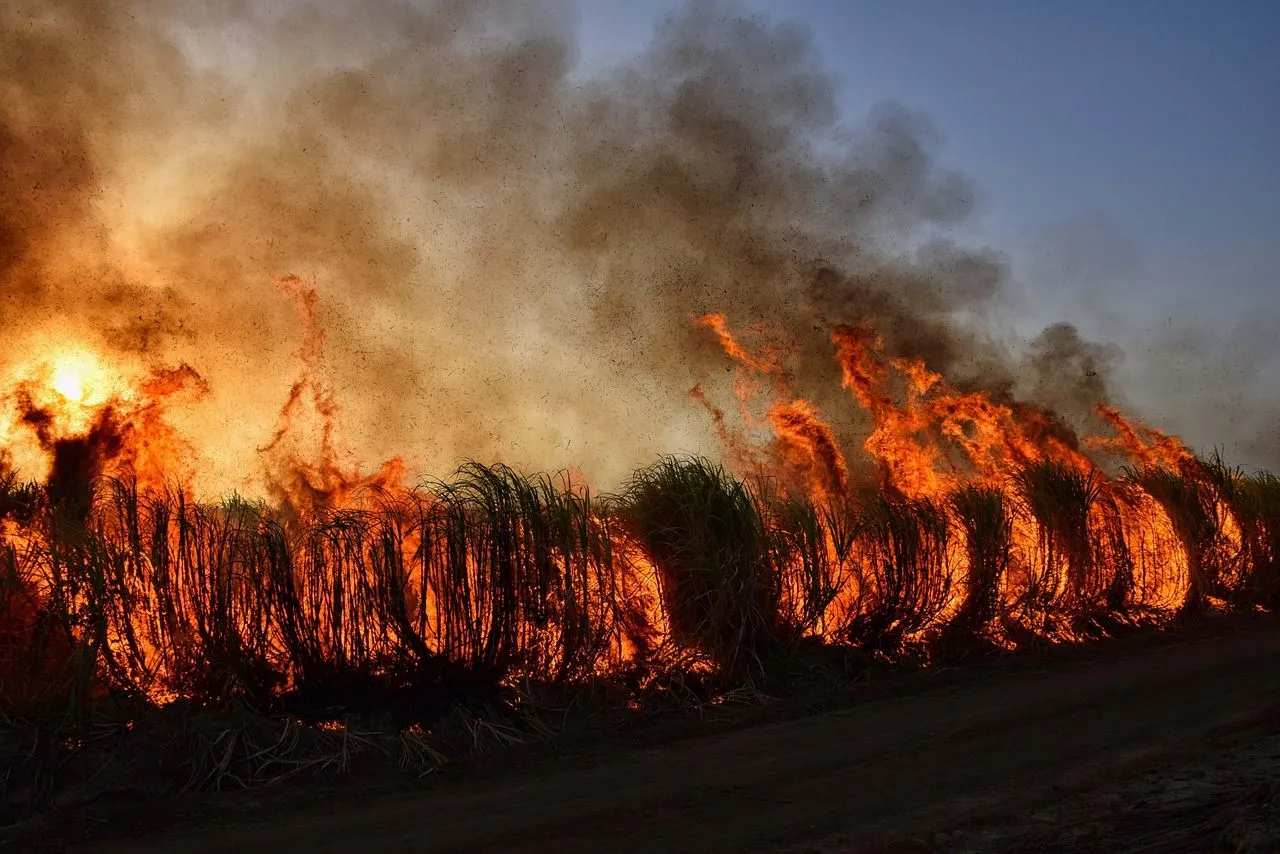

Foto di Patou Ricard da Pixabay
These numbers are truly shocking and I think that every citizen should be aware of the situation, in order to act with more awareness.
Thanks for stopping by my blog.
See you next time,
Delilha
Questi numeri sono davvero scioccanti e penso che ogni cittadino dovrebbe essere a conoscenza della situazione, per poter agire con più consapevolezza.
Grazie per essere passati sul mio Blog.
Alla prossima,
Delilha

Foto di Willfried Wende da Pixabay
Sources - Fonti:
https://eniscuola.eni.com/en-IT/environment/ecosystems/mediterranean-scrub.html
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/