In 2017, JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon called Bitcoin a 'fraud' and threatened to fire all employees who were trading it. Yesterday JPMorgan added two bitcoin exchanges – Coinbase and Gemini as their corporate banking customers. They would help these two exchanges to manage the cash in the US. It is good news for the crypto industry. Let’s come back to the title topic of the post. The third bitcoin halving happened on 11th May, 2020. I got calls from some of my friends. They wanted to understand the halving thing! No, one bitcoin didn’t become ½ bitcoin. Bitcoin block mining reward got reduced from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC. This was the third bitcoin halving in the history and it took place at the block height of 630,000. The first halving happened on 29th November, 2012 and the second halving took place on 10th July, 2016. Generally halving schedule is 4 years. In every halving event, bitcoin’s inflation or supply rate gets reduced. After the latest halving, bitcoin’s inflation drops from the previous rate of 3.6% to 1.7%. Okay cool! 1.7% is quite low. Bitcoin’s inflation rate is almost comparable to gold’s inflation now. But what happens to the miners?
Here is the case study – Miners start dumping Bitcoin
Bitcoin mining consumes high electricity. Many organizations and individuals are involved in mining. After Bitcoin halving, the price didn’t increase so much and their mining reward got halved. So, obviously their profitability gets reduced post halving. In such a scenario, the miners may start dumping their bitcoin rather than hodling. If you look at the below chart, you can see that the hash rate has dropped a bit although this drop isn’t unexpected.
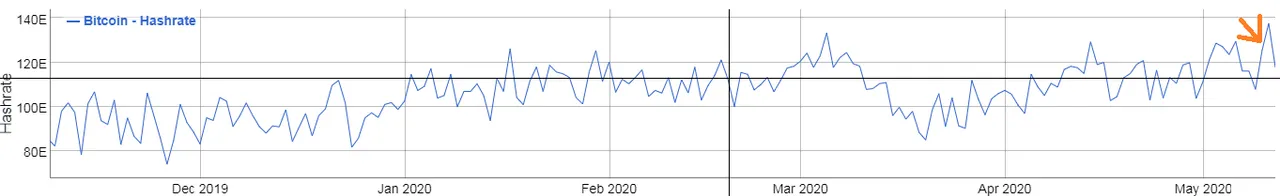
Bitcoin hash rate of last 6 months from bitinfocharts
Dropping hash rate means that there are fewer miners now. Some have left mining and some have reduced mining rate. It may be a temporary incident as big mining organizations work with a long term strategy. But if all these miners start to sell bitcoin at a massive rate due to low profitability, the price of bitcoin will come under pressure and it’ll fall. A short-term miner capitulation may occur and it happened previously also. ‘Bitcoin death spiral’ is a theoretical incident when the hash rate becomes zero.
Imagine a situation:
• Almost 99% miners leave mining job due to low profitability
• They start heavy dumping
• Bitcoin price falls heavily
• Hash rate becomes almost zero– ‘Death Spiral’
• Next what?
Bitcoin’s mining difficulty has been designed to adjust every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks). This adjustment happens as per the network’s hash rate and it keeps on changing. When hash rate comes down, the mining difficulty gets reduced too and it helps to solve new blocks easily. The miners come back again to mine blocks as it becomes easy for them to mine new blocks. The mining profitability increases although the inflation doesn’t change. More miners start mining blocks and the network hash rate increases. As mining becomes profitable due to less difficulty of mining, dumping doesn’t happen and bitcoin price increases due to simple demand-supply economics.
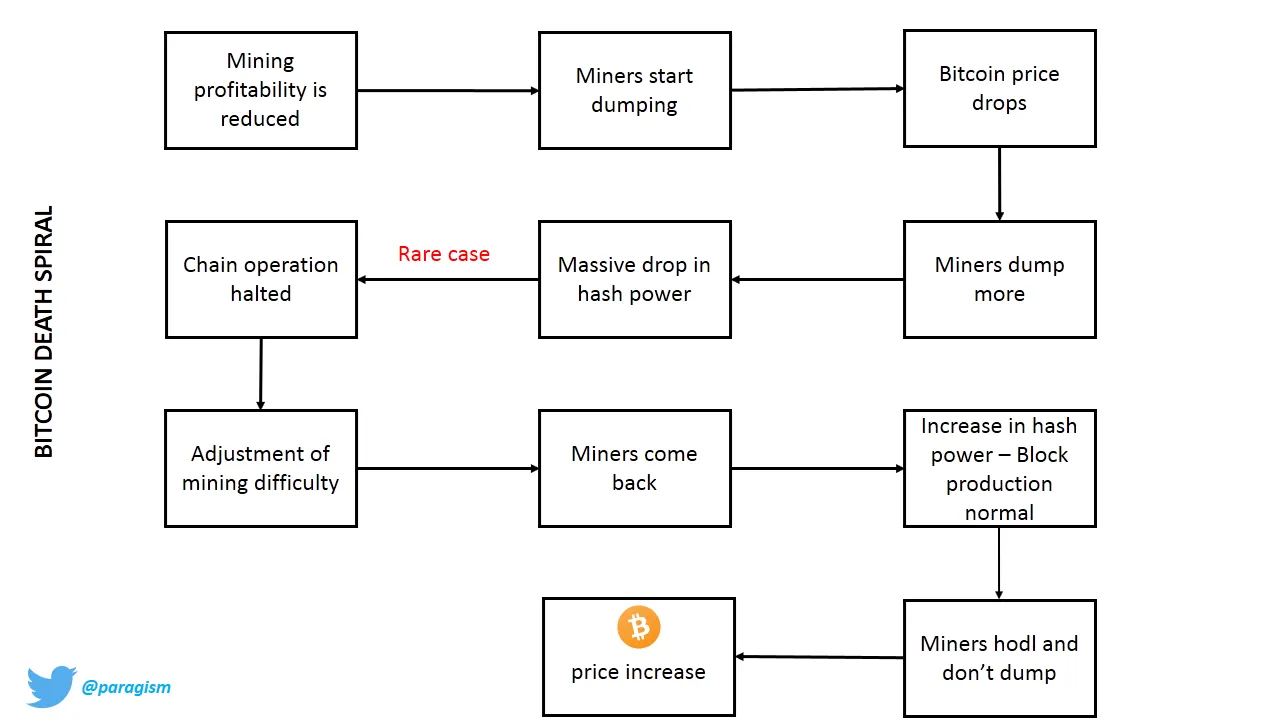
A diagrammatic representation of the situation made by me
The European Union introduced negative interest rates in 2014. Trump wants to bring negative interest rates to the US now. That means you need to pay banks to store your money. To be more precise, it is taxation on people’s savings. US dollar is heading towards a massive value erosion and banking system is becoming a joke. Satoshi Nakamoto wanted to fix this with his programmed money. He didn’t create Bitcoin as a digital useless asset. He envisioned bitcoin as ‘a peer-to-peer electronic cash system’. While creating a transparent & censorship-resistant monetary system, he took care of the economics of bitcoin too. Bitcoin’s price recovery mechanism is also inscribed into bitcoin! Sound money!
Note: The images (if not cited) are created by the author using free vectors.
