Diabetes mellitus, commonly referred to as diabetes or DM is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body's inability to produce or use insulin effectively. While diabetes affects millions of people worldwide, it is alarming that many individuals are not fully aware of the potential complications associated with the condition. In this post, we will discuss both the common and uncommon complications of diabetes, as well as provide advice on how to avoid them.
Common Complications of Diabetes:
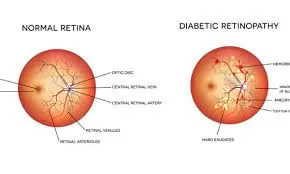
Diabetic Retinopathy:
This is a condition that affects the eyes and is a leading cause of blindness among adults. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to visual impairment or even permanent visual loss. Regular eye exams and maintaining good blood sugar control are essential in preventing this diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic Neuropathy:
This is a type of nerve damage that can affect various parts of the body, due to some small vessel diseases cause poor blood flow and sugar tone. It most commonly affect the feet and legs. It can cause numbness, tingling, or pain, and in severe cases, it may result in loss of sensation or muscle weakness. This loss of sensations may affect the foot leading to diabetic ulcers. Proper foot care, including regular inspections, keeping feet clean and moisturized, and wearing appropriate footwear, can help prevent diabetic foot ulcers.
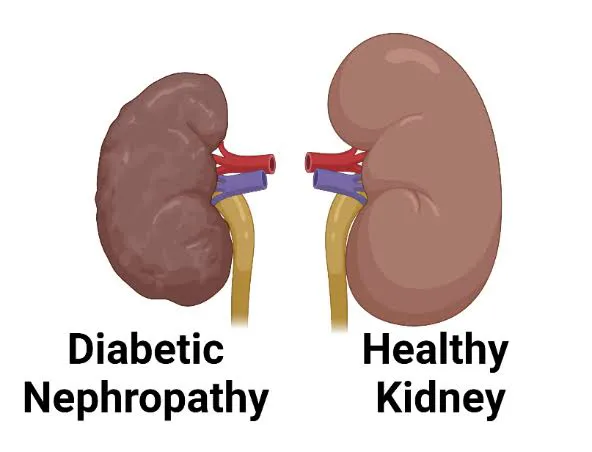
Diabetic Nephropathy:
High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys over time, leading to diabetic kidney diseases, which can progress to kidney failure, even requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation. As the diabetes prolongs, it results in certain changes happening in the kidney cause deposits and inflammations occuring within the kidney tissues. Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining healthy blood pressure, and regular kidney function tests are crucial in preventing diabetic nephropathy.
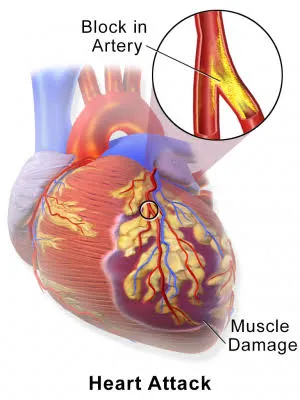
Cardiovascular Diseases:
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis which is a thickening of the blood vessel walls and other cardiovascular complications. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a healthy diet, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and avoiding smoking can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with diabetes.
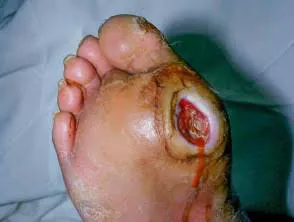
Diabetic Foot Ulcers:
Just as we discussed above, Diabetes can impair blood flow and sensation in the feet, making them vulnerable to wounds and infections that can result in foot ulcers. Proper foot care, regular foot inspections, and wearing appropriate footwear are crucial in preventing diabetic foot ulcers. Prompt medical attention should be sought for any foot wounds or infections to prevent them from worsening.
Uncommon Complications of Diabetes:
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): This is a life-threatening complication that occurs when the body lacks insulin and starts breaking down fats for energy, leading to a buildup of ketones in the blood. DKA can cause symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and can even result in even coma or death if not treated promptly. Strict blood sugar management, regular monitoring, and timely insulin administration can help prevent DKA.
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS): This is a condition characterized by extremely high blood sugar levels and severe dehydration. It can lead to symptoms such as excessive thirst, dry mouth, weakness, confusion, and can also result in coma or death if left untreated. Regular blood sugar monitoring, hydration, and timely medical intervention are very crucial in preventing HHS.
Gastroparesis: Diabetes can damage the nerves that control the stomach, leading to delayed gastric emptying or slow gastric movement, a condition known as gastroparesis, It can cause symptoms such as bloating, nausea, vomiting, early satiety, and abdominal pain. Managing blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy diet with smaller, more frequent meals, and medication interventions can help manage gastroparesis.
Sexual Dysfunction: Diabetes can affect sexual function in both men and women. In men, it can cause erectile dysfunction, while in women, it can lead to decreased libido, vaginal dryness, and difficulty achieving orgasm. Maintaining good blood sugar control, managing other risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, and discussing any sexual concerns with a healthcare provider can help address sexual dysfunction in individuals with diabetes.
Sudden Hypoglycemia:
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur in individuals with diabetes who are on certain medications such as insulin or sulfonylureas. However, in some cases, they may lose their ability to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia, leading to a dangerous condition called hypoglycemia unawareness. Regular blood sugar monitoring, awareness of hypoglycemia symptoms, and adjusting medication regimens as needed with the guidance of a healthcare provider can help prevent hypoglycemia unawareness.
MORE READING HERE
American Diabetes Association ADA
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
Hi,I am Jaydr, a Medical Doctor practicing in Nigeria, I have a passion for public health awareness, promotion, content creation, music, crypto and eternity.
MED-HIVE PROMPT 02: HYPERTENSION - GET UP AND GOIf you have loved this post, you may also want to check out some other medical posts I have written and shared on the med-hive Community here
PLAN THIS VALENTINE THE HEALTHY WAY
HIVES, ON THE SKIN (NO, NOT THE BLOCKCHAIN)
TRANSPARENT SKIN: YOUR SKIN DOES NOT LIE
Med-Hive January Prompt #1 : MY SKIN OR NOTHING
GLAUCOMA: THE EYE THAT CAN LOOK CAN'T SEE