IMPORTANCE
From ancestral times, thanks to agriculture, but above all, through the mastery of soil cultivation techniques for the controlled obtaining of vegetables, the solution for the regular supply of human beings was found, and with it, the reduction of the mortality of them. In this way, thanks to the social and economic progress made by the supply of food, and later, the development of trade, the necessary impulse for the economic growth of the countries was achieved.
Therefore, as the OECD argues, agriculture is considered one of the most essential economic, social and environmental activities for human beings. As it is known by all, in the first place, agriculture provides us with natural goods in the form of food, or raw materials for the textile industry; but it not only fulfills these primary functions. Agricultural activities also have environmental consequences, because they build the landscape and provide environmental benefits in soil conservation, preserving biodiversity and seeking a sustainable management of natural resources. It also represents one of the economic activities essential for the economic development of nations, since they promote the economic and social development of many rural areas
Agriculture is, therefore, a fundamental part of the primary economic sector together with livestock, and is an important basis for the growth of the countries' economy. Today, millions of people are supported by agriculture, as indicated by the latest reports prepared by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, promoting food security and boosting the economies of developing countries. .
Thus, agricultural policies, in all their areas (national, regional or international) have become indispensable tools for the development of countries in general, although, above all, for the least developed countries; They are the most effective means for reducing poverty in these areas, being a primary source of food and employment for the population of them.
In fact, as shown by the effort implemented by these policies in a comprehensive manner, the importance of agriculture, we can conclude, does not reside in one of its functions in particular, but lies in the development and conditioning in its three aspects, environmental, economic and social, so that they are interdependent with each other.
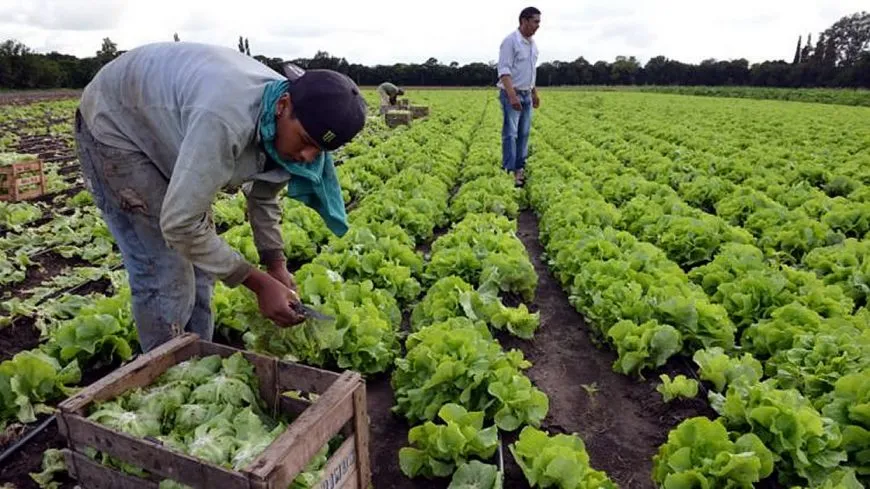

Intensive agriculture has allowed farmers to produce food in quantities needed to be able to offer safe food to society. In this article we give you the keys to know the intensive agriculture in all its aspects.
What is intensive agriculture?
The word intensive agriculture can induce negative thoughts, such as fruits and vegetables artificially manufactured in environments harmful to our health and harmful to the environment.
But the definition of intensive agriculture refers to producing crops in controlled environments and conditions to optimize the growth and development of the plants, with the aim that they can produce fruits to the maximum of their potential.

Intensive farming systems - Greenhouses
There are several forms of intensive agriculture. The first that comes to mind is usually the typical greenhouse areas of the south-east of the peninsula.
Some of the characteristics that lead these production systems to be classified as intensive agriculture are the following:
-Controlled temperature and humidity conditions
Supply of nutrients through irrigation, in the just amount that each plant needs at each stage of its growth
-Use of plant protection means to ensure the health of the crop: fungicides, herbicides and insecticides
Artificial light conditions (if required)
-Genetically improved varieties: use of plant material that has been selected to give high performance of its consumable parts. Eye to the data, and not to be confused with transgenic crops! Plant improvement has been practiced for centuries through the selection of the best plants

What is extensive agriculture?
Extensive agriculture (as opposed to intensive agriculture) is an agricultural production system that uses little labor, fertilizers and capital, in relation to the area of cultivated land.
Extensive farming most commonly refers to sheep and livestock in areas of low agricultural productivity, but may also refer to large-scale growing, wheat, barley and other grain crops in areas such as the Murray-Darling Basin. Here, due to the age and extreme poverty of the soils, the yields per hectare are very low, but the flat terrain and the large farms imply that the yields per unit of work are high. Nomadic herding is an extreme example of extensive farming, where shepherds move their animals to the use of feed from occasional rains.

Advantages of extensive agriculture
Extensive agriculture has a number of advantages with respect to intensive agriculture:
Less work is required per unit area to grow large areas.
Mechanization can be used more effectively in large and flat areas.
A higher efficiency of work generally means lower prices of the products.
Animal welfare is generally improved because the animals are not kept in a suffocating condition.
Decrease in the needs of inputs such as fertilizers.
If the animals feed on native grasses from the locality, they are less likely to have problems with exotic species.
The local environment and the soil are not damaged by the excessive use of chemical products.