
The mycelium may grow above or within the host's body. The color of this mycelium is white, brown, black and others. The fungus will grow rapidly when the surrounding conditions are very moist, acidic soil and always wet with temperatures around 25-30 degrees Celsius. In addition to damaging the living plants, the fungus also destroys the building's wood.
This fungus destroys the crops in various ways as the spores enter into the plant part and then divide by irregular cell enlargement causing ulcers. This irregular growth resulted in the working system of the water-carrying network being disrupted so that the plant life became miserable. For example this case is a root disease in cabbage caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae Wor.
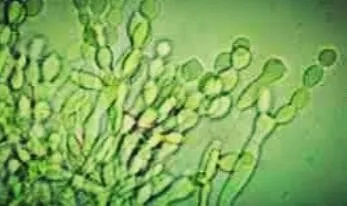
In general, symptoms arising from fungal attack are chlorosis or discoloration of plant tissue, decay in roots, stems, leaves or other plant parts, appearing fine hairs that cover the leaves or stems, and so on.
To control the breeding, these fungus cells can be switched off with fungicides. Based on how it works in turning off the fungus cells, the fungicide is divided into 3:
contact fungicides, examples of Dithane and Antracol.
systemic fungicides, eg Previcur N, Derosal 500 EC.
systemic contact fungicides, eg Delsene MX-200 and Ridomil MZ.
Systemic fungicides are chemical compounds which, when applied to plants, will translate to other parts. Applications can be through leaf penetration, through the soil to be subsequently absorbed by the roots, or injection via the stem.
Since this systemic fungicide enters the cultivation of plants, it must meet the following ideal requirements:
- In host plants work as toksikan.
- Disrupt the host's metabolism and affect physical or chemical resistance to the pathogens and does not reduce the quantity or quality of the plant.
- It can be absorbed well and transolated to the site of the pathogen and stable in the host plant.
- Against low-oxidized mammals.
- Able to improve host resilience.

Referring to the application, the fungicide may be administered as sharpen and protectant. Eruptions are applied when the disease-causing organism (pathogen) is present in the plant, or at the beginning of the infection on the surface of the plant, or before the damage symptoms become irrevers ible. For pathogens that are still present on the surface of the plant part is sufficiently controlled with a contact fungicide. However, for pathogens that have entered into plants can only be controlled with systemic fungicides.
Fungicides as a protectant are applied to the surface of the plant part, eg stems, leaves, and fruits before infection occurs, or even before the pathogen contacts with the plant part.
When viewed from its working function, the fungicide is distinguished on:
- fungicidal, ie killing the fungus.
- fungistatic, meaning only inhibits the growth of fungi.
- genestatic, which means preventing sporulation.

Fungicide forms are various. There are liquid for spraying, solid powder form for pollination, and gas form for fumigation. In addition to controlling the fungus attack in the planting area, fungicides are also widely applied to fruit and vegetables after harvest.
Deutsc

Fungizide sind Substanzen, die giftige chemische Verbindungen enthalten und zur Ausrottung und Vorbeugung von Pilzen / Pilzen eingesetzt werden können. Im Allgemeinen ist der Pilz wie ein feiner Faden geformt, der mit bloßem Auge nicht gesehen werden kann. Diese Sammlung von feinen Garnen, Mycel genannt, kann jedoch deutlich gesehen werden.
Das Mycel kann über oder innerhalb des Körpers des Wirts wachsen. Die Farbe dieses Myzels ist weiß, braun, schwarz und andere. Der Pilz wird schnell wachsen, wenn die Bedingungen sehr feucht sind, saurer Boden und immer feucht mit Temperaturen um 25-30 Grad Celsius. Der Pilz zerstört nicht nur die lebenden Pflanzen, sondern zerstört auch das Holz des Gebäudes.
Dieser Pilz zerstört die Pflanzen auf verschiedene Arten, da die Sporen in den Pflanzenteil eindringen und sich dann durch unregelmäßige Zellvergrößerung teilen, wodurch Geschwüre verursacht werden. Dieses unregelmäßige Wachstum führte dazu, dass das Arbeitssystem des wasserführenden Netzwerks gestört wurde, so dass das Pflanzenleben miserabel wurde. Zum Beispiel ist dieser Fall eine Wurzelkrankheit in Kohl verursacht durch Plasmodiophora brassicae Wor.

Im Allgemeinen sind Symptome, die von einem Pilzbefall herrühren, Chlorose oder Verfärbung des Pflanzengewebes, Zerfall in Wurzeln, Stängeln, Blättern oder anderen Pflanzenteilen, feine Federn, die Blätter oder Stängel bedecken, und so weiter.
Zur Steuerung der Züchtung können diese Pilzzellen mit Fungiziden abgeschaltet werden. Basierend auf der Funktionsweise der Pilzzellen wird das Fungizid in 3 unterteilt:
Kontakt Fungizide, Beispiele für Dithane und Antracol.
systemische Fungizide, zB Previcur N, Derosal 500 EC.
systemische Kontaktfungizide, zB Delsene MX-200 und Ridomil MZ.
Systemische Fungizide sind chemische Verbindungen, die bei Anwendung auf Pflanzen in andere Teile übertragen werden. Anwendungen können durch Blattpenetration, durch den Boden, der anschließend von den Wurzeln absorbiert wird, oder durch Injektion über den Stiel erfolgen.
Da dieces systemischen Fungizids gehört zum Pflanzenanbau, es muss folgende ideale Voraussetzungen erfüllen:
- In Wirtspflanzen arbeiten als Toksikan
- Störung des Metabolismus des Wirtes und Beeinflussung der Pathogene durch physikalische oder chemische Resistenzen und Verminderung der Quantität oder Qualität der Pflanze.
- Es kann gut absorbiert und an die Stelle des Pathogens translatiert werden und in der Wirtspflanze stabil sein.
- Gegen niedrig oxidierte Säugetiere.
- Kann die Ausfallsicherheit des Hosts verbessern.

Unter Bezugnahme auf die Anmeldung kann das Fungizid als Schärf- und Schutzmittel verabreicht werden. Eruptionen werden angewendet, wenn der krankheitserregende Organismus (Pathogen) in der Pflanze vorhanden ist, oder zu Beginn der Infektion auf der Oberfläche der Pflanze oder bevor die Schädigungssymptome irreversibel werden. Für Krankheitserreger, die noch auf der Oberfläche des Pflanzenteils vorhanden sind, wird mit einem Kontaktfungizid ausreichend kontrolliert. Für eingedrungene Erreger können Pflanzen jedoch nur mit systemischen Fungiziden bekämpft werden.
Das Fungizid unterscheidet sich von seiner Arbeitsfunktion her auf:
- fungizid, dh den Pilz töten.
- fungistatisch, dh hemmt nur das Wachstum von Pilzen.
- genestatisch, was bedeutet, dass die Sporulation verhindert wird.

Fungizide als Schutzmittel werden auf die Oberfläche des Pflanzenteils, z. B. Stengel, Blätter und Früchte, aufgebracht, bevor eine Infektion auftritt oder sogar bevor das Pathogen mit dem Pflanzenteil in Kontakt kommt.
Fungizidformen sind verschieden: Es gibt eine Flüssigkeit zum Sprühen, eine feste Pulverform zur Bestäubung und eine Gasform zum Begasen.Neben der Bekämpfung des Pilzbefalls in der Anbaufläche werden Fungizide nach der Ernte auch häufig bei Obst und Gemüse angewendet.