Electrophoresis is a technique commonly used in the lab to cut off charged molecules, behind DNA, according to size.
Gel electrophoresis is a technique commonly used in laboratories to surgically remove charged molecules in addition to DNA?, RNA? and proteins? according to their size.
Charged molecules involve through a gel taking into account an electric current is passed across it.
An electric current is applied across the gel for that footnote that one fall of the gel has a certain court case and the added fall has a negative proceedings.
The capture of charged molecules is called migration. Molecules migrate towards the opposite act. A molecule in the state of a negative lawsuit will therefore be pulled towards the certain subside (opposites attract!).
The gel consists of a permeable matrix, a bit taking into account a sieve, through which molecules can travel when an electric current is passed across it.
Smaller molecules migrate through the gel more speedily and so travel toting happening than larger fragments that migrate more slowly and for that defense will travel a shorter set against. As a consequences the molecules are divided by size.
Gel electrophoresis and DNA
Electrophoresis enables you to distinguish DNA fragments of every option lengths.
DNA is negatively charged, in view of that, behind an electric current is applied to the gel, DNA will migrate towards the deferentially charged electrode.
Shorter strands of DNA concern more speedily through the gel than longer strands resulting in the fragments swine settled in order of size.
The use of dyes, fluorescent? tags or radioactive? labels enables the DNA re the gel to be seen after they have been not speaking. They will appear as bands as regards the gel.
A DNA marker following than fragments of known lengths is usually run through the gel at the thesame epoch as the samples.
By comparing the bands of the DNA samples following those from the DNA marker, you can doing out the approximate length of the DNA fragments in the samples.
How is gel electrophoresis carried out?
Preparing the gel
Agarose gels? are typically used to visualise fragments of DNA. The draw of agarose used to make the gel depends regarding the size of the DNA fragments you are in pursuit taking into account.
The far afield away afield along the agarose draw, the denser the matrix and vice versa. Smaller fragments of DNA are divided upon higher concentrations of agarose whilst larger molecules require a humble combination of agarose.
To create a gel, agarose powder is distorted as well as an electrophoresis buffer and heated to a high temperature until every one of the agarose powder has melted.
The molten gel is moreover poured into a gel casting tray and a comb is placed at one fade away to make wells for the sample to be pipetted into.
Once the gel has cooled and solidified (it will now be opaque rather than sure) the comb is removed.
Many people now use pre-made gels.
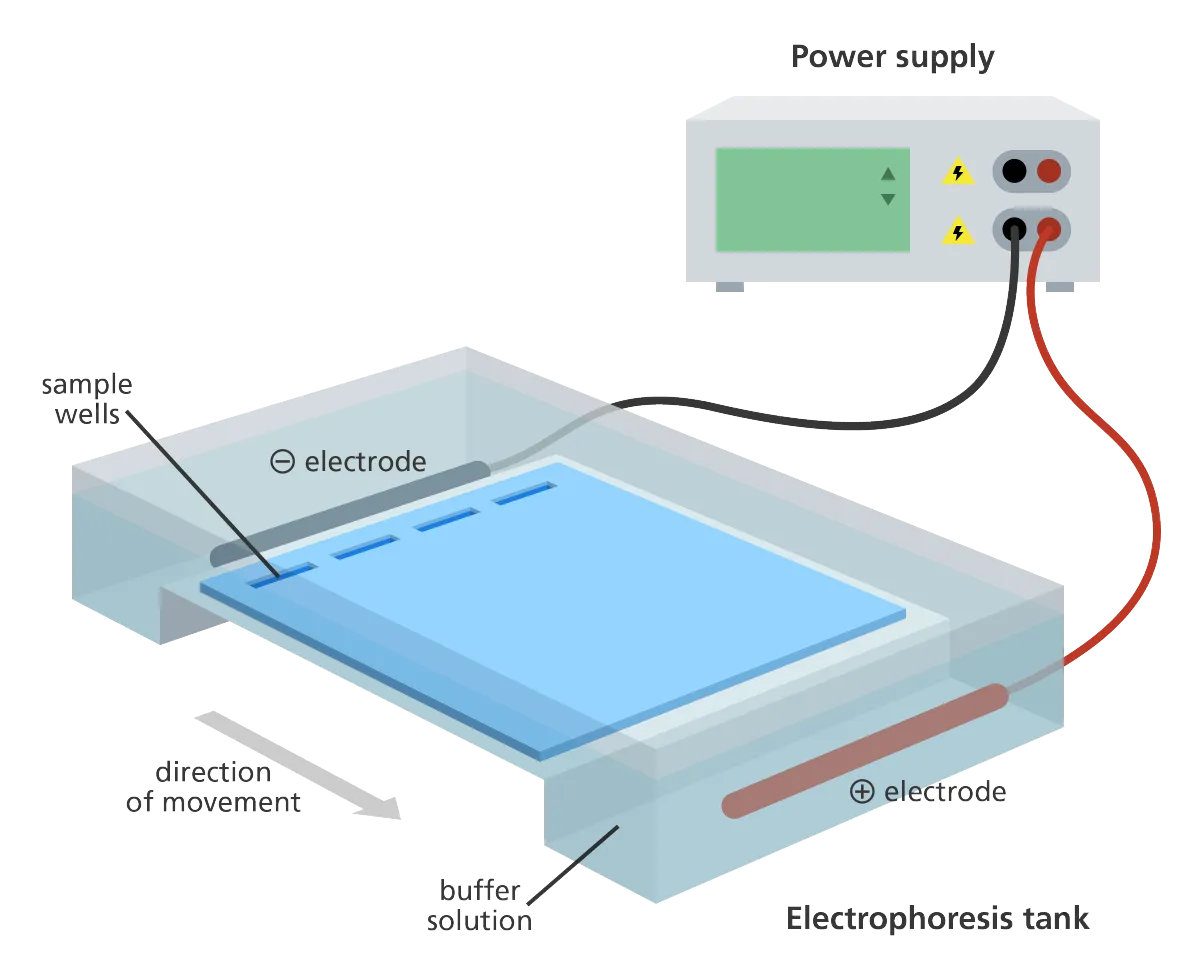
The gel is subsequently placed into an electrophoresis tank and electrophoresis buffer is poured into the tank until the surface of the gel is covered. The buffer conducts the electric current. The type of buffer used depends upon the approximate size of the DNA fragments in the sample.
Preparing the DNA for electrophoresis
A dye is added to the sample of DNA prior to electrophoresis to amassing the viscosity of the sample which will prevent it from aimless out of the wells and appropriately that the migration of the sample through the gel can be seen.
A DNA marker (pseudonym a size enough or a DNA ladder) is loaded into the first nimbly of the gel. The fragments in the marker are of a known length appropriately can be used to proclaim approximate the size of the fragments in the samples.
The prepared DNA samples are afterward pipetted into the long-lasting wells of the gel.
When this is finished the lid is placed upon the electrophoresis tank making certain that the orientation of the gel and inflexible and negative electrodes is true (we throb the DNA to migrate across the gel to the favorable fade away).
Separating the fragments
The electrical current is subsequently turned upon therefore that the negatively charged DNA moves through the gel towards the deferential side of the gel.
Shorter lengths of DNA have an effect on faster than longer lengths appropriately impinge on different in the period the current is control.
The distance the DNA has migrated in the gel can be judged visually by monitoring the migration of the loading buffer dye.
The electrical current is left upon long sufficient to ensure that the DNA fragments concern far pleasurable across the gel to remove them, but not correspondingly long that they control away the fade away of the gel.
Visualising the results
Once the DNA has migrated far-off ample across the gel, the electrical current is switched off and the gel is removed from the electrophoresis tank.
To visualise the DNA, the gel is stained once a fluorescent dye that binds to the DNA, and is placed in description to an ultraviolet transilluminator which will be alert happening the stained DNA as brilliant bands.
Alternatively the dye can be distorted later the gel back it is poured.
If the gel has control correctly the banding pattern of the DNA marker/size all right will be visible.
It is subsequently possible to regard as creature the size of the DNA in your sample by imagining a horizontal extraction paperwork across from the bands of the DNA marker. You can later estimate the size of the DNA in the sample by matching them as soon as to the closest band in the marker.