
Futures markets are organized markets that deal with standardized contracts, a representation of events that will occur on future dates, being future price. From the history of financial markets, it is established that Japan is home to the first futures market in the world in the early 1670’s in a place called Dojima.
Japan being heavily abundant in rice from both a consumption and trade market perspective, found that purchase and sale agreements between merchants exposed them to counterparty risk as a result of forward purchases, which is a pre-negotiated agreement between a buyer and seller for the delivery of rice fro, Dojima at a specified price. Because this contract(forward ) was between two individuals, it meant that the fulfillment and the carrying out of the terms and conditions including the purchase and delivery of the rice was held by one of the two entities resulting to a high undiversified embedded risk(systematic risk) .
Because of another characteristic of forward agreements being that they are not standardized, it meant that the contract was difficult to sell upon non-fulfillment of the T&C’s of the original two parties. If merchant X had made an agreement to purchase $1000 per ton of rice ,from Dojima, for a payment and delivery three months down the line and the price of rice fell to $500/ton, merchant x (the buyer) would most likely not hold up the original agreement, as he/she may find it to find another supplier at current prices, being $500. The original supplier from Dojima would then have bared the costs related to the agreement, including the profits that could have been made had the rice not been kept for merchant x-opportunity cost. Counterparty risk maybe understood from the above analogy.
For the supplier, because the agreements is unique between the two original parties, it would become difficult to enter into another agreement with a diiferent merchant who may find the unchanged T&C’s , acceptable and suitable for him/herself. This explains another characteristic of futures contracts, in that they are standardized, and therefore remove counter party risk associated with forward contracts.
The core characteristics of the futures exchange that started in Japan in the early 1670’s has been duplicated throughout the world.
Originally futures contract where based on commodities, however today there also exists futures contracts to buy or sell financial instruments such as S&P Futures.
Mechanics of Bitcoin Futures contracts and key terms:
Futures contracts are based on underlying asset (commodity), in this case, Bitcoin. When you sell a futures contract of a commodity like rice, what you are essentially doing is making an agreement to make actual delivery of the quantity of rice at the time of expiry of the contract eg after three months. It is because of this that futures contracts are mainly used as a hedge instead of for speculation purposes.
Bitcoin futures are more like S&P 500 Futures contract because they are cash settled-there-there is no delivery of bitcoin in the future, a feature which would have been interesting as it would have opened up another market place for the strategic purchasing of Bitcoins.
However I do not see this as something that is currently feasible at these early stages due to possible security exploits that can occur through the transferring of Bitcoins to a third party for safe “storage” as part of the T&C’s of the futures contract. Another reason why I currently do not see feasible that contracts where deliveries are made at expiry will happen ,is because it would undermine the ideology of Bitcoin, being it a decentralized, “peer-to-peer” cash network.
For futures to occur in this method i.e allowing a legitimate market participant to hedge, you would have to give your Bitcoin to the bank in exchange for a loan (collateralized loan), an unfavorable open position of the futures contract would may result in the forfeit of your loan and Bitcoin.
Such contracts would be of high benefit for Bitcoin holders, because the above conditions would cause the price of bitcoin to rise exponentially. Some say that prices that Bitcoin would reach in the next 5/6 years would be reached within a year. These contracts are currently not in play, making Bitcoin Futures Contracts purely speculative.
Another characteristics of Bitcoin Futures, although not limited to, is the concept of margin and margin call.
When you open a Bitcoin futures contract, or any other futures contract, there is a minimum margin (minimum amount of money) requirement by the broker. Upon closure of your open Bitcoin Futures contract position, you will receive the profits plus your initial margin deposit, or the balance of your margin after the deduction of any losses.
The margin require is a certain % of your open Futures contract e.g 5%, and therefore should your losses on the market and the margin not, for example, maintain that 5% relationship, you would get what is known as a margin call, meaning that would have to further fund your open position.
Similar to a stop loss, Futures contracts allow you to make use of what is known as limit up/down, which is to cap the range of movement of the underlying asset, being Bitcoin, which essentially limits your exposure.
Example of making money from long positions:
Let’s assume that that you had one long open Bitcoin futures contract where the current price of Bitcoin stood at $10 000, if you closed the position when the price of Bitcoin was at $15 000, it means that you would have made $5 000.00 per contract. Had you had 10 contracts, you’d have made $50 000($5000.000 x 10) profits, However had the price dropped, the reverse would be applicable.
NB: A Short contract is the reverse of the above where you sell a contract today and buy it in the future, making profits from the fall of the price of Bitcoin.
Due to the high volatility of Bitcoin, the circuit break was hit almost immediately which resulted in the suspension of trading.
The current contact unit is set at 5 Bitcoins as defined by the CME CF Bitcoin Reference Rate.
How to get started trading Bitcoin Futures Contracts:
BitMex is a Bitcoin derivatives exchange which allows you to trade futures contracts, and as a result of these being synthetic contracts, you can also get exposure to other crypto currencies.
1. Go to www.bitmex.com
2. Read the terms and conditions (https://www.bitmex.com/app/terms)
3. Register (www.bitmex.com/register)
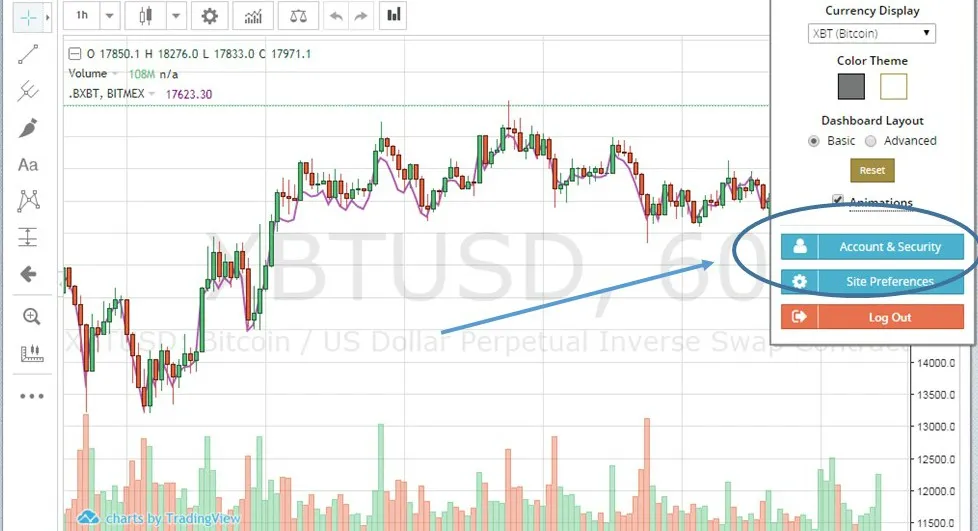
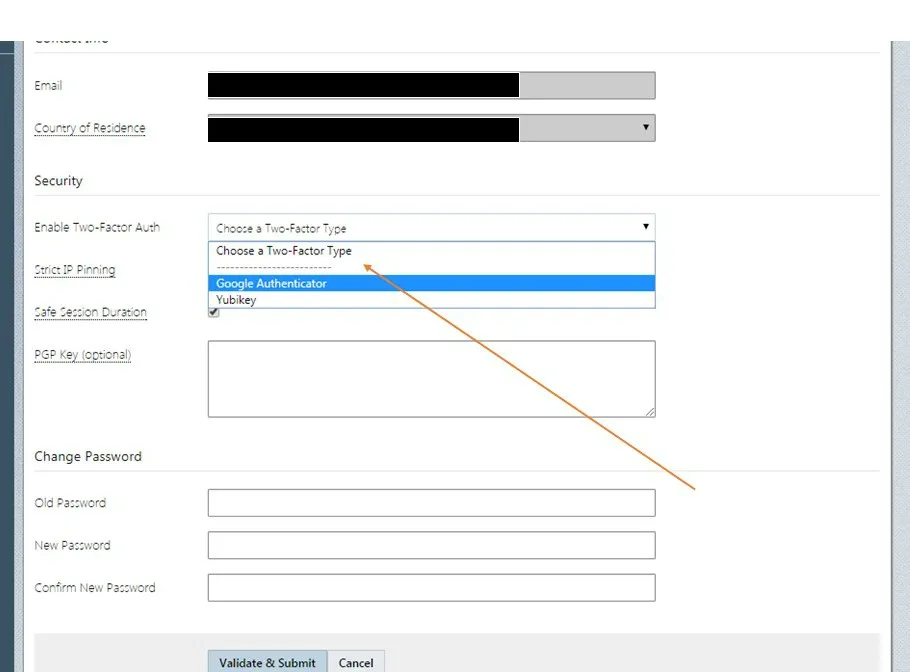
4. Create 2-Factor Authentication

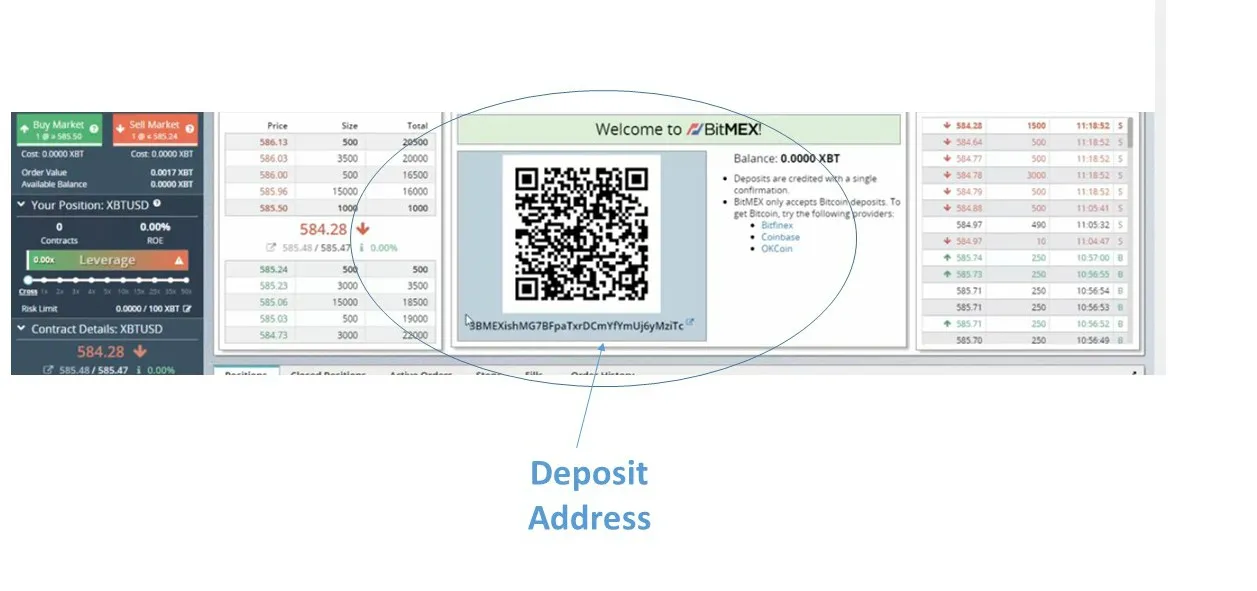
5. Make a deposit into your account
6. Start trading
As this is an introduction, you can subscribe to learn about the math’s behind the Bitcoin Futures Contract, how you profit from the mistakes of professionals that assume that Bitcoin is like any other commodity/asset.
Only if you found this blog valuable, please donate to us as we continue to advocate or blockchain and crypto technology. This will help us to reach greater mass.
bitcoin: 1HfqmGG4H7FE92N3jbiYAjBJ33tADgAPXY

Ether: 0xF5687D69e271Ed6f8D7605402B247cb3eDb4aF50
