
Hola amigos. Confío en Dios en que estén bien.
Padres, madres, este post nace en base a que mi hija es ORH negativo. Pensando en su futuro como madre y en el de otras mujeres que tienen la misma condición, creo pertinente e importante brindarles esta información, en la cual explicaré de la manera más sencilla posible, lo que significa ser madre "O RH Negativo", y sus implicaciones, con la finalidad de alentar la prevención y preparación al respecto.
Hello friends. I trust in God that you are well.
Fathers, mothers, this post is born based on the fact that my daughter is ORH negative. Thinking about her future as a mother and that of other women who have the same condition, I believe it is pertinent and important to provide you with this information, in which I will explain in the simplest way possible, what it means to be a mother "ORH Negative ", and its implications, with the purpose of encouraging prevention and preparation in this regard.
Debo decirles que soy bioanalista con más de 10 años de experiencia y a diario realizo este tipo de pruebas. Si necesitan alguna información al respecto, pueden comunicarse por este mismo medio y con gusto ayudaré a ampliar la información.
I must tell you that I am a bioanalyst with more than 10 years of experience and I perform this type of tests on a daily basis. If you need any information about it, you can contact me through this same means and I will gladly help to expand the information.
INFORMACIÓN BÁSICA
La sangre contiene tres tipos de células: glóbulos blancos (las defensas), glóbulos rojos (contienen la hemoglobina y transportan el oxígeno) y plaquetas (evitan sangrados). En la superficie de los glóbulos rojos, pueden haber o no, unas partículas microscópicas llamadas antígenos del tipo A, B, y las del Factor RH. Por lo tanto, si usted las tiene puede ser del tipo A+, B+, AB+, O+, y el factor RH (+). Si no las tiene puede ser A-, B-, AB-, O- y el RH -.
BASIC INFORMATION
Blood contains three types of cells: white blood cells (the defenses), red blood cells (contain hemoglobin and carry oxygen) and platelets (prevent bleeding). On the surface of the red blood cells, there may or may not be microscopic particles called type A, B, and RH Factor antigens. Therefore, if you have them, you may be A+, B+, AB+, O+, and RH factor (+). If you do not have them you can be A-, B-, AB-, O- and the RH -.
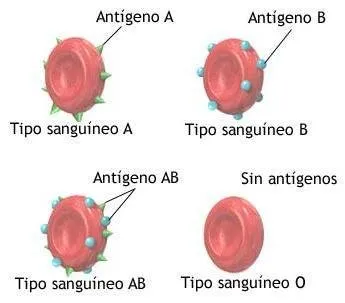
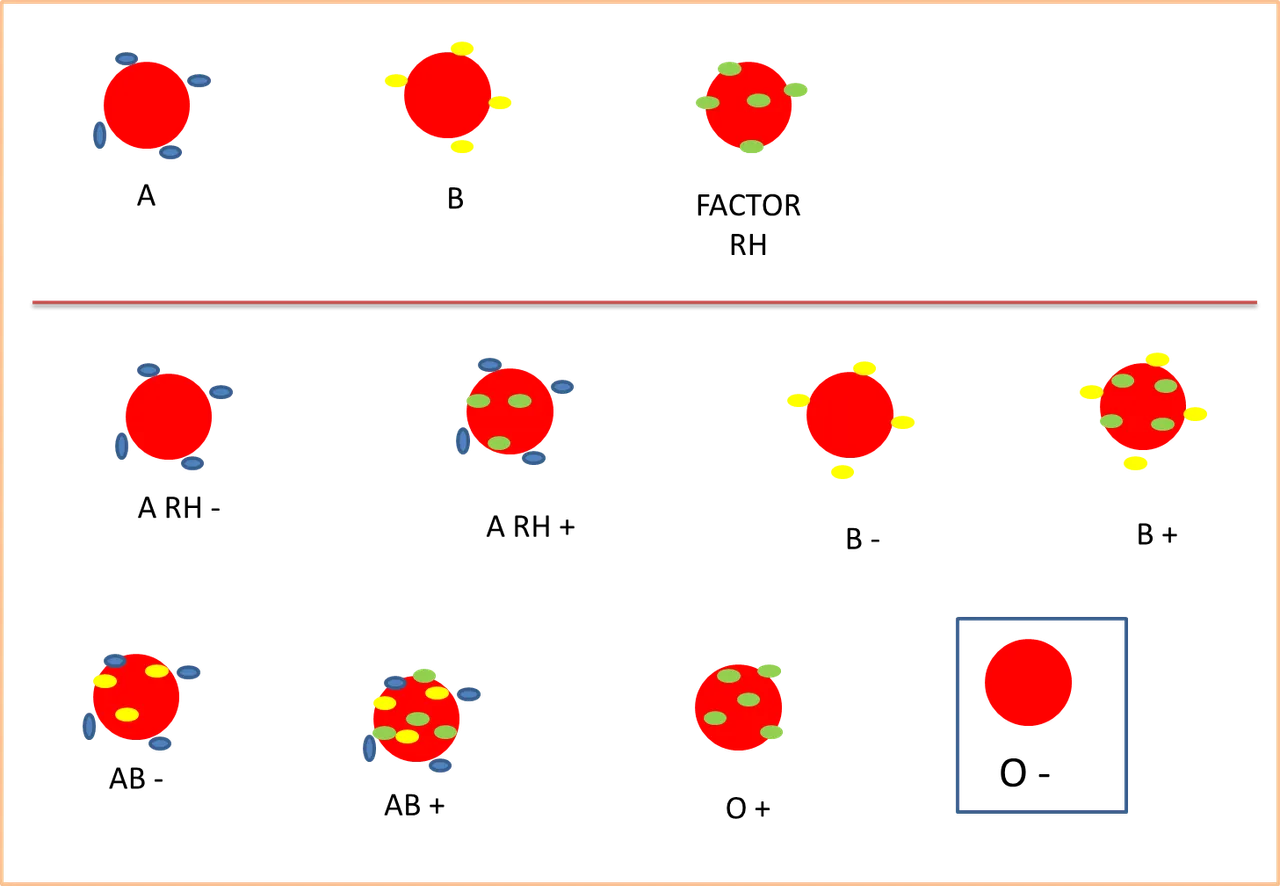
En este sentido, O RH NEGATIVO (O -) simplemente es un tipo de sangre cuyos glóbulos rojos no tienen nada en su superficie, determinado a través de una prueba llamada Tipiaje o Grupo Sanguíneo. Esto no es una enfermedad, sin embargo puede afectar el embarazo.
In this sense, O RH NEGATIVE (O -) is simply a blood type whose red blood cells have nothing on their surface, determined through a test called Typing or Blood Type. This is not a disease, however it can affect pregnancy.

IMPORTANCIA DEL RH Negativo EN EL EMBARAZO.
Cuando la sangre de la madre O - hace contacto con los antígenos del bebe O+ durante el embarazo, las defensas de la sangre de la madre, rechazarán los antígenos del niño, ya que no le son propios, y producirá anticuerpos en su contra.
IMPORTANCE OF RH NEGATIVE IN PREGNANCY
When the mother's blood O - makes contact with the antigens of the baby O+ during pregnancy, the mother's blood defenses will reject the antigens of the child, since they are not their own, and will produce antibodies against them.
Cuando se trata del primer embarazo, no hay mucho problema, aunque en el momento del parto sucede la primera exposición de la madre a estos antígenos, identificando al antígeno RH como ajeno. A partir de un segundo embarazo de un bebé RH Positivo, los anticuerpos de la madre atacarán a los glóbulos rojos del niño, empeorando con cada embarazo, con fuertes consecuencias que incluyen la posibilidad de una enfermedad hemolítica en el niño, llamada ERITROBLASTOSIS FETAL.
When it is the first pregnancy, there is not much of a problem, although at the time of delivery the first exposure of the mother to these antigens occurs, identifying the RH antigen as foreign. From a second pregnancy with a RH Positive baby, the mother's antibodies will attack the child's red blood cells, worsening with each pregnancy, with strong consequences that include the possibility of a hemolytic disease in the child, called FETAL ERITROBLASTOSIS.
En la eritroblastosis fetal, las defensas de la madre rechazan la sangre del niño, aglutinando la sangre del niño (forma grumos), rompiendo los glóbulos rojos (hemólisis), liberando la hemoglobina que luego se transforma en bilirrubina, y vuelve la piel amarilla (ictericia), pudiendo acumularse en el cerebro, dañando y destruyendo las neuronas, con el consecuente deterioro cerebral en los sobrevivientes y, en la mayoría de los casos, la muerte. De ahí la importancia de realizarse el tipiaje desde las primeras semanas de embarazo.
In erythroblastosis fetalis, the mother's defenses reject the child's blood, agglutinating the child's blood (forming clumps), breaking up the red blood cells (hemolysis), releasing hemoglobin which is then transformed into bilirubin, turning the skin yellow (jaundice), and can accumulate in the brain, damaging and destroying the neurons, with the consequent cerebral deterioration in the survivors and, in most cases, death. Hence the importance of typing from the first weeks of pregnancy.

QUÉ SE PUEDE HACER?
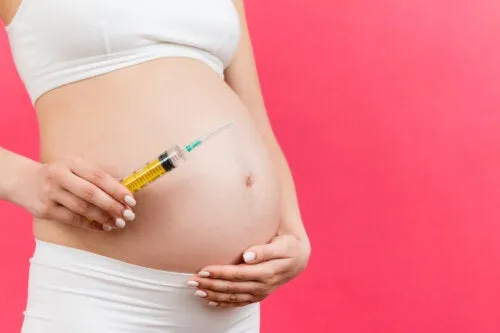
Debemos entender que una vez que la mujer ORH - sabe que está embarazada, debe colocarse una inyección (la más popular es la Rhogam), que evitará que la madre produzca anticuerpos contra el RH del bebé, lo cual sucede generalmente entre la semana 26 y la 28. Son administradas en dos dosis, una en las primeras semanas de gestación y la otra luego de unos días después del parto, si es necesario.
WHAT CAN BE DONE?
We must understand that once the ORH - woman knows she is pregnant, she must have an injection (the most popular is Rhogam), which will prevent the mother from producing antibodies against the baby's RH, which usually happens between the 26th and 28th week. They are administered in two doses, one in the first weeks of gestation and the other a few days after delivery, if necessary.
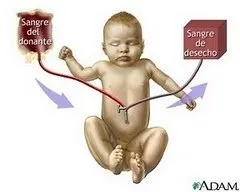
Cuando el panorama es grave para el bebé, se realiza un procedimiento en el niño llamado Exsanguíneotransfusión, con la finalidad de eliminar su sangre mezclada con los anticuerpos de la madre, para limpiarla, como en una diálisis, dentro del útero o después del parto, administrando al niño sangre RH negativa, sin anticuerpos.
When the outlook is serious for the baby, a procedure is performed on the child called Exsanguineous transfusion, with the purpose of eliminating its blood mixed with the mother's antibodies, to clean it, as in a dialysis, in utero or after delivery, giving the child RH-negative blood, without antibodies.

Es importante resaltar que con la llegada de la vacuna Rhogam, son muy pocos los casos de embarazos que llegan a este nivel de daño fetal
It is important to highlight that with the arrival of the Rhogam vaccine, very few pregnancies reach this level of fetal damage.
Esto es todo amigos. Mi intención es la de instruir al respecto, para que seamos parte de la solución y no del problema. Fue un placer.
That's all folks. My intention is to educate about it, so that we are part of the solution and not part of the problem. It was a pleasure.
Saludos!!!
Greetings!!!
Todas las imágenes sin fuente aquí presentadas son de mi autoría.
All unsourced images presented here are my own.
Este post fue traducido empleando el traductor DeepL.
This post was translated using the translator DeepL.
