All living organisms require energy in order to survive. This energy is required for different purposes. Cells need this energy to drive many metabolic reactions like building protein molecules, making copies of DNA and energy used to move chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. For example, every living cell must be able to move substances across its membranes against their concentration gradient with the help of active transport.
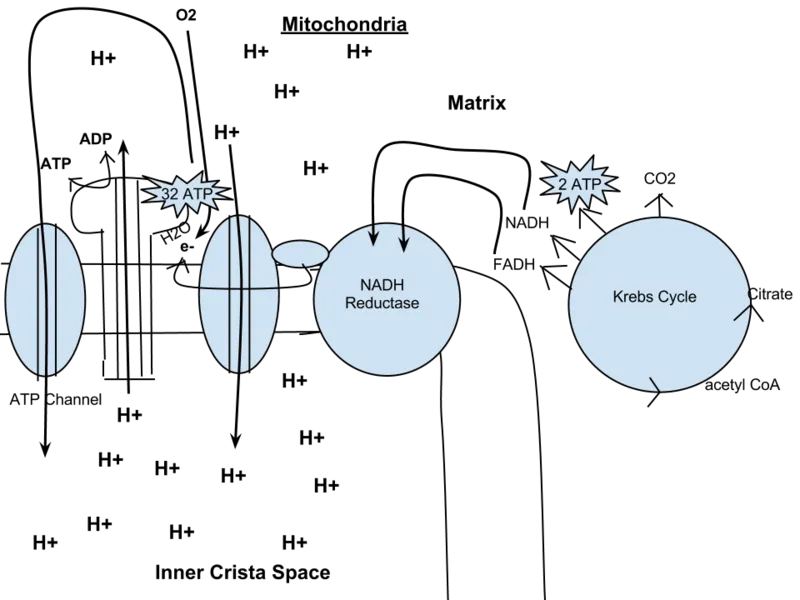
Cellular respiration is process by which cells in plants and animals breakdown sugar and convert it into energy. Respiration comprises of series of chemical reactions, which are performed in the mitochondria of living eukaryotic cells. As a result of these chemical reactions, energy is released to the rest of the cell. In aerobic respiration, oxygen & Glucose react together to form carbon dioxide and water. Each cell needs a certain structure for respiration because ATP can’t pass across its phospholipid membrane.
The purpose of respiration is to provide energy to the cells. This energy is required to fulfill certain functions of the cell. In anaerobic respiration, oxygen is not required but it produces less energy and lactic acid. The rate of respiration shows the activeness of an organism. Oxygen is carried to cells with the help of hemoglobin and later it diffuses into the cells and is used.
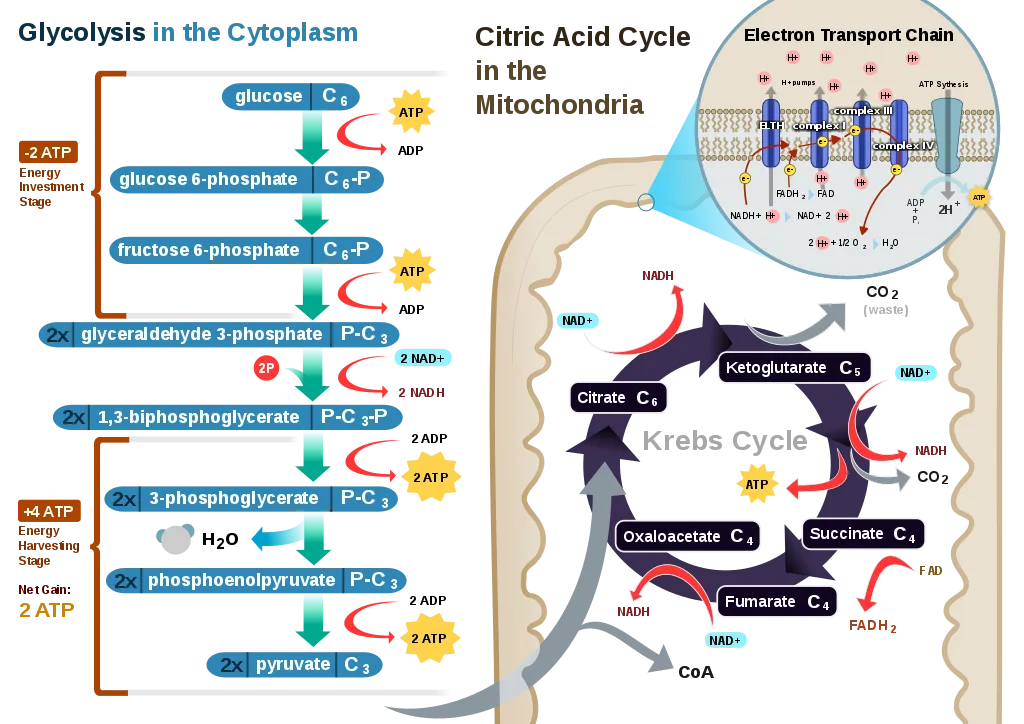
Sugar is oxidized in respiration reaction and carbon dioxide and water is released. If for any reasons, there is shortage of oxygen, lactates are produced. The mitochondria provides the energy to the cells and is considered as powerhouse of the cell. These are made of up double membrane which increase the surface area for diffusion.
Around 3000KJ/Mol energy is released as a result of complete combustion of glucose. This process is very quick and heat and light is also released. Inside the body, enzymes act as a catalyst and reduce the temperatures. Due to these reactions, 38 molecules of ATP are released.
Thank you for reading! Stay Safe!👋😌
References:
1- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellular_respiration
2- https://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k4ch7respirationnotes.html
