Introduction
Hello it's a me again Drifter Programming!
Today we continue with Electromagnetism to get into other ways of calculating Electric field energy, now that we covered Capacitance, and we will also get into Energy density!
All the mathematical equations will be drawn using quicklatex!
So, without further do, let's get straight into it!
Electric field energy
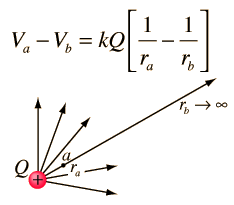
In the previous posts we defined a new concept, the concept of Capacitance, where the capacity was defined equal to:
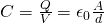
where the second part is true for parallel conductive plates!
A way of calculating the potential energy U was using the Work of the electric force F of an electric field E. But, when having a capacitor we can also use the equation Q = CV and change the integral for that a little bit!
Let's suppose u and q are elementary (small) changes of potential difference and charge respectively while "charging". Of course: u = q/C.
The Work dW that is needed to move the charge dq is:

The total Work W needed to increase the charge q from zero to Q is:

This is of course equal to the total Work produced from the electric field onto the charge q when discharging it from Q to zero.
Supposing the potential energy of an uncharged capacitor is zero then the potential energy and Work of the a charged capacitor are equal!
The potential difference between the conductive plates is: V = Q/C and so U and W can be expressed as:

Of course Q is in Coulomb (C), C in Farad (F = C/V), V in Volt (V = J/C) and U in Joule (J).
The last of those equations tells us:
The total work W is equal to the total charge Q that "moved" times half the potential difference V/2 during the duration of a charge.
Energy density
The stored energy U of a capacitor is of course strongly connected with the electric field E in between of it's conductive plates. We can clearly say that the potential energy is "stored" in the electric field between it's plates.
This is why we define the concept of energy density u as:

which calculates the energy per volume of the electric field of two parallel conductive plates with Area A and distance d.
We also know that the capacitance of such a capacitor can be calculated using:

The potential difference V and electric field E are binded by: V = Ed.
Using those two equation we end up with:
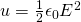
which gives us the energy density of this type of capacitor.
It's proven that this equation applies to any capacitor and electric field E that is in a vacuum space. During this series we will see that this also applies for non-vacuum areas!
How all this is useful
Potential energy equations:
The equations for electric potential energy give us another way of calculating the energy or other "variables" in this equations, which means that we can calculate 1 of them if we know 2 of the others.
Mostly, we will just use them to calculate the potential energy when knowing two of the variables: charge Q, potential difference V and capacitance C.
Energy density:
The equation of energy density and the ones that we get from it are useful when we know how much energy we want to store per cubic-meter in a vacuum and want to calculate the electric field magnitude E that is needed to be able to store that much per cubic-meter.
Sometimes we might even want to calculate the energy density "change" when increasing or decreasing the electric field magnitude E in some way.
Examples around that and the previous stuff will come in the final post of this "chapter" and so after we cover Dielectrics!
Previous posts about Physics
Intro
Physics Introduction -> what is physics?, Models, Measuring
Vector Math and Operations -> Vector mathematics and operations (actually mathematical analysis, but I don't got into that before-hand :P)
Classical Mechanics
Velocity and acceleration in a rectlinear motion -> velocity, accelaration and averages of those
Rectlinear motion with constant accelaration and free falling -> const accelaration motion and free fall
Rectlinear motion with variable acceleration and velocity relativity -> integrations to calculate pos and velocity, relative velocity
Rectlinear motion exercises -> examples and tasks in rectlinear motion
Position, velocity and acceleration vectors in a plane motion -> position, velocity and accelaration in plane motion
Projectile motion as a plane motion -> missile/bullet motion as a plane motion
Smooth Circular motion -> smooth circular motion theory
Plane motion exercises -> examples and tasks in plane motions
Force and Newton's first law -> force, 1st law
Mass and Newton's second law -> mass, 2nd law
Newton's 3rd law and mass vs weight -> mass vs weight, 3rd law, friction
Applying Newton's Laws -> free-body diagram, point equilibrium and 2nd law applications
Contact forces and friction -> contact force, friction
Dynamics of Circular motion -> circular motion dynamics, applications
Object equilibrium and 2nd law application examples -> examples of object equilibrium and 2nd law applications
Contact force and friction examples -> exercises in force and friction
Circular dynamic and vertical circle motion examples -> exercises in circular dynamics
Advanced Newton law examples -> advanced (more difficult) exercises
Electromagnetism
Getting into Electromagnetism -> electromagnetim, electric charge, conductors, insulators, quantization
Coulomb's law with examples -> Coulomb's law, superposition principle, Coulomb constant, how to solve problems, examples
Electric fields and field lines -> Electric fields, Solving problems around Electric fields and field lines
Electric dipoles -> Electric dipole, torque, potential and field
Electric charge and field Exercises -> examples in electric charges and fields
Electric flux and Gauss's law -> Electric flux, Gauss's law
Applications of Gauss's law (part 1) -> applying Gauss's law, Gauss applications
Applications of Gauss's law (part 2) -> more Gauss applications
Electric flux exercises -> examples in electric flux and Gauss's law
Electric potential energy -> explanation of work-energy, electric potential energy
Calculating electric potentials -> more stuff about potential energy, potential, calculating potentials
Equipotential surfaces and potential gradient -> Equipotential surface, potential gradient
Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment -> Millikan's experiment, electronvolt
Cathode ray tubes explained using electric potential -> cathode ray tube explanation
Electric potential exercises (part 1) -> applications of potential
Electric potential exercises (part 2) -> applications of potential gradient, advanced examples
Capacitors (Condensers) and Capacitance -> Capacitors, capacitance, calculating capacitance
How to solve problems around Capacitors -> combination, solving problems, simple example
And this is actually it for today!
Next time we will talk about Dielectric materials!
Bye!
