This post contains a video that takes a look at fiscal policy and monetary policy. The video explains what fiscal policy and monetary policy are. It explains what the differences are between these two policies and how they are often applied. The video looks at what fiscal and monetary policies are intended to do and the problems they are expected or supposed to solve. These problems include the following:
- Reduce inflation
- Promote economic growth
- Reduce unemployment
- Stimulate investment
- Reduce budget deficit
- Improve balance of payments
- Improve balance of trade
- Reduce debt
- Target deficient sectors in the economy

Fiscal policy relates to Government expenditure, taxation, and subsidies. Government expenditure can be used to target areas of the economy that require additional stimulation. Government expenditure tends to focus on hard infrastructure such as roads, transportation, hospitals, dams, power and energy plants, and schools. A key emphasis of Government expenditure is focused on ‘solutions’ rather than prevention of problems. Solutions that create other problems and eventually proliferate the existing problems are very popular with most Governments. It is important that solutions create other problems so that Government can continue to spend money in the future. Government expenditure also puts pressure on interest rates which increases the cost of private investment.

Cost benefit analysis (CBA) is sometimes used to support Government expenditure on infrastructure. CBA can help determine which investment produces the highest returns in terms of welfare produced. Unfortunately, CBA generally does not determine Government expenditure but is used as a tool of manipulation to make a Government projects look more impressive to the taxpayers.
Taxation is another part of fiscal policy. Higher taxation may reduce inflation be reducing disposable income and therefore, reducing demand. Lower taxation does the opposite and can stimulate economic growth and reduce unemployment. Tax is used to fund most forms of Government expenditure and is generally popular with ‘left wing’ Governments. ‘Right wing’ Governments tend to be expected to favour less active fiscal policy (less tax and less Government expenditure). Taxation is also a mechanism of transferring welfare from people on salaries and wages to those that run large corporations (multinational companies). A common furphy of taxation is that it reduces wealth and income inequality as income tax is structured to appear progressive.

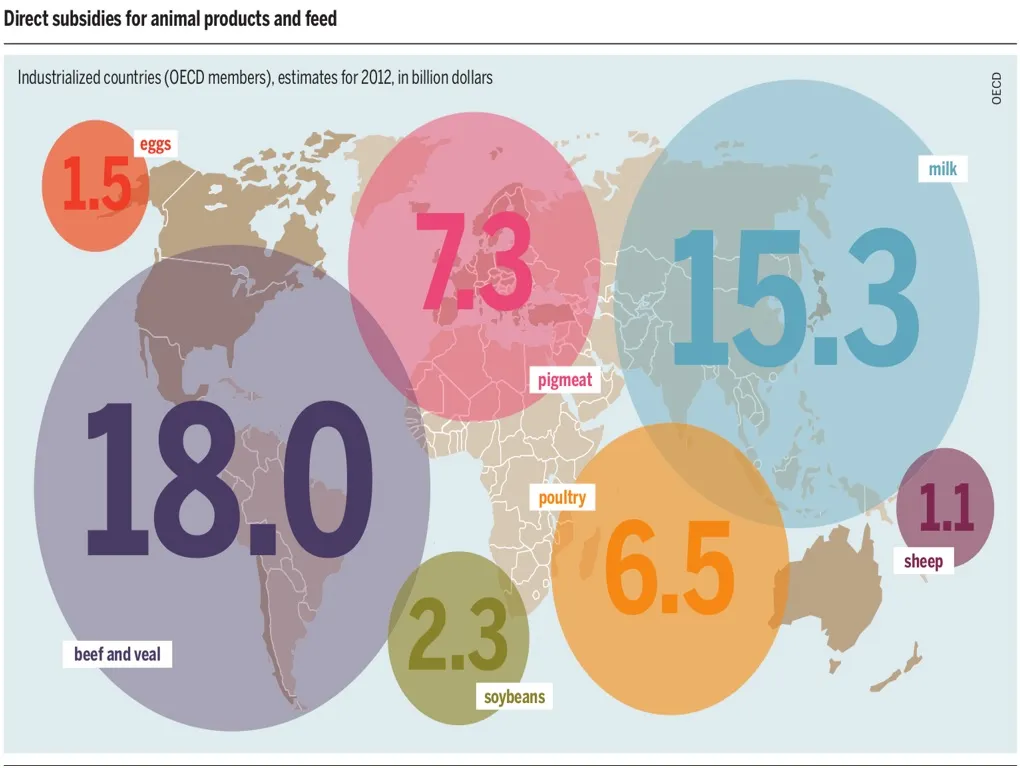
Subsidies are also a part of fiscal policy. Subsidies generally do not greatly stimulate the economy but are targeted at industries the Government would like to remain or become more competitive. The meat and dairy industries are quite heavily subsidized by the Government to help large corporations increase their profit margins at the expense of the environment and lives of animals.
Monetary policy relates to the Central Bank which controls the money supply. The Central Bank can increase money supply (expansionary monetary policy) which will lower interest rates and this will encourage increased borrowing and decreased savings. This is claimed to stimulate the economy, increase demand for goods and services and reduce unemployment. Expansionary monetary policy has a strong correlation to inflation, see inflation video in the macroeconomics series; link is at the bottom of the post with other links to videos. The Central Bank can also reduce money supply (more likely to increase money supply but at a decreasing rate), this is called contractionary monetary policy. Contractionary monetary policy increases interest rates, which reduces demand for money and is intended to reduce inflation. Contractionary monetary policy may also increase unemployment and reduce national income.

Monetary policy can be very dangerous as all the power lies with the Central Bank and the people have no influence on how the Central Bank conducts its business. The Central Bank is able to redistribute wealth through the increase in money supply. The value of money held by the people is reduced by inflation and wealth is transferred from the people to the banks that lend this newly created money. There is no restriction to the amount of money the Central Banks can print as this money is not supported by any tangible assets such as Gold. This money is known as fiat money and is backed by ‘faith’ and potentially could collapse at any time.
If you enjoyed this video remember to click the like button and subscribe for more interesting videos.
Watch the full video using the link below:
The macroeconomic series can be accessed at:

The inflation video can be accessed at:

The official Spectrum Economics website can be accessed at: https://www.spectrumecons.com
For more exciting videos go to my YouTube channel at https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCILwyLtjl7ZTlYOqFkAwLzw
You can find me on LinkedIn at: https://www.linkedin.com/in/waynedavies-spectrumecons/
You can find me on Facebook at: https://www.facebook.com/SpectrumEconomics/
You can find me on Steemit at: https://steemit.com/@spectrumecons


