Hello everyone,how are you all? Hope you all are doing well and i am too.very very long back ago i made a post on synovial joints which is one of the type of joints.there are three types of joints in our body we can see. Fibrous joint,cartilaginous joint and synovial joint.i am going to share the link of synovial joints at the end of the post.now we are going to learn about remaining two joints which are Fibrous joint and Cartilaginous joint
FIBROUS JOINT(SYNARTHROSES)
Fibrous joint is immobile joint.there are 3 types of fibrous joint that we can see.
- SUTURES
In sutures,there are 5 subtypes seen.
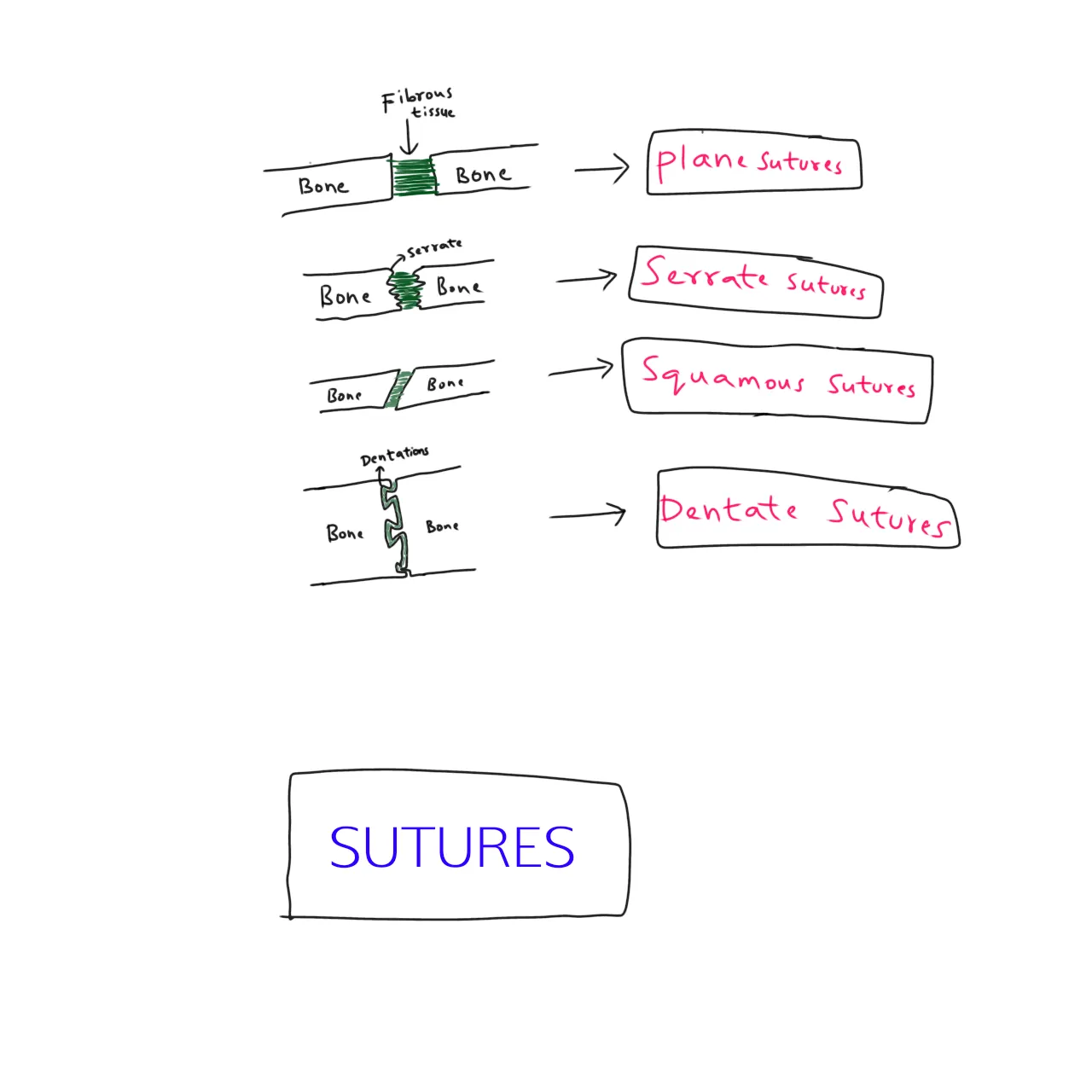
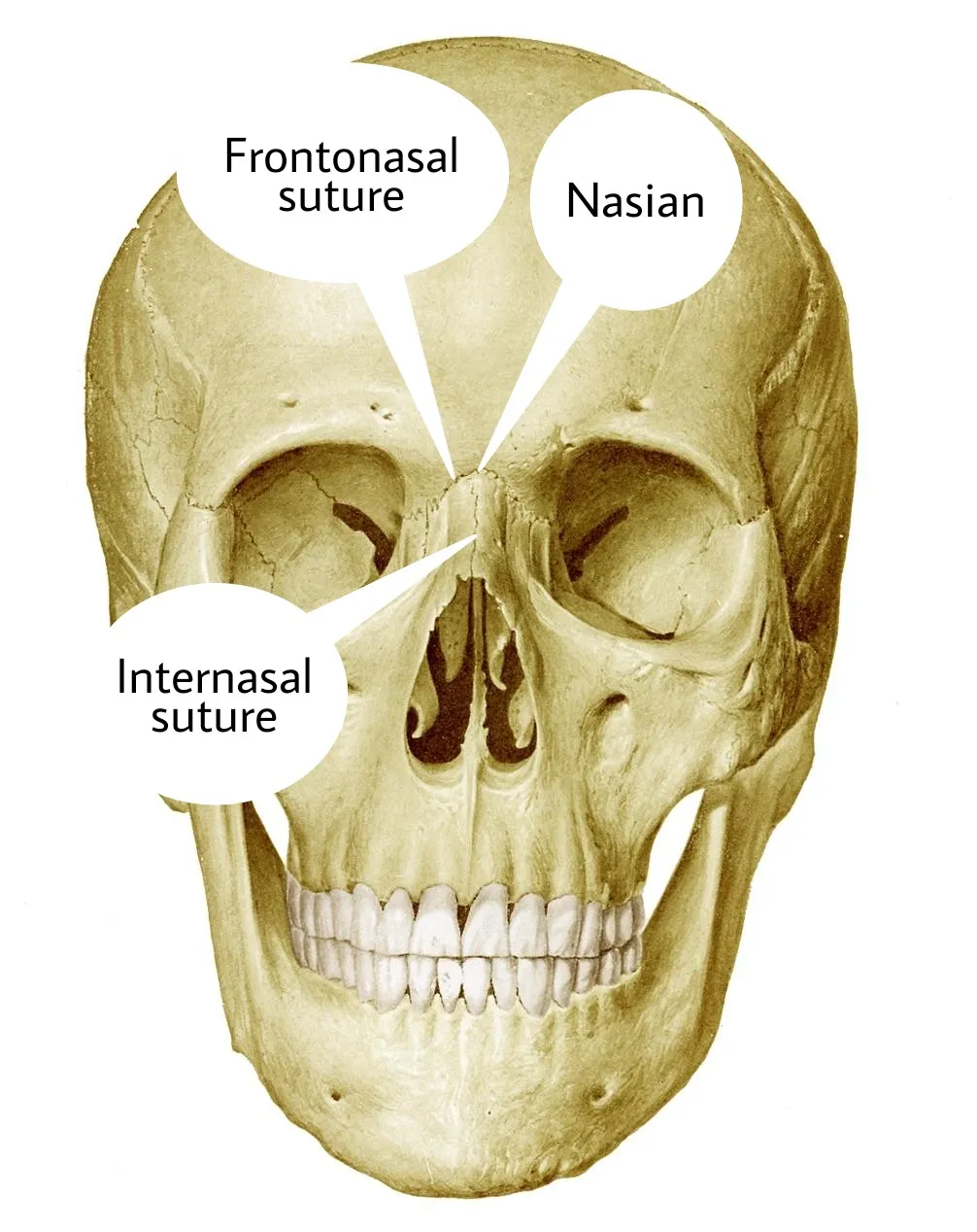
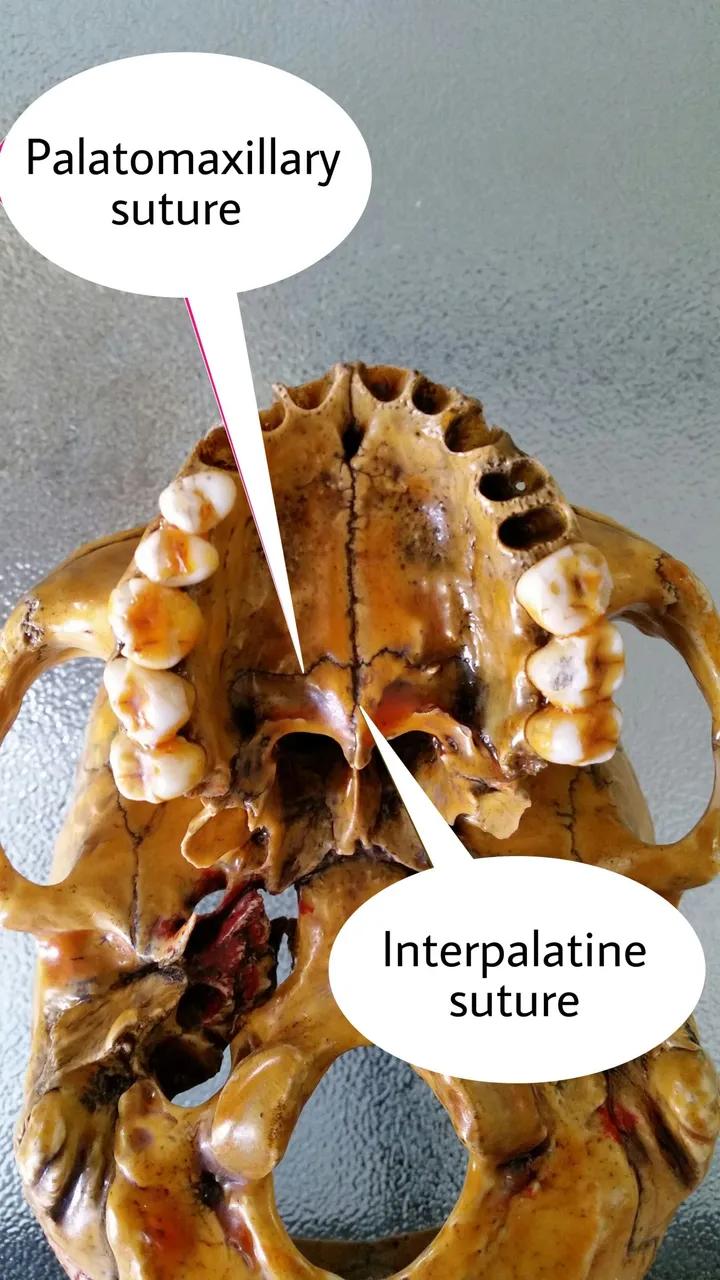
- PLANE SUTURES -
The end of the bones are plane and they are joined in the middle by the fibrous tissue.we can see them in the image.
Examples - (a)Internasal suture
(b)Interpalatine suture
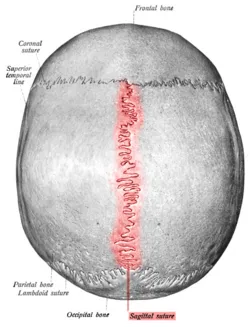
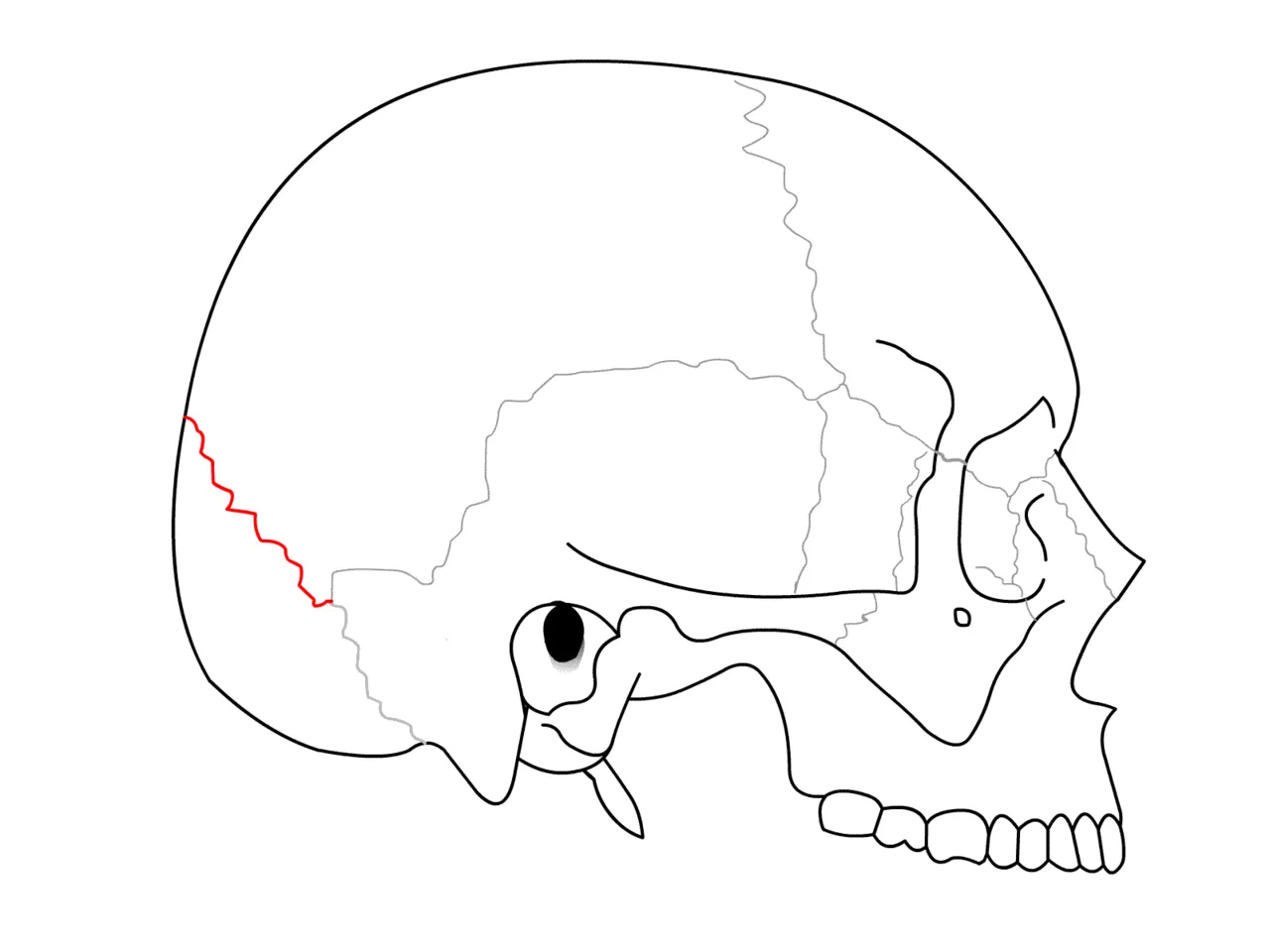
- SERRATE SUTURES -
The end of the bones are serrated and joined by fibrous tissue.
Example - Saggital suture
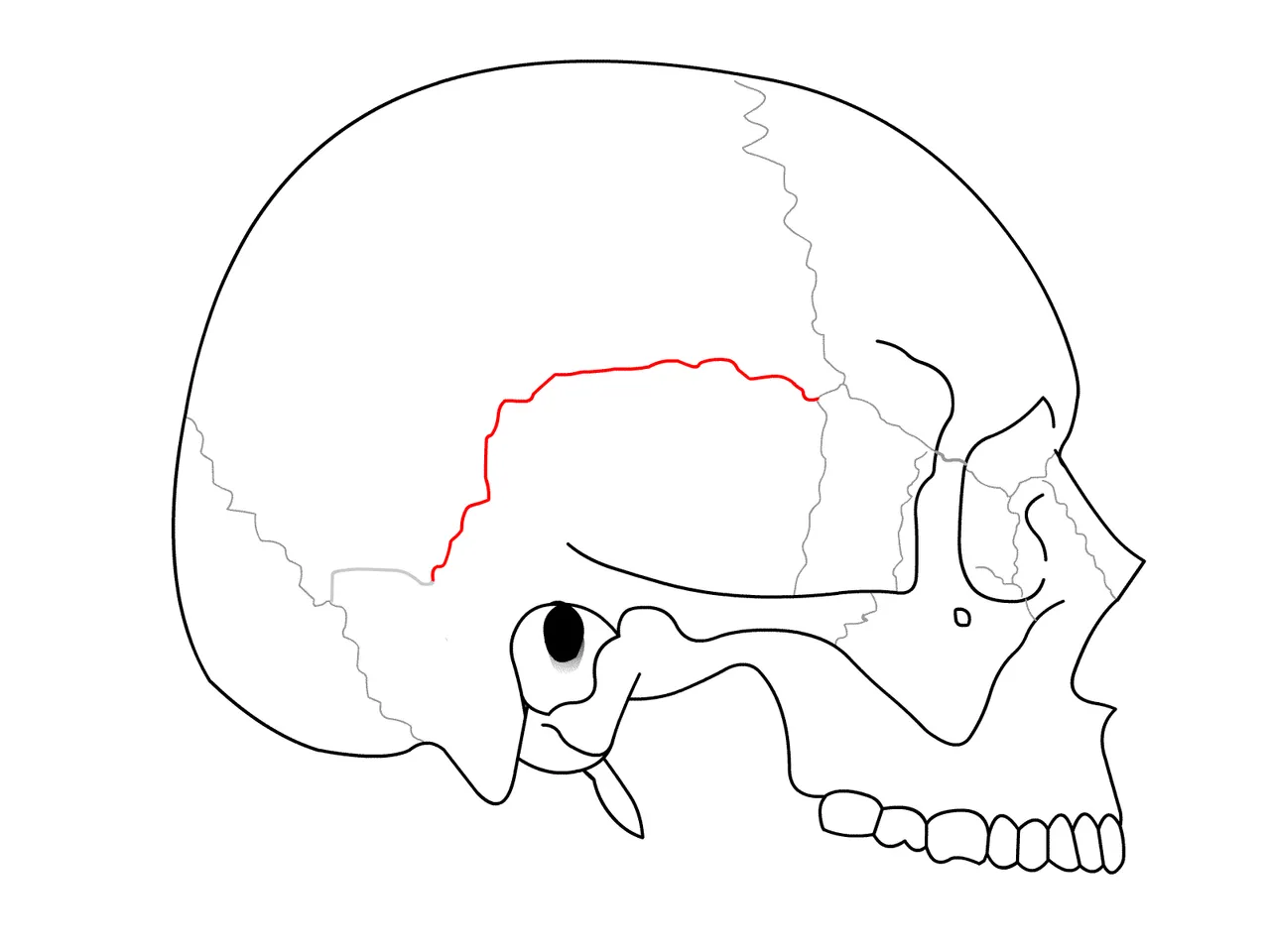
- SQUAMOUS SUTURES -
The end of one bone is overlapping with another bone and joined by fibrous tissue.
Example - Temporoparietal suture
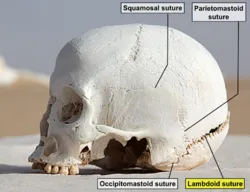
- DENTATE SUTURE -
The end of one bone has dentations and the other bone fot into those dentations.so it is the strongest suture.
Example - Lambdoid suture
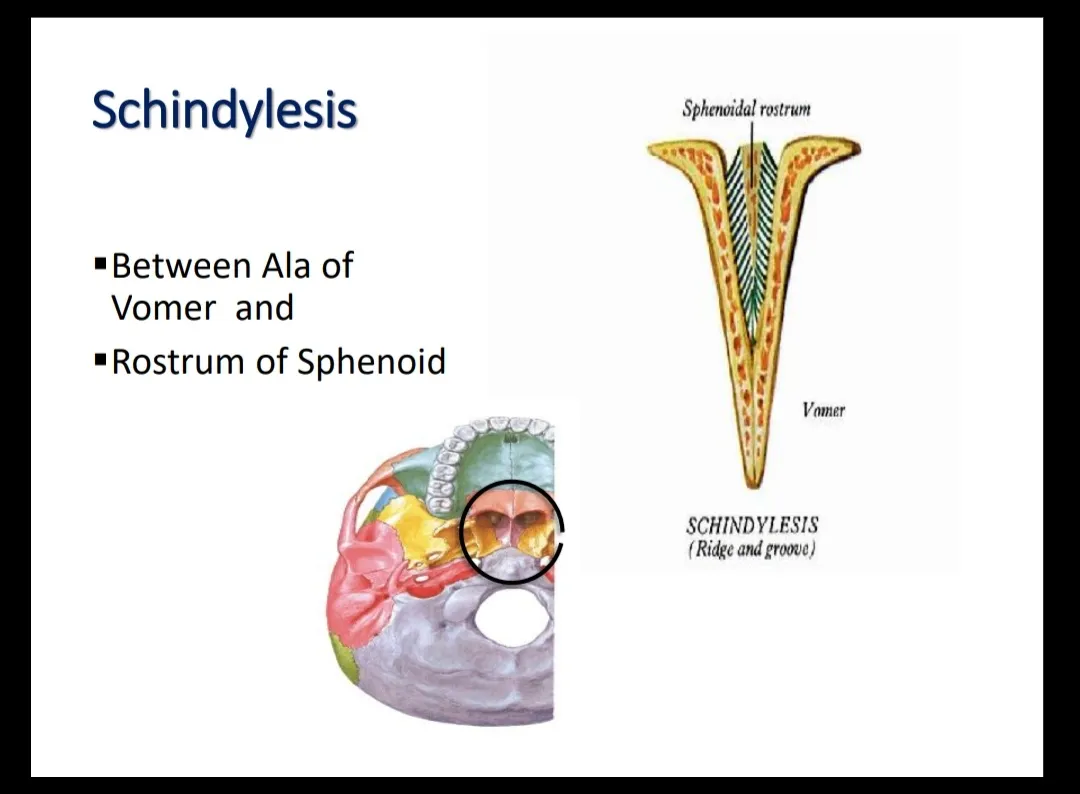
- SCHINDYLESIS(RIDGE & GROOVE) -
The rostrum of the sphenoid bone fits into the alae of the vomer.
See in the image and you will understand.
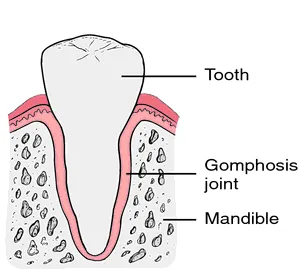
2)GOMPHOSIS
It is also called Dento-alveolar joint
It is joint between the tooth and the socket.
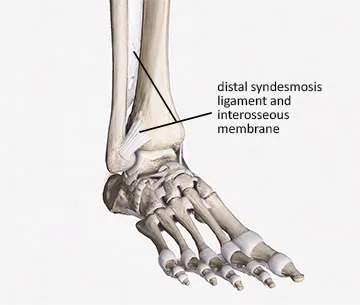
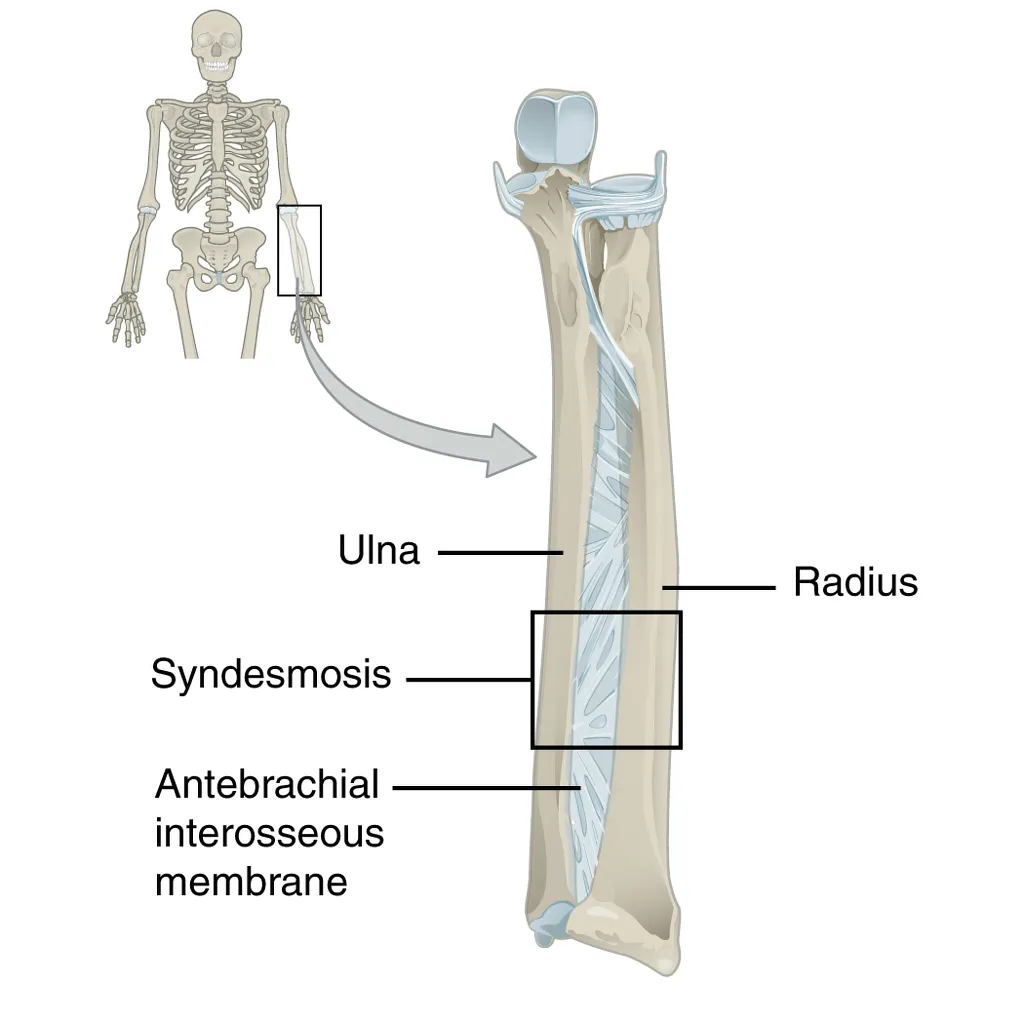
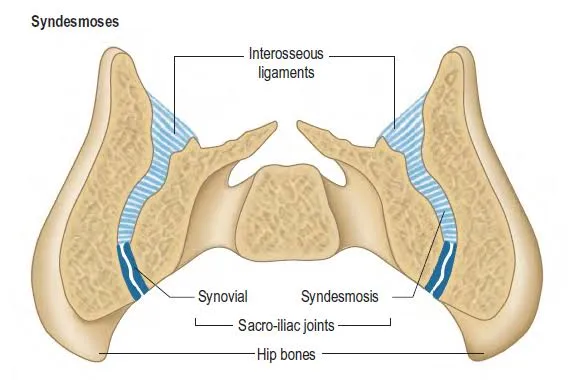
3)SYNDESMOSIS
In greek syndesmosis means "ligaments". The bones are connected by ligaments or strong membranes.
Examples - (a)The inferior tibiofibular joint is joined with a help of a membrane
(b) The middle radio-ulnar joint by the help of an interosseus membrane
(c)The sacroiliac joint
CARTILAGINOUS JOINT (AMPHIARTHROSES)
These are partially mobile joints and there are two types of it.
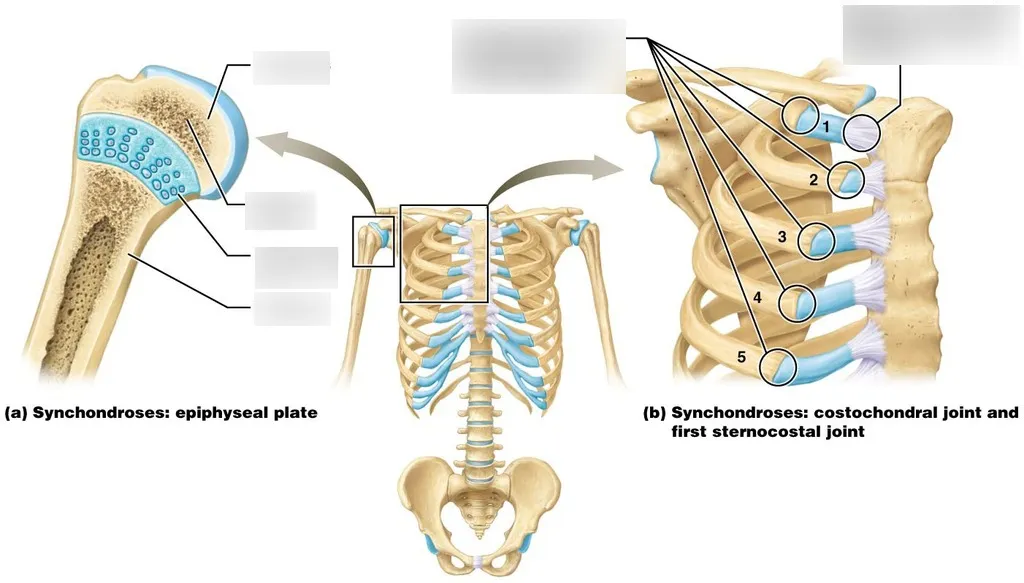
1.PRIMARY CARTILAGINOUS JOINT/SYNCHONDROSIS
The are joined in the middle with the help of a cartilage known as hyaline cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage has the property of ossification it means it gets ossified after certain age which later become a bone.Hence,it is a temporary joint.
so the synchondrosis becoming synostosis.
Examples - (a)The joint between epiphysis and diaphysis in long bones.
(b) All costochondral joints(joint between cartilage of ribs and ribs)
In the above image 1st chondrostenral joint(joint between manubrium and 1st costal cartilage) is given as example of synchondrosis(some books tells this).but,the first chondrosternal joint is an unusual variety of fibrous joint and not a plane synovial joint according to Gray's anatomy textbook.as grays anstomy is standard book we need to consider it.
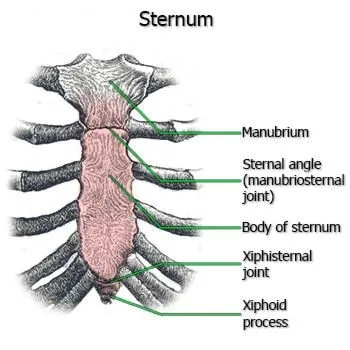
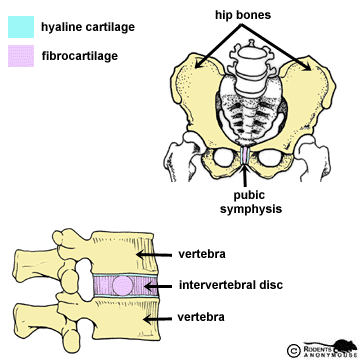
2.SECONDARY CARTILAGINOUS JOINT/SYMPHYSIS
The end of the bones are covered by hyaline cartilage & they in turn are attached by fibrous cartilage.
it is a permanent joint
Examples - All midline joints
(a) Manubriosternal joint
(b) Xiphisternal joint
(c) Intervertebral disc
(d) Pubic symphysis
Except symphysis menti which is a synostosis.even though it is midline joint it doesn'tcomes under secondary cartilaginous joints.
These joints are very important to pearm .especially for medical students as they come in exams.
For to read synovial joint -synovial joint
Thanks for reading,
With regards
REFERENCES -
- GRAY'S ANATOMY:THE ANATOMICAL BASICS OF CLINICAL PRACTICE,41st Edition Page number - 96,938 to 940