In my previous entry, I was speaking about how the ISS needs the cooperation of all the involved parties to continue operating. As we were talking about, the space station relies mostly in the Russian modules and the Russian Progress cargo spacecraft to lift the ISS and ensure it does not fall back to Earth in matter of months. But the idea of the station splitting up in two is not probable, because the Russian Orbital Segment relies on the US Orbital segment for power supply and control of the orientation.
In the moment of writing those lines, war had not broken out yet. After that happened, amid the whole train of sanctions that many nations are imposing on Russia, US President Joe Biden directly targeted the space program: "We estimate that we'll cut off more than half of Russia's high-tech imports. That will strike a blow to their ability to continue to modernize their military. It'll degrade their aerospace industry, including their space program,"
Roscosmos director (Russian Space Agency) has been proved to be quite vocal in twitter in the past, and has used the platform for the informational war. And we have been able to read a direct threat to the ISS indicating that Russia is safe from an uncontrolled reentry of the ISS from orbit.
In the last weeks, we have been reading the plans to deorbit the ISS in 2030, the objective is to force a controlled reentry into Point Nemo, the most isolated point in the Pacific Ocean. Because we need to set this clear: this 420 tons spacecraft, of the size of a football field, would not burn completely in the atmosphere and will hit the ground. Rogozin new statement is clear: Russia is safe from the reentry path, but neither Europe or the US are, and also other powers like India or China would not be happy with the risk of the spacecraft falling over their territory.
Which are the alternatives? This February of 2022, a Cygnus cargo spacecraft has arrived to the ISS. This is a resupply mission, manufactured by the American company Orbital Sciences. And coincidentally, this spacecraft that has arrived is the first of its type ready to provide re-boost capabilities for the ISS.
As a less clear alternative, Elon Musk has tweeted about the possibility of SpaceX coming to the rescue. But no more information is available about the specifics. Probably their plan passes through trying to use some derivative of the Dragon spacecraft.

Soyuz Booster Rocket. Source: Public Domain
A very big (geopolitical and technical) deal: transportation systems
We were talking that the Cygnus resupply spacecraft could be a solution, right? Maybe it is not that easy. It is launched using the Northrop Grumman Antares rocket, which first stage is manufactured in Ukraine by Yuzhnoye State Design Office and Yuzhmash Machine Building, using RD-181 rocket engines manufactured by Russia’s NPO Energomash. Some American launchers have been heavy relying on the RD-180 and RD-181 engines, and partially the need to cut its dependency is behind the Rocket engine development race we are seeing in the present.
Truth is, space transportation (going to space, e.g. Rockets) is relying heavily in the Russian industry. Soyuz rockets have over thousand successful launches with a very effective delivery to orbit. They have been typically launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, but in 2003 the European Space Agency started a cooperation with Roscosmos to launch from the European Spaceport in French Guiana. This was ensuring a new source of income to the Russian space industry, that could benefit from the attractive position of this launching place, only 5 degrees over the equator.
This Saturda, @lemouth was putting into the spotlight a link with some news indicating how, as a result of the European sanctions imposed to Russia, Roscosmos was suspending this cooperation. Using twitter again, Rogozin claimed: "In response to EU sanctions against our enterprises, Roscosmos is suspending cooperation with European partners in organizing space launches from the Kourou cosmodrome and withdrawing its technical personnel, including the consolidated launch crew, from French Guiana,"

Source: Twitter
Thierry Breton, European Commissioner in charge of the Space Programme, quickly came with an statement indicating the European capabilities to confront this situation. One of the main users of the Soyuz launchers from Kourou was the Galileo geolocation program (that we could call the European version of the GPS), and everything was ready for a new launch of two satellites in mid-2022. A new launcher will be most surely required. We cannot forget that when the Crimea crisis exploded, it already impacted some strategic launches. Radar imaging satellite PAZ was going to be launched using the Dnpr Rocket and in the end was launched by SpaceX after years of delay.
Other satellites of the European Earth Observation Programme Copernicus were launched in the past from Russia using the Rockot-M launcher (an intercontinental ballistic missile reconverted into launcher), but their baseline design allows them to use the European Vega launcher. However, Europe is in a complicated situation, because it loses a middle size launcher in between the Vega and the Ariane launcher and in a point in which their launcher families are in a transition, waiting for the maiden flight of Ariane-6 and Vega-C. The last launches of the previous members of the family are already scheduled. And they first flights of the new launchers are not likely going to be ready to fly in 2022.
Additionally, Russia was in conversations with NASA to be able to send Russian cosmonauts in the SpaceX Crew Dragons to the ISS. There is not new information regarding this topic, but maybe it will become difficult.
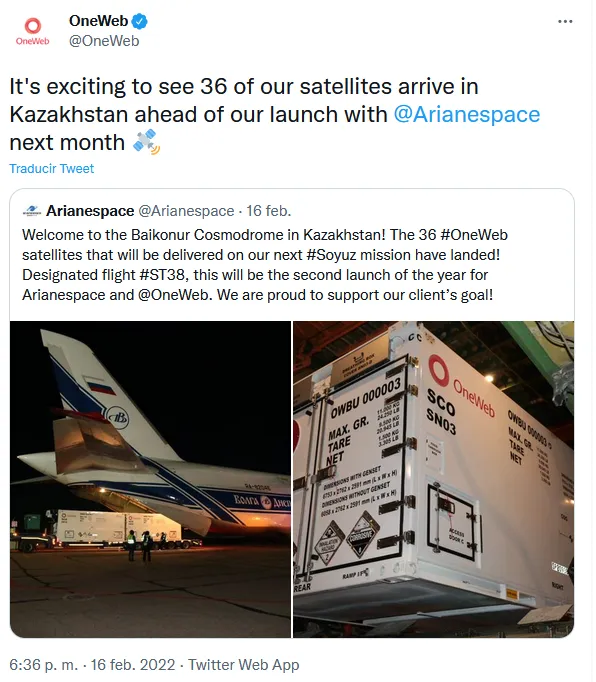
In a complicated situation is the UK based company OneWeb. In order to deploy their communications constellation, they are launching their satellites with the Soyuz family both from Kourou and Kazakhstan. The last of the badge of satellites arrived to Kazakhstan in February 2022 and situation is unclear right now.
Source: Twitter
How is the situation for other scientific missions?
In the beginning of last week, the cooperation in between Roscosmos and ESA for the Exomars 2022 mission looked still ongoing. Crews will have to travel to Kazakhstan in the short term for the integration of the spacecraft in the launchers. This mission aims to launch a European rover, that will descend in a Russian landing platform. Any problem would involve missing the launch window and having to postpone the launch for 26 months, probably situation is in a hot state and we will hear more in the incoming weeks. Euclid space telescope will probably suffer delays, it was going to be launched with a Russian launcher so next days would probably bring some updates.
The mission that has been openly cancelled ins the cooperation in between US and Roscosmos to launch Venera-D, a Venus exploration mission that continues the Venera soviet missions that opened the interplanetary exploration era. However, it looks like there has been little progress in the last years towards the success of the mission.
Last remarks
Situation is unclear right now. We will have to wait to see how the situation evolves. One thing is clear, the space industry is quite interconnected and Russia remains an important actor, mostly in Space transportation. It was not surprising how this month we saw some tentative projects to try to develop a European system to launch their own astronauts to orbit and we will continue observing the trend to invest in rocket launcher start-ups.
A very last surprising point. All this conversations, all this declarations, are happening in Twitter, which looks like it has become the most extended way to communicate (or to participate in the public debate). What do you think about a centralized social network becoming the pre-defined communications technology, at least in the so-called Western countries?
