By FatM1ke , Public Domain, Wikimedia
Historically, obesity was taken to be a disease of the developed nations. But currently, the narration has changed and there is a rapid upsurge in the incidence of obesity in developing and underdeveloped countries.
In some parts of African regions, obesity was seen as a sign of affluence and evidence of good living. This is seen in some cultures where 'fatting room' is practiced. In this practice, a woman in her pre-conceptive period is put in a room called the fatting room. There only what she does is eat whatever she wants, sleep, and eat again. There, she is not allowed to do anything till the period is over.
It is believed that after the fatting period, she will look robust enough for her husband and will also be physically ready for childbearing. This practice has predisposed many women to obesity. With increased awareness and a better understanding of the negative effects of obesity, this practice is gradually phasing out, however, it is still practiced in some communities to date.
Obesity is a disease condition just like every other disease and has been renamed as Adiposity Based Chronic Disease (ABCD). This disease is a state of malnutrition that exists on the other end of the malnutrition spectrum. Malnutrition has two ends; undernutrition and overnutrition (obesity). Obesity is currently the most prevalent form of malnutrition.
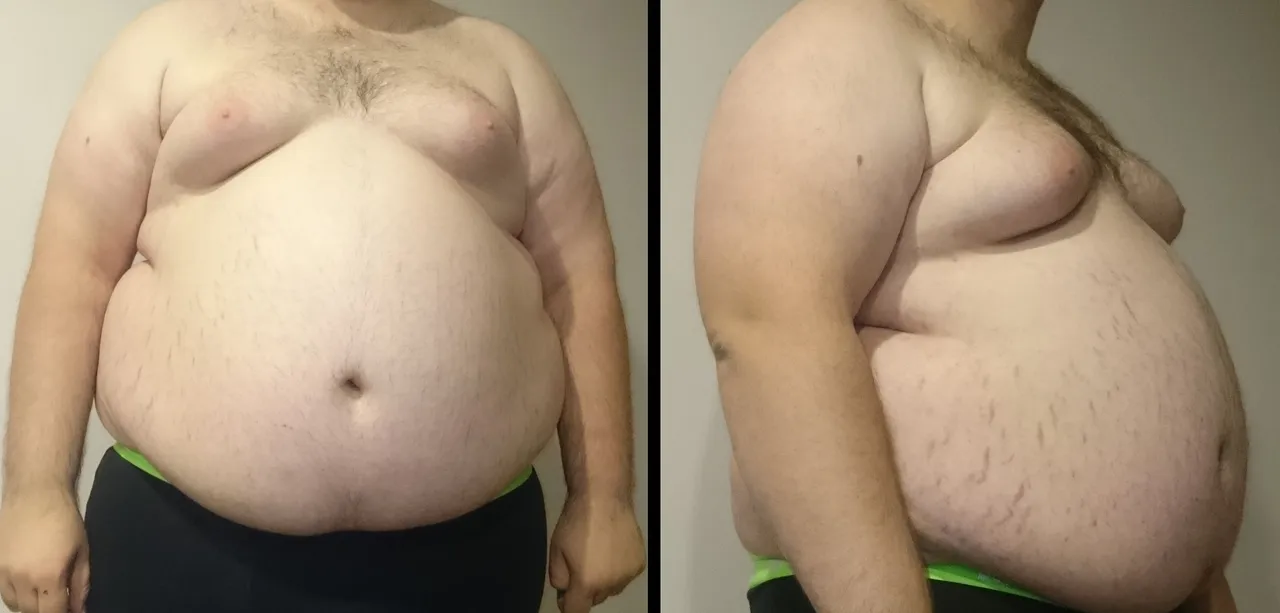
Obesity occurs as a result of an imbalance between calorie intake and calorie utilization. When people consume diets rich in fats and sugars, without a commiserate expenditure of these calories, it results in the state of an excessive storage of body fats which poses a danger to health.

By Kgbo - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
This pathophysiology of obesity explains why the incidence of obesity is highly on the increase in the developing and underdeveloped world at the moment. The shift to high fats and calorie diets, fast foods, etc as well as an increase in sedentary lifestyles, and office jobs, without physical activity, is the major driver of obesity in the African region.
In our traditional African dietary pattern which is predominantly whole grains, tubers, fruits, and vegetables as well as increased physical activities through farming, trading, and other social activities, people consumed fewer fats and also had various means of burning the fats and calories through physical activities.
With increasing urbanization, we migrated to western dietary patterns and a sedentary lifestyle. Now people move from air-conditioned houses to air-conditioned cars to air-conditioned offices and back to the air-conditioned house again and the cycle continues. No means of burning calories.
Genetics is also a very important factor in the etiology of obesity. Obesity is usually seen in families, however, genetics only loads the gun, while the environment pulls the trigger. The environment here is the increased consumption of energy-dense, high-fat, and high calories food as well as a lack of physical activities (sedentary lifestyle).
Certain hormonal disorders, medications, and psychological factors have also been implicated in the etiology of obesity.

By Australian Human Rights Commission from Sydney, Australia - 171208_0895, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia
OBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT OF OBESITY
Obesity is assessed with a simple tool called the body mass index. It is the measure of the weight to the height of the individual and the values can either classify one as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
The body mass index (BMI) is calculated by dividing the body's weight by the square of the height. A value of 18 - 24.9 kg/m² is regarded as the normal weight. A value of 25 - 29.9 kg/m² is overweight while from 30 - 39.9 kg/m² is regarded as obesity. Above 40 kg/m² is morbid obesity.
THE BURDEN OF OBESITY
Obesity was declared a pandemic by the WHO (1995) due to its rapidly increasing prevalence.
In 2013, the American Medical Association classified obesity as a disease. Obesity is the 5th leading global risk for mortality and 2.8 million people die each year as a result of being overweight or obese.
EFFECTS / COMPLICATIONS OF OBESITY
Cardiovascular diseases;
Obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases like hypertension, coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmia, thromboembolism, etc.
Endocrine disorders;
Many endocrine disorders like type 2 diabetes mellitus, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, dyslipidemia, etc have been associated with obesity.
Malignancies;
Obesity is a major risk factor for many cancers like prostate cancer, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, etc.
Other systems;
Virtually all the systems of the body are affected by obesity. Obesity is also tightly associated with diseases like stroke, obstructive sleep apnea, osteoarthritis, stress incontinence, GERD, cholelithiasis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, acanthosis nigricans, dementia, etc.
Psychological effects;
Obesity is also associated with psychological effects like low self-esteem, social stigmatization and depression.
From the above discussion, it can be seen that the effects of obesity are enormous and obesity is the bedrock of many diseases. So it is very important to prevent this disease from occurring and to manage it properly when it occurs. So, let's talk about the management and prevention of obesity.
MANAGEMENT OF OBESITY
Treatment of Obesity starts with lifestyle modifications which include dietary modification and exercise. There are various diets and eating habits targeted to reduce weight and avoid weight regain. Goal setting and self-monitoring of progress are important. Many diets have been used to manage obesity, including the ketogenic diet. However, the ideal diet for managing obesity is still a subject of debate.

By The U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Public Domain, Wikimedia
Exercise and physical activities are also very important tools in maintaining a healthy weight and preventing weight gain. A combination of behavioral modification and physical activities is always the first and best approach in the management of obesity.
However, for those who fail to achieve weight loss after 3 months of exercise and dietary modification, medications can be used. Drugs like lorcaserin, orlistat, phentermine, etc can be used.
When medical therapy fails, surgery can also be an effective treatment option. Some of the available surgical options are gastric bypass, vertical sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric band, and liposuction.
PREVENTION OF OBESITY
The effects and complications of obesity are enormous. Therefore, we must make conscious efforts to prevent obesity. Some of the preventive measures include;
Education and awareness on the causes of obesity, the effects and prevention.
Increased physical activities and aerobic exercises like walking, running, gardening, cycling, dancing, etc, including physical activities in schools.
Limiting the consumption of high-fat and calorie diets and increasing the consumption of fruits, vegetables, and adequate intake of clean water.
Policies to regulate the consumption of high calories foods and sugar-sweetened beverages. Some of these policies include moderating the sales of these beverages in places like schools and banks, imposing heavy taxes on them, and regulating their sugar and calorie contents.
Corporate organizations should also formulate policies to enable their workers to engage in regular exercises and physical activities.
Individuals should also check their body mass index (BMI) regularly to know when they are gaining weight and to commence behavioral modifications and exercise immediately.

By Dolphyb - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
In summary, Obesity is a disease that is currently on a rapid rise globally. Though the incidence was previously low in sub-Saharan Africa, westernization and change in dietary patterns from traditional African dietary patterns to the western dietary pattern as well as reduced physical activities has led to a rise in the incidence of obesity in this region.
Obesity affects all systems of the body and is the bedrock of many other diseases. Therefore, all hands must be on deck to maintain a healthy weight at all times. Obesity is very preventable and involves the government, communities, and individual efforts to curb this rising pandemic.
Thanks so much for reading.
For references and further reading, please check: