Theory
Moving averages are used as a basis for many technical indicators. A moving average is a sort of local average around a given point. In signal processing terms the moving average acts as a lowpass filter, removing high frequency "noise" from the signal.
Implementation
The signal parameter is a one dimensional array. It makes sense to use the typical price as this input.
import numpy as npdef simple_moving_average(signal, points): """ Calculate the N-point simple moving average of a signal Inputs: signal: numpy array - A sequence of price points in time points: int - The size of the moving average Outputs: moving_average: numpy array - The moving average at each point in the signal """ moving_average = np.zeros(len(signal)) for i in range(points): moving_average[i] = np.sum(signal[0:i + 1])/(i+1) for i in range(points, len(signal)): moving_average[i] = np.sum(signal[i + 1 - points:i + 1])/(points) return moving_averageResults
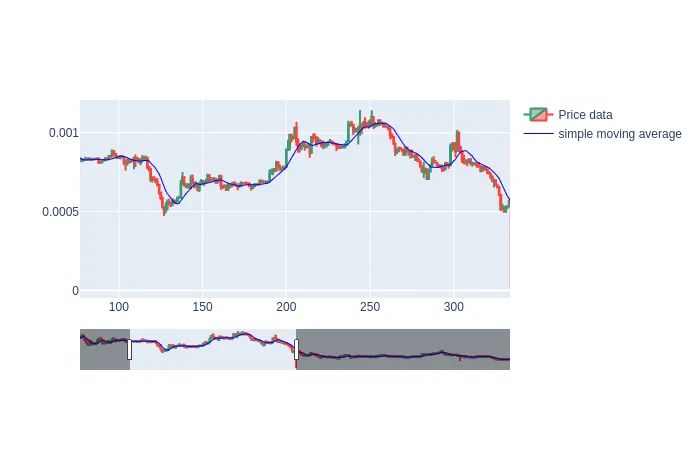
Comparing the simple moving average to the typical price reveals the behaviour of the SMA: it is smoother than the typical price signal and it lags behind the typical price signal.
It is also worth comparing moving averages of different periods:
Note that the 20 point moving average is smoother than the 10 point moving average and lags even further behind the typical price.
