~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
23-05-2024 - Principles of economy (3/10) [EN]-[IT]
Human capital
formula for the change in human capital
The formula for calculating the change in human capital is shown below.
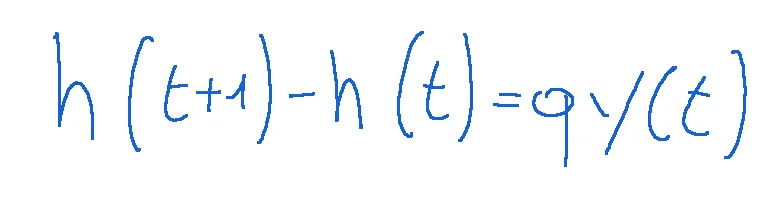
Where h is human capital
Where q is the part of s allocated to investment in human capital
Investing in human capital means investing in training, new younger workers, new workers with more education, etc...etc...
Technical progress
Formula of technical progress
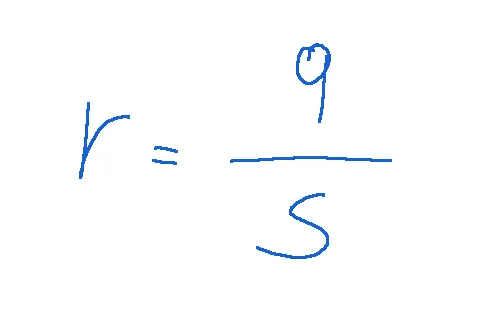
The role of progress
If we refer to the Solow model of endogenous growth we can understand that long-term growth can be generated by technical progress based on the role of human capital.
endogenous growth formula
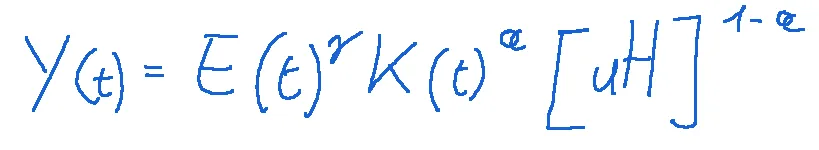
Where:
Y(t) is the total production
E(t)γ is technical progress
μ is the fraction of human capital allocated to the production of goods and services
Long-term growth is given by technical progress and therefore by the development of
new products, new services, new machinery, new production processes and new business models.
Isoquants and isocosts
If the isoquants tell us how we can combine production factors and their replacement.
Isocosts, on the other hand, tell us how much the production factors cost us depending on their combination (a sort of constraint of
corporate balance sheet).
We can say that the isoquant is the set of different combinations of production factors that allow the same quantity of total production to be produced.
We can say that an isocost is the set of combinations of two production factors that determine the same overall production cost
Minimum cost
By combining the isoquant and isocost curves we can determine the least cost equilibrium.
The minimum cost condition is given by the point of tangency between the isoquant curve and the isocost line
Company decisions
Profit Maximization
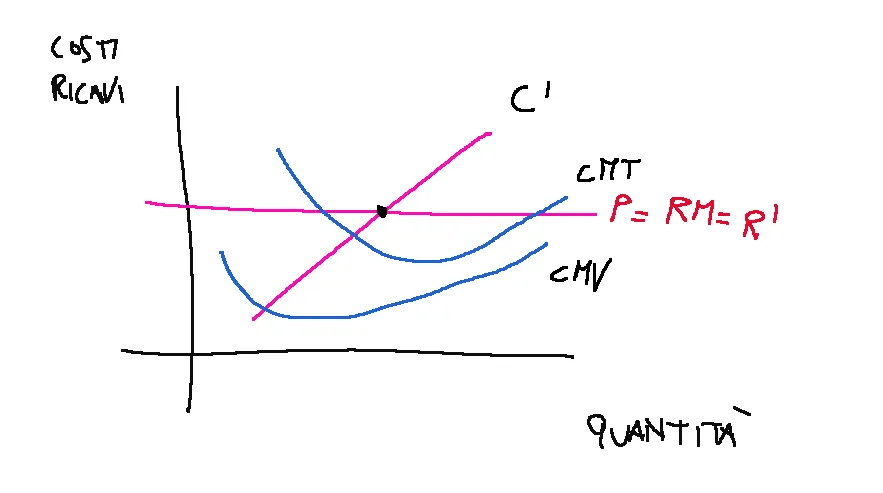
The main objective of a business is profit maximization.
Profit maximization is given by the equality between marginal cost and marginal revenue. So in a free competition market this means profit maximization is where P=RM=R' meet C'.
Where:
P = Price
RM = average revenue
R' = marginal revenue
C' = marginal cost
Business difficulty
An important moment for the company is when it is not able to maximize profit, indeed it is affected by general market conditions or when its product and therefore market is now mature or at the end of its cycle. Then the first losses appear.
In the event of temporary closure, the company will have to take fixed costs into account.
In the case of permanent closure then you will be able to eliminate costs and sell everything.
Another event to consider when a company is in difficulty is suspension. Logic suggests that the company should stop production if variable costs are higher than revenue,
The closure of a company involves its exit from the market. By exiting the market, the company, as in the case of temporary suspension, will not be able to sell its products and therefore will not have any revenue.
This time, however, the company will not bear both variable and fixed costs.
Profit measurement
Profit is total revenue minus total cost.
Conclusions
In conclusion, long-term growth, according to the Solow model, is given by endogenous growth based on the fact that a country or a company invests in R&D.
It must be understood that beyond a certain level the increase in human capital or physical capital is not sufficient, technical progress is needed to guarantee a future for a company.
Request
How important do you think it is for a company to invest in the training of its employees?

ITALIAN
23-05-2024 - Principles of economy (3/10) [EN]-[IT]
Il capitale umano
formula della variazione del capitale umano
Qui di seguito è mostrata la formula per calcolare la variazione del capitale umano.
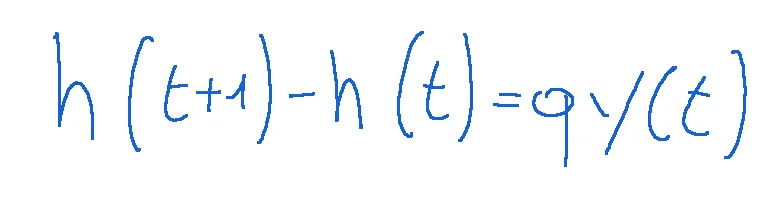
Dove h è il capitale umano
Dove q è la parte di s destinata all’investimento in capitale umano
Investire nel capitale umano significa investire in formazione, nuovi lavoratori più giovani, nuovi lavoratori più scolarizzati, ecc...ecc...
Il progresso tecnico
Formula del progresso tecnico
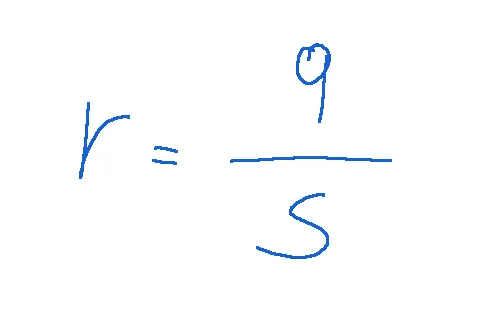
Il ruolo del progresso
Se facciamo riferimento al modello Solow della crescita endogena possiamo comprendere che la crescita di lungo periodo può essere generata dal progresso tecnico basato sul ruolo del capitale umano.
formula della crescita endogena
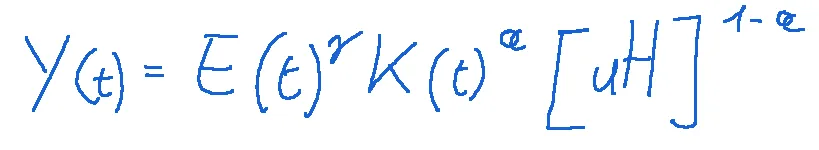
Dove:
Y(t) è la produzione totale
E(t)γ è il progresso tecnico
μ è la frazione di capitale umano destinata alla produzione di beni e servizi
La crescita di lungo periodo è data dal progresso tecnico e quindi dallo sviluppo di
nuovi prodotti, Nuovi servizi, Nuovi macchinari, Nuovi processi produttivi e Nuovi modelli di business.
Isoquanti e isocosti
Se gli isoquanti ci indicano come possiamo combinare i fattori produttivi e la loro sostituzione.
Gli isocosti ci indicano invece quanto ci costano i fattori produttivi a seconda della loro combinazione (una sorta di vincolo di
bilancio delle imprese).
Possiamo dire che l'isoquanto è l'insieme delle diverse combinazioni dei fattori produttivi che consentono di produrre la stessa quantità di produzione totale.
Possiamo dire che un isocosto è l'insieme delle combinazioni di due fattori produttivi che determinano lo stesso costo di produzione complessivo
Minimo costo
Combinando le curve di isoquanti e isocosti possiamo determinare l'equilibrio di minimo costo.
La condizione di minimo costo è data dal punto di tangenza tra la curva di isoquanto e la retta di isocosto
Decisioni impresa
Massimizzazione del profitto
L'obiettivo principale di un impresa è la massimizzazione del profitto.
La massimizzazione del profitto è data dall’eguaglianza tra costo marginale e ricavo marginale. Quindi in un mercato di libera concorrenza questo significa la massimizzazione del profitto è dove P=RM=R’ incontrano C’.
Dove:
P = Prezzo
RM = ricavo medio
R’ = ricavo marginale
C’ = costo marginale

Difficoltà d'impresa
Un momento importante per l’impresa è quando essa non è in grado di massimizzare il profitto, anzi risenta delle condizioni generali del mercato oppure che il proprio prodotto e quindi mercato è ormai maturo o a fine ciclo. Quindi si manifestano le prime perdite.
In caso di chiusura temporanea, l’impresa dovrà tenere conto dei costi fissi.
Nel caso di chiusura definitiva allora sarà in grado di azzerare i costi e vendere tutto.
Altro evento da considerare quando un'impresa è in difficoltà è la sospensione. La logica suggerisce che l’impresa dovrebbe interrompere la produzione nel caso in cui i costi variabili siano superiori al ricavo,
La chiusura di un'impresa prevede l'uscita di questa dal mercato. Uscendo dal mercato, l’impresa così come nel caso di temporanea sospensione, non potrà vendere i propri prodotti e quindi non avrà alcun ricavo.
Questa volta però l’impresa non sosterrà sia i costi variabili e sia i costi fissi.
Misurazione del profitto
Il profitto è il ricavo totale meno il costo totale.
Conclusioni
In conclusione, la crescita di lungo periodo, secondo il modello Solow, è data dalla crescita endogena basata sul fatto che un paese o un’impresa investe in R&S.
Bisogna capire che oltre un certo livello l’aumento di capitale umano o di capitale fisico non è sufficiente, ci vuole appunto un progresso tecnico per garantire un futuro ad un'impresa.
Domanda
Quanto pensiate sia importante per un'impresa investire nella formazione dei propri dipendenti?
THE END
