The relationship between delinquency rates on credit card loans, the economy's status, and interest rates is multifaceted and influenced by various factors.
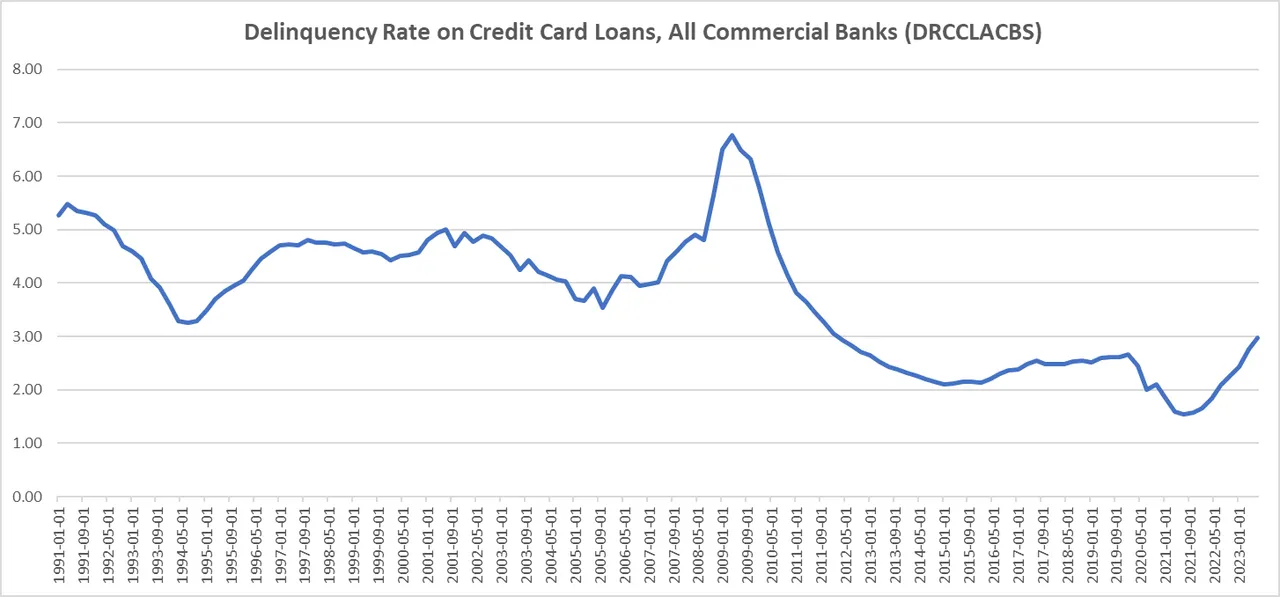
Economic Status and Credit Card Delinquency Rates
During recessions, job losses often lead to an increase in credit card delinquencies as people may reduce or stop payments on credit card debt due to reduced income.
Credit card delinquency rates were notably high during the global financial crisis, primarily due to increased job losses.
Economic conditions in specific areas also play a role. Areas with weaker economic conditions tend to have higher delinquency rates and larger declines in consumption.
The COVID-19 recession saw an unusual trend where, despite economic challenges, delinquency rates remained low due to forbearance programs, restrained spending during lockdowns, and government benefits.
Impact of Interest Rates on Credit Card Delinquencies
Rising interest rates, along with high inflation, have been putting pressure on consumer financing. However, the credit card market and consumer spending have been resilient despite these challenges.
Despite the pressures of rising interest rates, delinquency rates have remained low by historical standards, suggesting that consumers have been effectively managing their finances even in a period of increasing prices.
The yield on credit card portfolios for major issuers increased in 2022, indicating a response to the rising interest rates.
Broader Considerations
The relationship between these factors is complex and can vary based on other economic conditions, such as inflation, consumer confidence, and overall economic growth.
The historical context is essential; for example, different trends were observed during the global financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic.
While economic downturns and higher interest rates generally lead to increased credit card delinquency rates, the actual impact can vary based on a range of factors, including government interventions, consumer behavior changes, and broader economic conditions.
