Author: Dr. Yu Tang
Dr. Yu Tang, from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Research Area: Network security, block chain technology, cryptography
Since the publication of the EOS’s whitepaper, as a pop star of encryption currency circle, it has got the attention from many aspects. The supporters constantly recharge faith into it, expecting it to be the unicorn of blockchain’s forerunners, at the meantime, criticism of critics is also invariably heard. The characteristic of 21 super-nodes receives a mixed reaction all the time, But I think the design of “21 super nodes” is exactly the prudent decision EOS team made after they got thorough comprehension of blockchain technology.
Is EOS a “fake blockchain”?
If we need appraise the blockchain technology of EOS, first of all, we need an accurate definition of it. We would separately adapt the definition from The whitepaper of blockchain technology and application development which published by MIIT 2016, as well as the description of blockchain from the academic paper published by IBM 2018 Hyperledger Fabric:A Distributed Operating System for Permissioned Blockchains to explain if EOS possess the technical features of blockchain. From the definition of The white paper of block chain technology and application development,narrowly speaking, Blockchain is a kind of linked data structure combined by the data block according to the time sequence, and it is also a temper-resistant, unforgeable distributed ledgers ensured in encryption way. Generally speaking, Blockchain technology is a brand new distributed infrastructure and computing paradigm that is using block chain to verify and store data, using distributed node consensus algorithm to generate and update data, using cryptology to ensure data transmission and safety of visiting, and using intelligent contract consist of automated script codes to programme and control data. In EOS, users could sign the transaction and broadcast to super nodes, then super nodes will get received transaction verified,packed and consented, to from a temper-resistant, unforgeable distributed ledger on which could run automated scripts. The whole process still equipped with block chain data structure, distributed node consensus algorithm, transaction protected by cryptology and intelligent contract. Therefore, EOS with many technical features of block chain could be defined as block chain.
IBM defined block chain in this way “A blockchain can be defined as an immutable ledger for recording transactions, maintained within a distributed network of mutually untrusting peers. Every peer maintains a copy of the ledger. The peers execute a consensus protocol to validate transactions, group them into blocks, and build a hash chain over the blocks. This process forms the ledger by ordering the transactions, as is necessary for consistency.” Compare to the definition of block chain given by MIIT, the description of IBM specially emphasized on “untrusting peers”. Indeed, the usage scenario of block chain must reach a consensus among a group of untrusting nodes, this is also the most conspicuous advantage compare to traditional distributed data base. In EOS, the super nodes are voted by the people who own EOS coin, the voted nodes would maximize the dividend of the voters, therefore, after the super nodes reached a consensus in an untrusting environment, then trust would be passed through all the nodes in the whole network.
In summary, regardless of the blockchain definition given by domestic authoritative organizations, or well-known foreign companies, EOS is an unconditional blockchain project.
1.Is EOS “decentralized”?
Since the inception of bitcoin, decentralization is the most important feature of Blockchain. It can’t be denied that Bitcoin and Ethereum are the two largest block chain projects, its successful operation make people really appreciate the charm of decentralization. Currently, the degree of decentralization of each blockchain project often targets the two projects. But Adem Efe Gencer team from Cornell University recently carried out scientific measurement and rigorous analysis to the degree of decentralization of these two projects. According to their measurement, they found out that Over 50% of the mining power has exclusively been shared by eight miners in Bitcoin and five miners in Ethereum throughout the observed period. Even 90% of the mining power seems to be controlled by only 16 miners in Bitcoin and only 11 miners in Ethereum. . Hence, both platforms rely heavily on very few distinct mining entities to maintain the blockchain. In other words, the authority of production is a consensus reached among the untrusting nodes in a small scale.
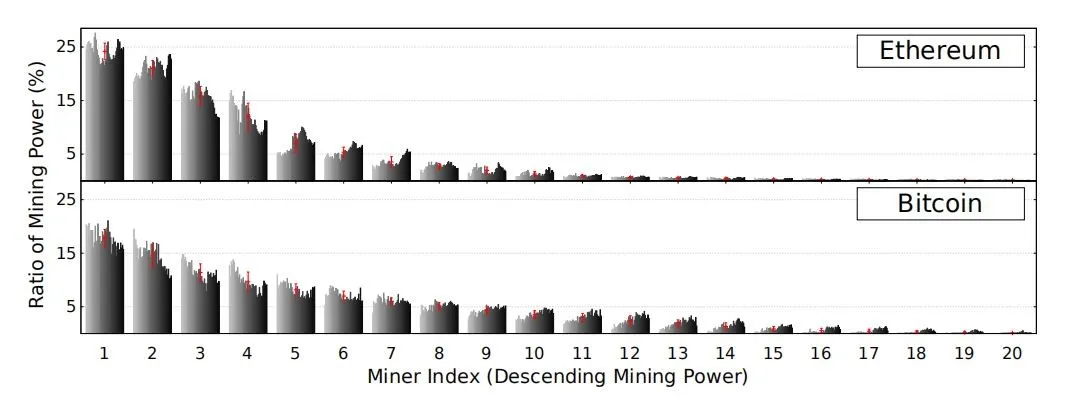
•By matching the mining rights ratio and the number of miners, we could get the exponential distribution of bitcoin’s and Ethereum’s Mining capacity trend which are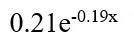 and
and 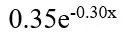 respectively.These results show that a Byzantine quorum system of size 20 could achieve better decentralization than proof-of-work mining at a much lower resource cost.
respectively.These results show that a Byzantine quorum system of size 20 could achieve better decentralization than proof-of-work mining at a much lower resource cost.
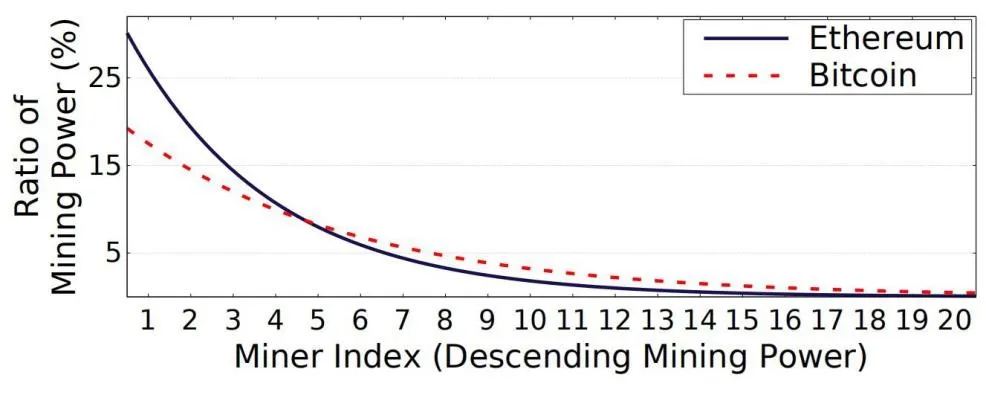
Therefore, the major consensus tasks of bitcoin and Ethereum concentrate on few key nodes, the essence of POW algorithm is to select the producers through workload, if a large amount of resources got consumed during the selection process, the consensus process would be inefficient. In order to concentrate all the resource into the consensus task, the selection of key nodes need to be replaced by low-energy algorithm. DPoS-BFT consensus algorithm in EOS conducted election and voted 21 super nodes with production authority, and then introduce Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism among the super nodes, then allocate the resources to super nodes to conduct high-efficient consensus to reach a high handling system. (In DPoS, only when it’s turn for each super node to produce, it could be considered as the confirmation to the previous block. In this way, the transaction confirmation time would be 45 seconds long. By introducing BFT mechanism, after each super node produced, it needs broadcast to other super nodes, the block could finish confirmation after received 2/3 super nodes confirmation info, this progress could significantly shorten the block confirmation time. )
In summary, the selection of 21 super nodes by EOS is not only a conflict of “decentralization” but an optimal balance between decentralization and high-efficiency consensus.
To answer which is a better blockchain architecture, first of all, a reasonable evaluation system, we can have intuitive judgments of the merits within the same evaluation system, and we can only say which is better in the evaluation system. Since blockchain technology is an emerging technology, there is no mature evaluation system in the industry. Therefore, this paper uses the CAP principles in traditional distributed storage systems to analyze EOS, BTC, and ETH.
CAP principle means in a distributed system, there cannot have Consistency、Availability、Partition tolerance at the same time.
Consistency(C) : Back up all the data in the distributed system to see if they have same value at the same time.
Availability(A): After a group of nodes in the cluster failed, whether the entire cluster still respond to clients’ read-write request.
Partition tolerance(P): In practical terms, partition is like the time limit of communication. If the system can’t reach data consistency during the time limit, it means there’s a partition, and we have to make choice between C and A.
In block chain system, we interpret “consistency” as anti-bifurcation capability, “Availability” as tolerance to the fault node, “Partition tolerance” is considering as block intervals (to reach availability, we have to give up strong consistency and pursue final consistency) Regarding to “consistency”, the Bitcoin based on PoW algorithm is to choose the longest link to add new blocks, so it’s hard to resist the bifurcation attack caused by “selfish mining”. Based on GHOST protocol, ETH adds new blocks by choosing the link consists the most subtrees, though this progress could enhance the produce speed, but it still cannot escape from the spell of 51% attack. While EOS uses DPoS-BFT algorithm, the authority of production could be owned in turn by the sequence of negotiation among 21 super nodes (Producing the blocks alternatively in the negotiated sequence could optimize the block-losing problem caused by random network delay).Even if there are 7 malicious super nodes, it is difficult to cause the bifurcation of the main chain. These three distributed systems all satisfied the feature “Availability”. At last, about “Partition tolerance”, Each block of Bitcoin is about 10 minutes produced, each block of Ethereum is about 15 seconds produced, and each block of EOS is about 0.5 seconds produced. So, from the above aspects, EOS is indeed a better block chain framework than bitcoin and ETH by using CAP principle to analyze.
Reference:
【1】中国工信部. 中国区块链技术和应用发展白皮书. 2016
【2】IBM. Hyperledger Fabric:A Distributed Operating System for Permissioned Blockchains. 2018
【3】block.one . EOS.IO技术白皮书. 2017
【4】Block.one. EOS.IO Dawn 2.0. 2017
【5】Adem Efe Gencer. Decentralization in Bitcoin and Ethereum Networks. 2018
【6】Nancy Lynch. Brewer's conjecture and the feasibility of consistent, available, partition-tolerant web services. 2002
【7】Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008
EOS地址:0x82a358c08575e2e77ee0adefc77ad2c9fc4447cc
