Benign tumors develop when the body's cells begin to divide and grow at an excessive rate. Treatment is not always necessary, such as the treatment of malignancies, because it is non-cancerous growth in the body. Unlike cancerous tumors, benign tumors do not spread to other parts of the body.
The benign tumors can be made up anywhere. If you discover a lump or lump in your body you can see from the outside, you may immediately assume that it is cancerous. For example, women who find lumps in the breast during self-examination often feel panic. However, most breast tumors are benign, and in fact many tumors around the body are benign.
Causes of benign tumors.
The exact cause of benign tumors is often unknown. It develops when cells begin to divide and grow at an excessive rate, and the body is usually able to balance cell growth and division. Old or damaged cells die, and are replaced by new and healthy cells. In the case of tumors, the dead cells remain and form a tumor known as the tumor.
Cancer cells grow in the same way. However, unlike cells in benign tumors, cancer cells can invade neighboring tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Types of benign tumors.
There are a lot of benign tumors that can develop in different parts of the body. Benign tumors are classified in terms of growth. These are different types of benign tumors below:
Tumors form in a thin layer of tissue that covers the glands, organs, and internal structures of the body, such as benign tumors that form in the colon or tumors in the liver.
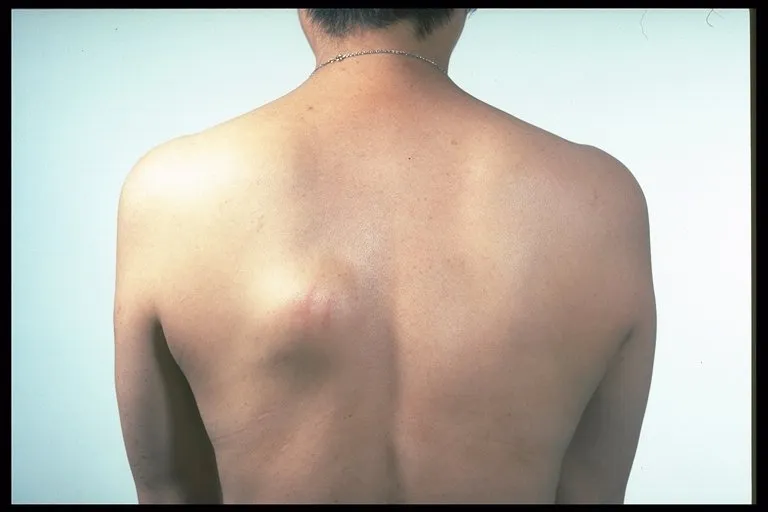
Lipid tumors that grow in fat cells are the most common type of benign tumors, often found on the back, arms, or neck, and are usually soft and round, and can be moved slightly under the skin.
Myomas tumors are in the muscles or in the walls of blood vessels, as they can grow in smooth muscles, such as those that exist inside organs such as the uterus or stomach.
Moles are also known to be non-cancerous growths in the skin and are very common.
Fibroids can grow in the fibrous tissue of any organ, the most common type being in the uterus, where uterine fibroids are known.
In many cases benign tumors are carefully monitored, such as moles or benign tumors in the colon and pancreas, and can be transformed into cancer later.
Some types of internal benign tumors may cause other problems, such as fibroids in the womb can cause pelvic pain and abnormal bleeding. Some internal tumors may restrict a blood vessel or cause pain by squeezing the nerve.
Anyone can show up with benign tumors, including children, although adults are more likely to develop with age.
Symptoms of benign tumors.
Not all cancerous or benign tumors have symptoms. Depending on the location of the tumor it can affect the function of important organs or senses. For example if you have a benign brain tumor, you may suffer from headaches, vision problems, or poor memory.
If the tumor is close to the skin or in the area of soft tissue such as the abdomen, you may feel tactile mass.
Depending on the location, the possible symptoms of benign tumors include:
Chills.
Discomfort or pain.
Fatigue.
Fever.
Anorexia.
Night sweats.
Lose weight.
Tumors may be benign large enough to detect, especially if they are close to the skin, however, most tumors are not large enough to cause discomfort or pain, and can be removed if they lipoides. They may be large enough to detect, but are generally soft, moving and painless.
There may be discoloration in the skin is obvious in the presence of benign tumors appear on the skin, such as moles. If anything seems abnormal you should consult your doctor immediately.
Diagnosis of benign tumors.
Doctors have used a variety of techniques to diagnose benign tumors, the key to diagnosis is to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant, and only laboratory tests can determine this for sure.
Your doctor will start a physical examination, collect the patient's medical history, and will ask you about the symptoms you are experiencing.
To find internal benign tumors, perform imaging tests including:
CT scan.
Magnetic resonance imaging.
Mammography.
Ultrasound.
X ray.
Often benign tumors are visual through the protective sac that helps doctors diagnose the tumor as benign. The doctor may also ask for blood tests to check for signs of cancer.
In other cases, doctors take a sample of the tumor to determine if it is benign or malignant. The sample is large or small by tumor location.
Treatment of benign tumors.
Not all benign tumors need treatment. If the tumor is small and does not cause any symptoms, your doctor may recommend leaving the tumor better than removing it because in some cases, treatment can be more dangerous than leaving the tumor.
If the doctor decides to continue treatment, the method of treatment depends on the location of the tumor and can be removed for cosmetic reasons if it is located on the face or neck, other tumors affecting the organs, nerves, or blood vessels are removed by surgery to prevent further problems.
Oncology is performed using endoscopic techniques. This technique requires small surgical incisions to remove the tumor.
Procedures such as top endoscopy and colonoscopy require time for recovery, although patients need someone to take them home and are likely to sleep for the rest of the day. The cutaneous tumors of the tumors take a few weeks to fully heal and require basic recovery procedures such as changing the bandage and keeping them covered.
If the surgery can not safely reach the tumor, the doctor may prescribe radiation therapy to help reduce its size or prevent it from growing further.
A healthy lifestyle, exercising, and a balanced diet can prevent health problems including some cancers. There are no natural or alternative treatments for benign tumors on their own.
Living and dealing with benign tumors.
Many benign tumors can be left alone if they show no symptoms, or any complications. You just keep an eye on them and observe the changes.
If the tumor is fix, the doctor performs routine exams and scans to ensure that the tumor does not grow larger.
As long as the tumor does not cause you pain or does not change or increases, it can live with the benign tumor indefinitely.
When you see your doctor:
While many growth rates and tumors will turn out to be benign, it is always a good idea to schedule an appointment with your doctor as soon as possible to detect growth or new symptoms that can indicate a tumor, and this includes non-skin lesions or moles Regular.
It is also important to visit your doctor if you notice any changes in the tumor that have been previously diagnosed as benign in terms of growth or change in symptoms.